本文参考自 github repo demopark/sequelize-docs-Zh-CN,文章内容主要针对 mysql,其他 db 请参考原文档。
在 Node.js 社区中,sequelize 是一个广泛使用的 ORM(Object Relational Mapping,对象关系映射) 框架,它支持 MySQL、PostgreSQL、SQLite 和 MSSQL 等多个数据源。
Sequelize 文档
Getting started - 入门
安装
// 通过 npm 安装
npm install --save sequelize
还需要手动安装对应的数据库驱动程序:
# 选择对应的安装:
$ npm install --save pg pg-hstore # Postgres
$ npm install --save mysql2
$ npm install --save mariadb
$ npm install --save sqlite3
$ npm install --save tedious # Microsoft SQL Server
建立连接
要连接到数据库,你必须创建 Sequelize 实例. 这可以通过将连接参数分别传递给 Sequelize 构造函数或传递单个连接 URI 来完成:
const Sequelize = require('sequelize');
//方法1:单独传递参数
const sequelize = new Sequelize('database', 'username', 'password', {
host: 'localhost',
dialect: /* 'mysql' | 'mariadb' | 'postgres' | 'mssql' 之一 */
});
// 方法2: 传递连接 URI
const sequelize = new Sequelize('postgres://user:pass@example.com:5432/dbname');
连接池 (生产环境)
如果从单个进程连接到数据库,则应仅创建一个 Sequelize 实例. Sequelize 将在初始化时设置连接池. 可以通过构造函数的 options 参数(使用options.pool)配置此连接池,如以下示例所示:
const sequelize = new Sequelize(/* ... */, {
// ...
pool: {
max: 5,
min: 0,
acquire: 30000,
idle: 10000
}
});
如果从多个进程连接到数据库,则必须为每个进程创建一个实例,但每个实例应具有最大连接池大小,以便遵守总的最大大小.例如,如果你希望最大连接池大小为 90 并且你有三个进程,则每个进程的 Sequelize 实例的最大连接池大小应为 30.
测试连接
.authenticate()
sequelize
.authenticate()
.then(() => {
console.log('Connection has been established successfully.');
})
.catch(err => {
console.error('Unable to connect to the database:', err);
});
关闭连接
Sequelize 将默认保持连接持续,并对所有查询使用相同的连接. 如果需要关闭连接,请调用 sequelize.close() (这是异步的并返回Promise).
表建模
模型是一个继承自 Sequelize.Model 的 class,可以用两种方式定义,
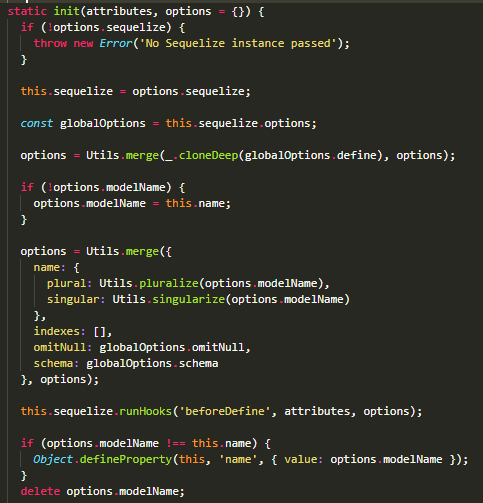
Sequelize.Model.init(attributes, options)
init
const Model = Sequelize.Model;
class User extends Model {}
User.init({
// attributes
firstName: {
type: Sequelize.STRING,
allowNull: false
},
lastName: {
type: Sequelize.STRING
// allowNull defaults to true
}
}, {
sequelize,
modelName: 'user'
// options
});
sequelize.define

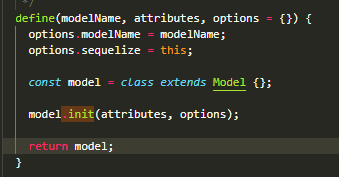
const User = sequelize.define('user', {
// attributes
firstName: {
type: Sequelize.STRING,
allowNull: false
},
lastName: {
type: Sequelize.STRING
// allowNull defaults to true
}
}, {
// options
});
Sequelize 还默认为每个模型定义了字段 id(主键) , createdAt 和 updatedAt .
更改默认模型参数
const sequelize = new Sequelize(connectionURI, {
define: {
// `timestamps` 字段指定是否将创建 `createdAt` 和 `updatedAt` 字段.
// 该值默认为 true, 但是当前设定为 false
timestamps: false
}
});
// 这里 `timestamps` 为 false,因此不会创建 `createdAt` 和 `updatedAt` 字段.
class Foo extends Model {}
Foo.init({ /* ... */ }, { sequelize });
// 这里 `timestamps` 直接设置为 true,因此将创建 `createdAt` 和 `updatedAt` 字段.
class Bar extends Model {}
Bar.init({ /* ... */ }, { sequelize, timestamps: true });
Dialect 方言
在 new Sequelize(db, username, password, options) 时,options 中需要指定 dialect。
MySQL
为了让 Sequelize 与 MySQL 一起更好地工作,你需要安装 mysql2@^1.5.2 或更高版本
const sequelize = new Sequelize('database', 'username', 'password', {
dialect: 'mysql'
})
MariaDB
const sequelize = new Sequelize('database', 'username', 'password', {
dialect: 'mariadb',
dialectOptions: {connectTimeout: 1000} // mariadb 连接参数
})
or
const sequelize = new Sequelize('mariadb://user:password@example.com:9821/database')
SQLite
const sequelize = new Sequelize('database', 'username', 'password', {
// sqlite!
