vm.$delete()
vm.$delete用法见官网。
为什么需要Vue.delete()?
在ES6之前, JS没有提供方法来侦测到一个属性被删除了, 因此如果我们通过delete删除一个属性, Vue是侦测不到的, 因此不会触发数据响应式。
见下面的demo。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge" />
<title>Vue Demo</title>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
名字: {{ user.name }} 年纪: {{ user.age }}
<button @click="addUserAgeField">删除一个年纪字段</button>
</div>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
user: {
name: "test",
age: 10
}
},
mounted() {},
methods: {
addUserAgeField() {
// delete this.user.age; // 这样是不起作用, 不会触发数据响应式更新
this.$delete(this.user, 'age') // 应该使用
}
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
源码分析内部实现
源码位置vue/src/core/instance/state.js的stateMixin方法
export function stateMixin (Vue: Class<Component>) {
...
Vue.prototype.$set = set
Vue.prototype.$delete = del
...
}
然后查看del函数位置, vue/src/core/observer/index.js。
/**
* Delete a property and trigger change if necessary.
* target: 将被删除属性的目标对象, 可以是对象/数组
* key: 删除属性
*/
export function del (target: Array<any> | Object, key: any) {
// 非生产环境下, 不允许删除一个原始数据类型, 或者undefined, null
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' &&
(isUndef(target) || isPrimitive(target))
) {
warn(`Cannot delete reactive property on undefined, null, or primitive value: ${(target: any)}`)
}
// 如果target是数组, 并且key是一个合法索引,通过数组的splcie方法删除值, 并且还能触发数据的响应(数组拦截器截取到变化到元素, 通知依赖更新数据)
if (Array.isArray(target) && isValidArrayIndex(key)) {
target.splice(key, 1)
return
}
// 获取ob
const ob = (target: any).__ob__
// target._isVue: 不允许删除Vue实例对象上的属性
// (ob && ob.vmCount): 不允许删除根数据对象的属性,触发不了响应
if (target._isVue || (ob && ob.vmCount)) {
process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && warn(
'Avoid deleting properties on a Vue instance or its root $data ' +
'- just set it to null.'
)
return
}
// 如果属性压根不在对象上, 什么都不做处理
if (!hasOwn(target, key)) {
return
}
// 走到这一步说明, target是对象, 并且key在target上, 直接使用delete删除
delete target[key]
// 如果ob不存在, 说明target本身不是响应式数据,
if (!ob) {
return
}
// 存在ob, 通过ob里面存储的Dep实例的notify方法通知依赖更新
ob.dep.notify()
}
工具函数
// 判断是否v是未定义
export function isUndef (v: any): boolean %checks {
return v === undefined || v === null
}
// 判断v是否是原始数据类型(基本数据类型)
export function isPrimitive (value: any): boolean %checks {
return (
typeof value === 'string' ||
typeof value === 'number' ||
// $flow-disable-line
typeof value === 'symbol' ||
typeof value === 'boolean'
)
}
// 判断对象上是否有属性
const hasOwnProperty = Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty
export function hasOwn (obj: Object | Array<*>, key: string): boolean {
return hasOwnProperty.call(obj, key)
}
关于__ob__属性, 在很多源码地方我们都会看到类似这样获取ob(Observer实例)
const ob = (target: any).__ob__
牢记只要数据被observe过就会打上这个私有属性, 是在Observer类的构造器里面发生的
export class Observer {
constructor (value: any) {
this.value = value
// 依赖是存在Observe上的dep属性, 再次通知依赖更新时候我们一般使用__ob__.dep.notify()
this.dep = new Dep()
this.vmCount = 0
// 定义__ob__
def(value, '__ob__', this)
if (Array.isArray(value)) {
if (hasProto) {
protoAugment(value, arrayMethods)
} else {
copyAugment(value, arrayMethods, arrayKeys)
}
this.observeArray(value)
} else {
this.walk(value)
}
}
...