dialect: 'sqlite',
// sqlite 的存储引擎
// - default ':memory:'
storage: 'path/to/database.sqlite'
})
or
const sequelize = new Sequelize('sqlite:/home/abs/path/dbname.db')
const sequelize = new Sequelize('sqlite:relativePath/dbname.db')
PostgreSQL
PostgreSQL,需要两个库,pg@^7.0.0 和 pg-hstore
const sequelize = new Sequelize('database', 'username', 'password', {
// postgres!
dialect: 'postgres'
})
MSSQL
安装 tedious@^6.0.0
const sequelize = new Sequelize('database', 'username', 'password', {
dialect: 'mssql'
})
Datatypes - 数据类型
CHAR
Sequelize.STRING // VARCHAR(255)
Sequelize.STRING(1234) // VARCHAR(1234)
Sequelize.STRING.BINARY // VARCHAR BINARY
Sequelize.TEXT // TEXT
Sequelize.TEXT('tiny') // TINYTEXT
NUMBER
Sequelize.INTEGER // INTEGER
Sequelize.BIGINT // BIGINT
Sequelize.BIGINT(11) // BIGINT(11)
Sequelize.FLOAT // FLOAT
Sequelize.FLOAT(11) // FLOAT(11)
Sequelize.FLOAT(11, 10) // FLOAT(11,10)
Sequelize.DOUBLE // DOUBLE
Sequelize.DOUBLE(11) // DOUBLE(11)
Sequelize.DOUBLE(11, 10) // DOUBLE(11,10)
Sequelize.DECIMAL // DECIMAL
Sequelize.DECIMAL(10, 2) // DECIMAL(10,2)
TIME
Sequelize.DATE // mysql / sqlite 为 DATETIME, postgres 为带时区的 TIMESTAMP
Sequelize.DATE(6) // DATETIME(6) 适用 mysql 5.6.4+. 小数秒支持最多6位精度
Sequelize.DATEONLY // DATE 不带时间.
BOOLEAN
Sequelize.BOOLEAN // TINYINT(1)
ENUM
Sequelize.ENUM('value 1', 'value 2') // 一个允许值为'value 1'和'value 2'的ENUM
blob
Sequelize.BLOB // BLOB (PostgreSQL 为 bytea)
Sequelize.BLOB('tiny') // TINYBLOB (PostgreSQL 为 bytea. 其余参数是 medium 和 long)
GEOMETRY
Sequelize.GEOMETRY // Spatial 列. 仅 PostgreSQL (带有 PostGIS) 或 MySQL.
Sequelize.GEOMETRY('POINT') // 带有 geometry 类型的 spatial 列. 仅 PostgreSQL (带有 PostGIS) 或 MySQL.
Sequelize.GEOMETRY('POINT', 4326) // 具有 geometry 类型和 SRID 的 spatial 列. 仅 PostgreSQL (带有 PostGIS) 或 MySQL.
integer, bigint, float 和 double 还支持 unsigned 和 zerofill 属性
Sequelize.INTEGER.UNSIGNED // INTEGER UNSIGNED
Sequelize.INTEGER(11).UNSIGNED // INTEGER(11) UNSIGNED
Sequelize.INTEGER(11).ZEROFILL // INTEGER(11) ZEROFILL
Sequelize.INTEGER(11).ZEROFILL.UNSIGNED // INTEGER(11) UNSIGNED ZEROFILL
Sequelize.INTEGER(11).UNSIGNED.ZEROFILL // INTEGER(11) UNSIGNED ZEROFILL
对象表示
// 对于枚举:
class MyModel extends Model {}
MyModel.init({
states: {
type: Sequelize.ENUM,
values: ['active', 'pending', 'deleted']
}
}, { sequelize })
Model definition - 模型定义
定义模型和表之间的映射,使用 define 方法。
// Model 挂载在 Sequelize 上,
// const Sequelize = require('sequelize');
// const Model = Sequelize.Model;
class Project extends Model {}
Project.init({
title: Sequelize.STRING,
description: Sequelize.TEXT
}, { sequelize, modelName: 'project' });
Model 定义示例
class Foo extends Model {}
Foo.init({
// 如果未赋值,则自动设置值为 TRUE
flag: { type: Sequelize.BOOLEAN, allowNull: false, defaultValue: true},
// 设置默认时间为当前时间
myDate: { type: Sequelize.DATE, defaultValue: Sequelize.NOW },
// 将allowNull设置为false会将NOT NULL添加到列中,
// 这意味着当列为空时执行查询时将从DB抛出错误.
// 如果要在查询DB之前检查值不为空,请查看下面的验证部分.
title: { type: Sequelize.STRING, allowNull: false},
// 创建具有相同值的两个对象将抛出一个错误. 唯一属性可以是布尔值或字符串.
// 如果为多个列提供相同的字符串,则它们将形成复合唯一键.
uniqueOne: { type: Sequelize.STRING, unique: 'compositeIndex'},
uniqueTwo: { type: Sequelize.INTEGER, unique: 'compositeIndex'},
// unique属性用来创建一个唯一约束.
someUnique: {type: Sequelize.STRING, unique: true},
// 这与在模型选项中创建索引完全相同.
{someUnique: {type: Sequelize.STRING}},
{indexes: [{unique: true, fields: ['someUnique']}]},
// primaryKey用于定义主键.
identifier: { type: Sequelize.STRING, primaryKey: true},
// autoIncrement可用于创建自增的整数列
incrementMe: { type: Sequelize.INTEGER, autoIncrement: true },
// 你可以通过'field'属性指定自定义列名称:
fieldWithUnderscores: { type: Sequelize.STRING, field: 'field_with_underscores' },
// 这可以创建一个外键:
bar_id: {
type: Sequelize.INTEGER,
references: {
// 这是引用另一个模型
model: Bar,
// 这是引用模型的列名称
key: 'id',
// 这声明什么时候检查外键约束. 仅限PostgreSQL.
deferrable: Sequelize.Deferrable.INITIALLY_IMMEDIATE
}
},
// 仅可以为 MySQL,PostgreSQL 和 MSSQL 的列添加注释
commentMe: {
type: Sequelize.INTEGER,
comment: '这是一个包含注释的列名'
}
}, {
sequelize,
modelName: 'foo'
});
时间戳
默认情况下,Sequelize 会将 createdAt 和 updatedAt 属性添加到模型中,以便你能够知道数据库条目何时进入数据库以及何时被更新.如果不想要自动添加,则定义如下:
const sequelize = new Sequelize(connectionURI, {
define: {
// `timestamps` 字段指定是否将创建 `createdAt` 和 `updatedAt` 字段.
// 该值默认为 true, 但是当前设定为 false
timestamps: false
}
});
如果你使用 Sequelize 迁移,则需要将 createdAt 和 updatedAt 字段添加到迁移定义中:
module.exports = {
up(queryInterface, Sequelize) {
return queryInterface.createTable('my-table', {
id: {
type: Sequelize.INTEGER,
primaryKey: true,
autoIncrement: true,
},
// 时间戳
createdAt: Sequelize.DATE,
updatedAt: Sequelize.DATE,
})
},
down(queryInterface, Sequelize) {
return queryInterface.dropTable('my-table');
},
}
Getters & Setters
Getters和Setters可以通过两种方式定义(你可以混合使用这两种方式):
- 作为属性定义的一部分
- 作为模型参数的一部分
注意: 如果在两个地方定义了getter或setter,那么在相关属性定义中找到的函数始终是优先的.
定义为属性定义的一部分
class Employee extends Model {}
Employee.init({
name: {
type: Sequelize.STRING,
allowNull: false,
get() {
const title = this.getDataValue('title');
// 'this' 允许你访问实例的属性
return this.getDataValue('name') + ' (' + title + ')';
},
},
title: {
type: Sequelize.STRING,
allowNull: false,
set(val) {
this.setDataValue('title', val.toUpperCase());
}
}
}, { sequelize, modelName: 'employee' });
Employee
.create({ name: 'John Doe', title: 'senior engineer' })
.then(employee => {
console.log(employee.get('name')); // John Doe (SENIOR ENGINEER)
console.log(employee.get('title')); // SENIOR ENGINEER
})
定义为模型参数的一部分
class Foo extends Model {
get fullName() {
return this.firstname + ' ' + this.lastname;
}
set fullName(value) {
const names = value.split(' ');
this.setDataValue('firstname', names.slice(0, -1).join(' '));
this.setDataValue('lastname', names.slice(-1).join(' '));
}
}
Foo.init({
firstname: Sequelize.STRING,
lastname: Sequelize.STRING
}, {
sequelize,
modelName: 'foo'
});
// 或使用 `sequelize.define`
sequelize.define('Foo', {
firstname: Sequelize.STRING,
lastname: Sequelize.STRING
}, {
getterMethods: {
fullName() {
return this.firstname + ' ' + this.lastname;
}
},
setterMethods: {
fullName(value) {
const names = value.split(' ');
this.setDataValue('firstname', names.slice(0, -1).join(' '));
this.setDataValue('lastname', names.slice(-1).join(' '));
}
}
![]()
});
用于 getter 和 setter 定义内部的 Helper 方法
- 检索底层属性值 - 总是使用
this.getDataValue()
/* 一个用于 'title' 属性的 getter */
get() {
return this.getDataValue('title')
}
- 设置基础属性值 - 总是使用
this.setDataValue()
/* 一个用于 'title' 属性的 setter */
set(title) {
this.setDataValue('title', title.toString().toLowerCase());
}
属性验证器
class ValidateMe extends Model {}
ValidateMe.init({
bar: {
type: Sequelize.STRING,
validate: {
is: ["^[a-z]+$",'i'], // 只允许字母
is: /^[a-z]+$/i, // 与上一个示例相同,使用了真正的正则表达式
not: ["[a-z]",'i'], // 不允许字母
isEmail: true, // 检查邮件格式 (foo@bar.com)
isUrl: true, // 检查连接格式 (http://foo.com)
isIP: true, // 检查 IPv4 (129.89.23.1) 或 IPv6 格式
isIPv4: true, // 检查 IPv4 (129.89.23.1) 格式
isIPv6: true, // 检查 IPv6 格式
isAlpha: true, // 只允许字母
isAlphanumeric: true, // 只允许使用字母数字
isNumeric: true, // 只允许数字
isInt: true, // 检查是否为有效整数
isFloat: true, // 检查是否为有效浮点数
isDecimal: true, // 检查是否为任意数字
isLowercase: true, // 检查是否为小写
isUppercase: true, // 检查是否为大写
notNull: true, // 不允许为空
isNull: true, // 只允许为空
notEmpty: true, // 不允许空字符串
equals: 'specific value', // 只允许一个特定值
contains: 'foo', // 检查是否包含特定的子字符串
notIn: [['foo', 'bar']], // 检查是否值不是其中之一
isIn: [['foo', 'bar']], // 检查是否值是其中之一
notContains: 'bar', // 不允许包含特定的子字符串
len: [2,10], // 只允许长度在2到10之间的值
isUUID: 4, // 只允许uuids
isDate: true, // 只允许日期字符串
isAfter: "2011-11-05", // 只允许在特定日期之后的日期字符串
isBefore: "2011-11-05", // 只允许在特定日期之前的日期字符串
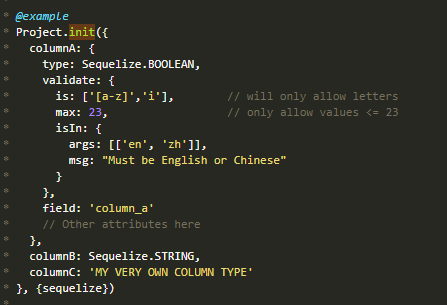
max: 23, // 只允许值 <= 23
min: 23, // 只允许值 >= 23
isCreditCard: true, // 检查有效的信用卡号码
// 自定义验证器的示例:
isEven(value) {
if (parseInt(value) % 2 !== 0) {
throw new Error('Only even values are allowed!');
}
}
isGreaterThanOtherField(value) {
if (parseInt(value) <= parseInt(this.otherField)) {
throw new Error('Bar must be greater than otherField.');
}
}
}
}
}, { sequelize });
class Pub extends Model {}
Pub.init({
name: { type: Sequelize.STRING },
address: { type: Sequelize.STRING },
latitude: {
type: Sequelize.INTEGER,
allowNull: true,
defaultValue: null,
validate: { min: -90, max: 90 }
},
longitude: {
type: Sequelize.INTEGER,
allowNull: true,
defaultValue: null,
validate: { min: -180, max: 180 }
},
}, {
validate: {
bothCoordsOrNone() {
if ((this.latitude === null) !== (this.longitude === null)) {
throw new Error('Require either both latitude and longitude or neither')
}
}
},
sequelize,
})
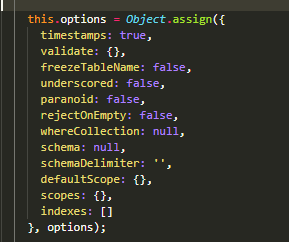
配置
class Bar extends Model {}
Bar.init({ /* bla */ }, {
// 模型的名称. 该模型将以此名称存储在`sequelize.models`中.
// 在这种情况下,默认为类名,即Bar.
// 这将控制自动生成的foreignKey和关联命名的名称
modelName: 'bar',
// 不添加时间戳属性 (updatedAt, createdAt)
timestamps: false,
// 不删除数据库条目,但将新添加的属性deletedAt设置为当前日期(删除完成时).
// paranoid 只有在启用时间戳时才能工作
paranoid: true,
// 将自动设置所有属性的字段参数为下划线命名方式.
// 不会覆盖已经定义的字段选项
underscored: true,
// 禁用修改表名; 默认情况下,sequelize将自动将所有传递的模型名称(define的第一个参数)转换为复数. 如果你不想这样,请设置以下内容
freezeTableName: true,
// 定义表的名称
tableName: 'my_very_custom_table_name',
// 启用乐观锁定. 启用时,sequelize将向模型添加版本计数属性,
// 并在保存过时的实例时引发OptimisticLockingError错误.
// 设置为true或具有要用于启用的属性名称的字符串.
version: true,
// Sequelize 实例
sequelize,
})
如果你希望sequelize处理时间戳,但只想要其中一部分,或者希望你的时间戳被称为别的东西,则可以单独覆盖每个列:
class Foo extends Model {}
Foo.init({ /* bla */ }, {
// 不要忘记启用时间戳!
timestamps: true,
// 我不想要 createdAt
createdAt: false,
// 我想 updateAt 实际上被称为 updateTimestamp
updatedAt: 'updateTimestamp',
// 并且希望 deletedA t被称为 destroyTime(请记住启用paranoid以使其工作)
deletedAt: 'destroyTime',
paranoid: true,
sequelize,
})
你也可以更改数据库引擎,例如 变更到到 MyISAM, 默认值是 InnoDB.
class Person extends Model {}
Person.init({ /* attributes */ }, {
engine: 'MYISAM',
sequelize
})
// 或全局的
const sequelize = new Sequelize(db, user, pw, {
define: { engine: 'MYISAM' }
})
可以为MySQL和PG中的表指定注释
class Person extends Model {}
Person.init({ /* attributes */ }, {
comment: "我是一个表注释!",
sequelize
})
导入
还可以使用 import 方法将模型定义存储在单个文件中. 返回的对象与导入文件的功能中定义的完全相同. 由于 Sequelizev1:5.0 的导入是被缓存的,所以当调用文件导入两次或更多次时,不会遇到问题.
// 在你的服务器文件中 - 例如 app.js
const Project = sequelize.import(__dirname + "/path/to/models/project")
// 模型已经在 /path/to/models/project.js 中定义好
// 你可能会注意到,DataTypes与上述相同
module.exports = (sequelize, DataTypes) => {
class Project extends sequelize.Model { }
Project.init({
name: DataTypes.STRING,
description: DataTypes.TEXT
}, { sequelize });
return Project;
}
import 方法也可以接受回调作为参数.
sequelize.import('project', (sequelize, DataTypes) => {
class Project extends sequelize.Model {}
Project.init({
name: DataTypes.STRING,
description: DataTypes.TEXT
}, { sequelize })
return Project;
})
乐观锁定
默认情况下禁用乐观锁定,可以通过在特定模型定义或全局模型配置中将version属性设置为true来启用.
乐观锁定允许并发访问模型记录以进行编辑,并防止冲突覆盖数据. 它通过检查另一个进程是否已经读取记录而进行更改,并在检测到冲突时抛出一个OptimisticLockError.
Querying - 查询
属性
Model.findAll({
attributes: ['foo', 'bar']
});
// SELECT foo, bar ...
属性可以使用嵌套数组来重命名:
Model.findAll({
attributes: ['foo', ['bar', 'baz']]
});
// SELECT foo, bar AS baz ...
也可以使用 sequelize.fn 来进行聚合:
Model.findAll({
attributes: [[sequelize.fn('COUNT', sequelize.col('hats')), 'no_hats']]
});
// SELECT COUNT(hats) AS no_hats ...
详细的功能函数请看:

使用聚合功能时,必须给它一个别名,以便能够从模型中访问它. 在上面的例子中,你可以使用 instance.get('no_hats') 获得帽子数量.
有时,如果你只想添加聚合,则列出模型的所有属性可能令人厌烦:
// This is a tiresome way of getting the number of hats...
Model.findAll({
attributes: ['id', 'foo', 'bar', 'baz', 'quz', [sequelize.fn('COUNT', sequelize.col('hats')), 'no_hats']]
});
// This is shorter, and less error prone because it still works if you add / remove attributes
Model.findAll({
attributes: { include: [[sequelize.fn('COUNT', sequelize.col('hats')), 'no_hats']] }
});
// SELECT id, foo, bar, baz, quz, COUNT(hats) AS no_hats ...
同样,它也可以排除一些指定的表字段:
Model.findAll({
attributes: { exclude: ['baz'] }
});
// SELECT id, foo, bar, quz ...
Where
可以传递一个 where 对象来过滤查询。where 通常用 attribute:value 键值对获取一个对象,其中 value 可以是匹配等式的数据或其他运算符的键值对象,也可以通过嵌套 or 和 and 运算符的集合来生成复杂的 AND/OR 条件.
const Op = Sequelize.Op;
Post.findAll({
where: {
authorId: 2
}
});
// SELECT * FROM post WHERE authorId = 2
Post.findAll({
where: {
authorId: 12,
status: 'active'
}
});
// SELECT * FROM post WHERE authorId = 12 AND status = 'active';
Post.findAll({
where: {
[Op.or]: [{authorId: 12}, {authorId: 13}]
}
});
// SELECT * FROM post WHERE authorId = 12 OR authorId = 13;
Post.findAll({
where: {
authorId: {
[Op.or]: [12, 13]
}
}
});
// SELECT * FROM post WHERE authorId = 12 OR authorId = 13;
Post.destroy({
where: {
status: 'inactive'
}
});
// DELETE FROM post WHERE status = 'inactive';
Post.update({
updatedAt: null,
}, {
where: {
deletedAt: {
[Op.ne]: null
}
}
});
// UPDATE post SET updatedAt = null WHERE deletedAt NOT NULL;
Post.findAll({
where: sequelize.where(sequelize.fn('char_length', sequelize.col('status')), 6)
});
// SELECT * FROM post WHERE char_length(status) = 6;
操作符

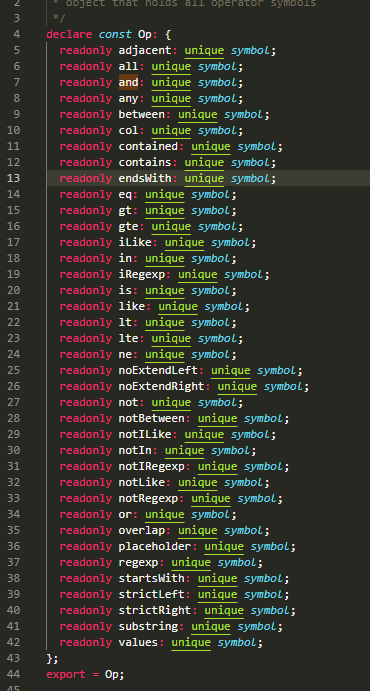
const Op = Sequelize.Op
[Op.and]: {a: 5} // 且 (a = 5)
[Op.or]: [{a: 5}, {a: 6}] // (a = 5 或 a = 6)
[Op.gt]: 6, // id > 6
[Op.gte]: 6, // id >= 6
[Op.lt]: 10, // id < 10
[Op.lte]: 10, // id <= 10
[Op.ne]: 20, // id != 20
[Op.eq]: 3, // = 3
[Op.not]: true, // 不是 TRUE
[Op.between]: [6, 10], // 在 6 和 10 之间
[Op.notBetween]: [11, 15], // 不在 11 和 15 之间
[Op.in]: [1, 2], // 在 [1, 2] 之中
[Op.notIn]: [1, 2], // 不在 [1, 2] 之中
[Op.like]: '%hat', // 包含 '%hat'
[Op.notLike]: '%hat' // 不包含 '%hat'
[Op.iLike]: '%hat' // 包含 '%hat' (不区分大小写) (仅限 PG)
[Op.notILike]: '%hat' // 不包含 '%hat' (仅限 PG)
[Op.startsWith]: 'hat' // 类似 'hat%'
[Op.endsWith]: 'hat' // 类似 '%hat'
[Op.substring]: 'hat' // 类似 '%hat%'
[Op.regexp]: '^[h|a|t]' // 匹配正则表达式/~ '^[h|a|t]' (仅限 MySQL/PG)
[Op.notRegexp]: '^[h|a|t]' // 不匹配正则表达式/!~ '^[h|a|t]' (仅限 MySQL/PG)
[Op.iRegexp]: '^[h|a|t]' // ~* '^[h|a|t]' (仅限 PG)
[Op.notIRegexp]: '^[h|a|t]' // !~* '^[h|a|t]' (仅限 PG)
[Op.like]: { [Op.any]: ['cat', 'hat']} // 包含任何数组['cat', 'hat'] - 同样适用于 iLike 和 notLike
[Op.overlap]: [1, 2] // && [1, 2] (PG数组重叠运算符)
[Op.contains]: [1, 2] // @> [1, 2] (PG数组包含运算符)
[Op.contained]: [1, 2] // <@ [1, 2] (PG数组包含于运算符)
[Op.any]: [2,3] // 任何数组[2, 3]::INTEGER (仅限PG)
[Op.col]: 'user.organization_id' // = 'user'.'organization_id', 使用数据库语言特定的列标识符, 本例使用 PG
组合
{
rank: {
[Op.or]: {
[Op.lt]: 1000,
[Op.eq]: null
}
}
}
// rank < 1000 OR rank IS NULL
{
createdAt: {
[Op.lt]: new Date(),
[Op.gt]: new Date(new Date() - 24 * 60 * 60 * 1000)
}
}
// createdAt < [timestamp] AND createdAt > [timestamp - 1d]
{
[Op.or]: [
{
title: {
[Op.like]: 'Boat%'
}
},
{
description: {
[Op.like]: '%boat%'
}
}
]
}
// title LIKE 'Boat%' OR description LIKE '%boat%'
运算符别名
const Op = Sequelize.Op;
const operatorsAliases = {
$gt: Op.gt
}
const connection = new Sequelize(db, user, pass, { operatorsAliases })
[Op.gt]: 6 // > 6
$gt: 6 // 等同于使用 Op.gt (> 6)
运算符安全性
默认情况下,Sequelize 将使用 Symbol 运算符. 使用没有任何别名的 Sequelize 可以提高安全性.没有任何字符串别名将使得运算符可能被注入的可能性降到极低,但你应该始终正确验证和清理用户输入.
为了更好的安全性,强烈建议在代码中使用 Sequelize.Op 中的符号运算符,如 Op.and / Op.or,而不依赖于任何基于字符串的运算符,如 $and / $or. 你可以通过设置 operatorsAliases 参数来限制应用程序所需的别名,
如果你想继续使用所有默认别名(不包括旧版别名)而不发出警告,你可以传递以下运算符参数 -
const Op = Sequelize.Op;
const operatorsAliases = {
$eq: Op.eq,
$ne: Op.ne,
$gte: Op.gte,
$gt: Op.gt,
$lte: Op.lte,
$lt: Op.lt,
$not: Op.not,
$in: Op.in,
$notIn: Op.notIn,
$is: Op.is,
$like: Op.like,
$notLike: Op.notLike,
$iLike: Op.iLike,
$notILike: Op.notILike,
$regexp: Op.regexp,
$notRegexp: Op.notRegexp,
$iRegexp: Op.iRegexp,
$notIRegexp: Op.notIRegexp,
$between: Op.between,
$notBetween: Op.notBetween,
$overlap: Op.overlap,
$contains: Op.contains,
$contained: Op.contained,
$adjacent: Op.adjacent,
$strictLeft: Op.strictLeft,
$strictRight: Op.strictRight,
$noExtendRight: Op.noExtendRight,
$noExtendLeft: Op.noExtendLeft,
$and: Op.and,
$or: Op.or,
$any: Op.any,
$all: Op.all,
$values: Op.values,
$col: Op.col
};
const connection = new Sequelize(db, user, pass, { operatorsAliases });
limit, offset(分页, 限制)
// 获取10个实例/行
Project.findAll({ limit: 10 })
// 跳过8个实例/行
Project.findAll({ offset: 8 })
// 跳过5个实例,然后取5个
Project.findAll({ offset: 5, limit: 5 })
order(排序)
order 需要一个条目的数组来排序查询或者一个 sequelize 方法.一般来说,你将要使用任一属性的 tuple/array,并确定排序的正反方向.
Subtask.findAll({
order: [
// 将转义标题,并根据有效的方向参数列表验证DESC
['title', 'DESC'],
// 将按最大值排序(age)
sequelize.fn('max', sequelize.col('age')),
// 将按最大顺序(age) DESC
[sequelize.fn('max', sequelize.col('age')), 'DESC'],
// 将按 otherfunction 排序(`col1`, 12, 'lalala') DESC
[sequelize.fn('otherfunction', sequelize.col('col1'), 12, 'lalala'), 'DESC'],
// 将使用模型名称作为关联的名称排序关联模型的 created_at.
[Task, 'createdAt', 'DESC'],
// Will order through an associated model's created_at using the model names as the associations' names.
[Task, Project, 'createdAt', 'DESC'],
// 将使用关联的名称由关联模型的created_at排序.
['Task', 'createdAt', 'DESC'],
// Will order by a nested associated model's created_at using the names of the associations.
['Task', 'Project', 'createdAt', 'DESC'],
// Will order by an associated model's created_at using an association object. (优选方法)
[Subtask.associations.Task, 'createdAt', 'DESC'],
// Will order by a nested associated model's created_at using association objects. (优选方法)
[Subtask.associations.Task, Task.associations.Project, 'createdAt', 'DESC'],
// Will order by an associated model's created_at using a simple association object.
[{model: Task, as: 'Task'}, 'createdAt', 'DESC'],
// 嵌套关联模型的 created_at 简单关联对象排序
[{model: Task, as: 'Task'}, {model: Project, as: 'Project'}, 'createdAt', 'DESC']
]
// 将按年龄最大值降序排列
order: sequelize.literal('max(age) DESC')
// 按最年龄大值升序排列,当省略排序条件时默认是升序排列
order: sequelize.fn('max', sequelize.col('age'))
// 按升序排列是省略排序条件的默认顺序
order: sequelize.col('age')
// 将根据方言随机排序 (而不是 fn('RAND') 或 fn('RANDOM'))
order: sequelize.random()
})
常用查询方法
findAll
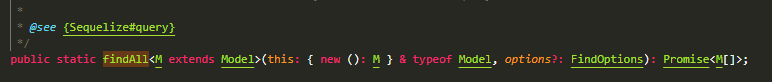
Model.findAll({
where: {
attr1: 42,
attr2: 'cake'
}
})
// WHERE attr1 = 42 AND attr2 = 'cake'
Model.findAll({
where: {
attr1: {
gt: 50
},
attr2: {
lte: 45
},
attr3: {
in: [1,2,3]
},
attr4: {
ne: 5
}
}
})
// WHERE attr1 > 50 AND attr2 <= 45 AND attr3 IN (1,2,3) AND attr4 != 5
Model.findAll({
where: Sequelize.and(
{ name: 'a project' },
Sequelize.or(
{ id: [1,2,3] },
{ id: { gt: 10 } }
)
)
})
// WHERE name = 'a project' AND (id` IN (1,2,3) OR id > 10)
findByPk
Model.findByPk(1)
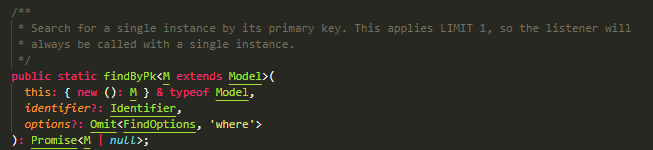
findOne
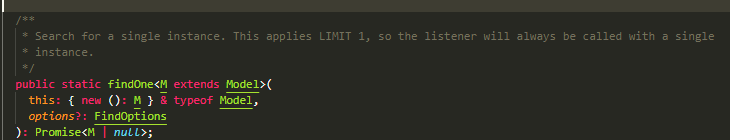
aggregate
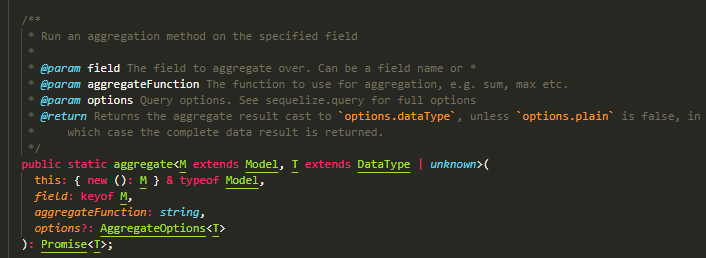
count
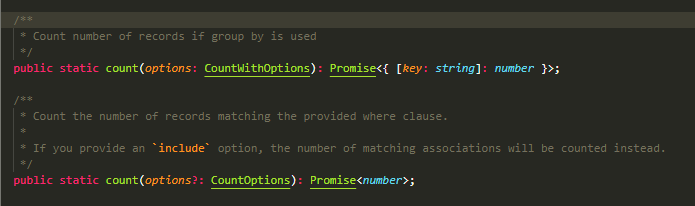
findAndCountAll
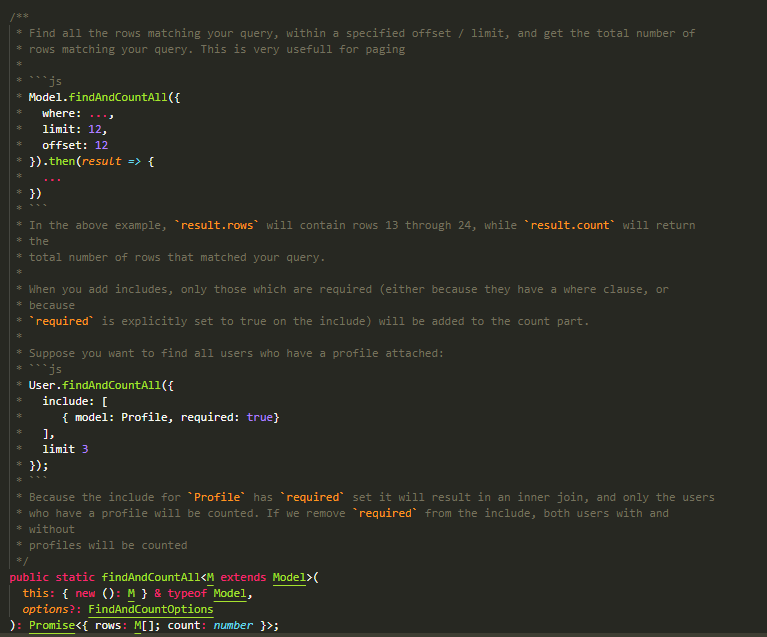
max
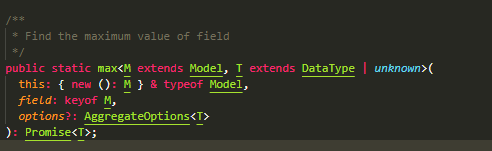
min
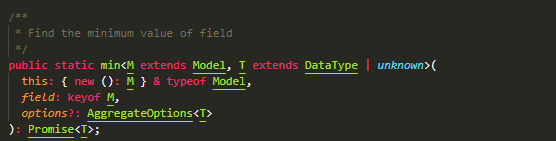
sum
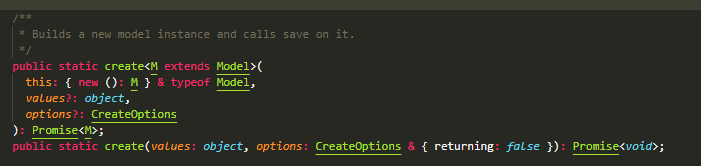
create
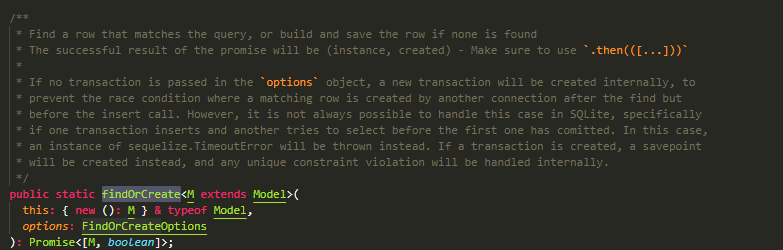
findOrCreate
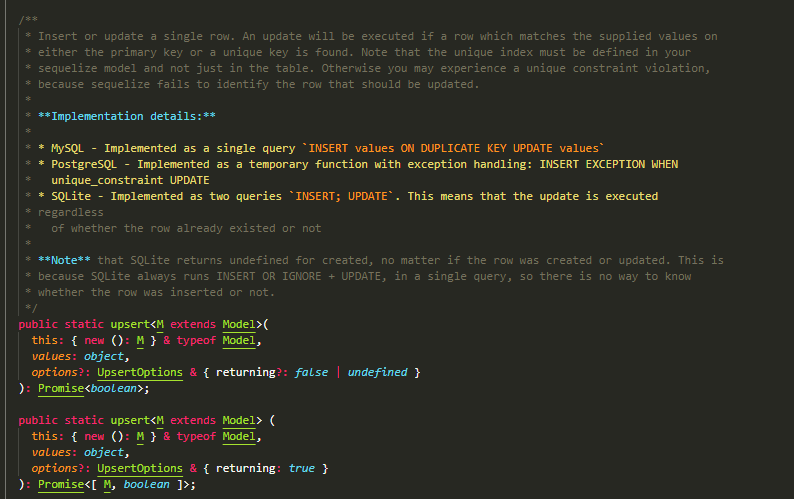
upsert
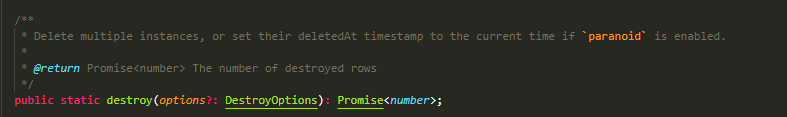
destroy
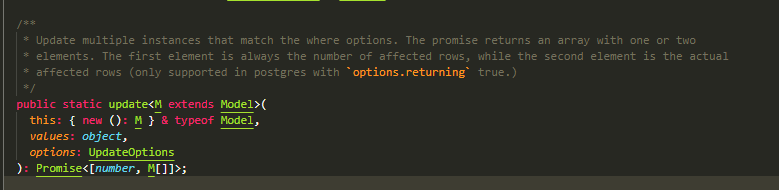
update