}
Vue.use()
大家都知道这个方法是用来安装插件的, 是全局api。 具体使用见官网。
通过Vue.use()源码+Vuex部分源码分析插件的安装过程
Vue.use()什么时候被绑在Vue原型上
源码位置: vue/src/core/index.js
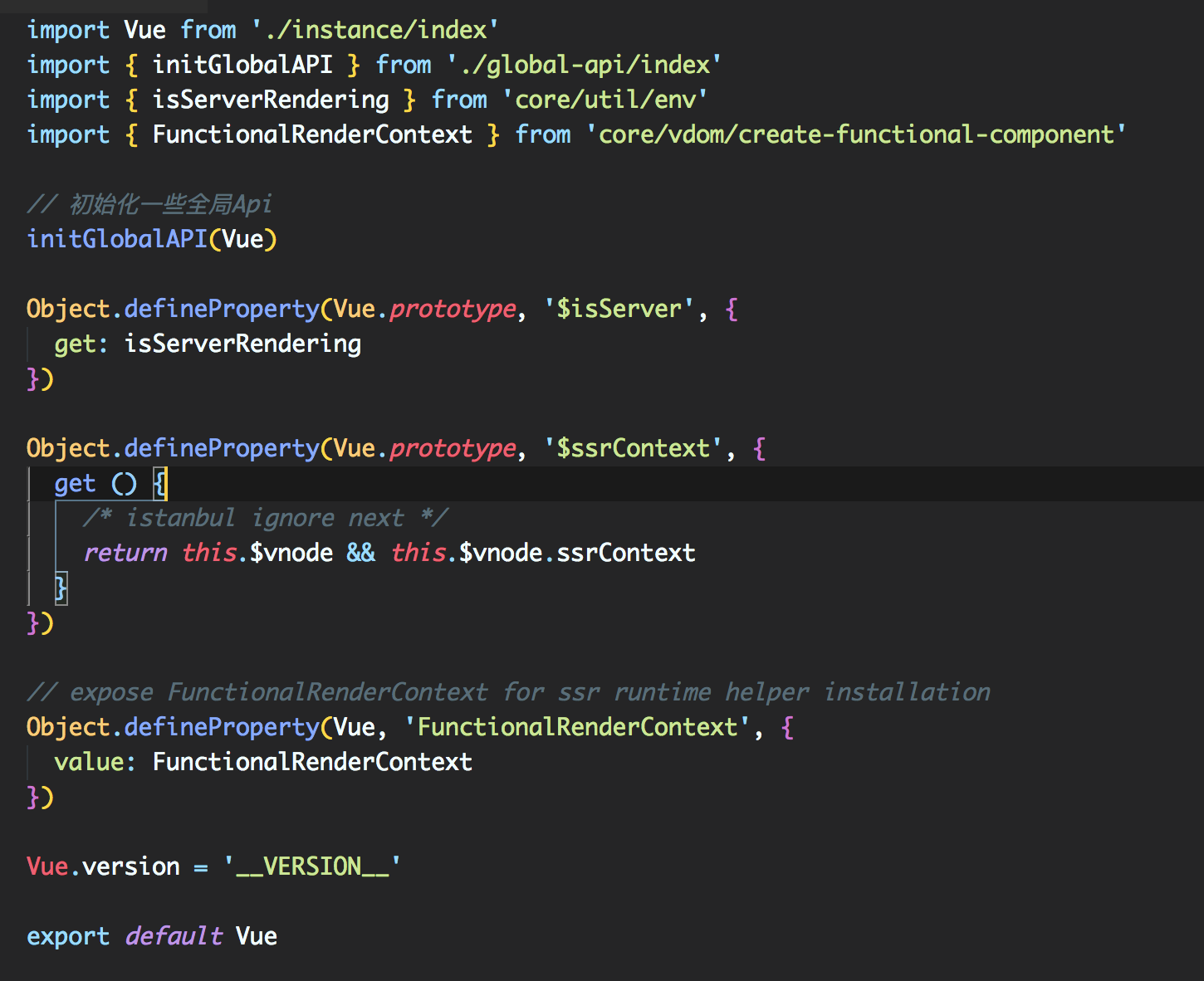
initGlobalAPI()
源码位置: vue/src/core/global-api/index.js
export function initGlobalAPI (Vue: GlobalAPI) {
...
// 初始化use()
initUse(Vue)
...
}
initUse()
源码位置: vue/src/core/global-api/use.js
export function initUse (Vue: GlobalAPI) {
// 这里的Vue是构造器函数.
// 通过以下源码:
// vue-dev/src/core/global-api/index.js initGlobalAPI()中
// vue-dev/src/core/index.js 这里执行了initGlobalAPI() => 初始化一些全局api
// Vue.use(): 安装Vue.js的插件
// 如果插件是一个对象,必须提供 install 方法
// 如果插件是一个函数,它会被作为 install 方法
// install 方法调用时,会将 Vue 作为参数传入
Vue.use = function (plugin: Function | Object) {
// installedPlugins存储install后的插件
const installedPlugins = (this._installedPlugins || (this._installedPlugins = []))
if (installedPlugins.indexOf(plugin) > -1) {
// 同一个插件只会安装一次
return this
}
// additional parameters
// 除了插件外的其他参数 Vue.use(MyPlugin, { someOption: true })
const args = toArray(arguments, 1)
// 往args存储Vue构造器, 供插件的install方法使用
args.unshift(this)
// 分情况执行插件的install方法, 把this(Vue), 参数抛回给install方法
// 所以我们常说, install这个方法的第一个参数是 Vue 构造器,第二个参数是一个可选的选项对象:
if (typeof plugin.install === 'function') {
// plugin是一个对象
plugin.install.apply(plugin, args)
} else if (typeof plugin === 'function') {
// plugin是一个函数
plugin.apply(null, args)
}
// install之后会存储该插件避免重复安装
installedPlugins.push(plugin)
return this
}
}
Vuex源码
我们都知道开发一个Vue.js 的插件应该暴露一个 install 方法。这个方法的第一个参数是 Vue 构造器,第二个参数是一个可选的选项对象:
那么我们首先就是看Vuex的install方法是怎么实现的
源码位置: vuex-dev/src/store.js
let Vue // bind on install
// install: 装载vuex到vue, Vue.use(Vuex)也是执行install方法
// 关于Vue.use()源码. vue-dev/src/core/global-api/use.js
export function install (_Vue) {
if (Vue && _Vue === Vue) {
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
console.error(
'[vuex] already installed. Vue.use(Vuex) should be called only once.'
)
}
return
}
// 首次安装插件, 会把局部的Vue缓存到全局的window.Vue. 主要为了避免重复调用Vue.use()
Vue = _Vue
applyMixin(Vue)
}
applyMixin()
源码位置: vuex/src/mixin.js
export default function (Vue) {
const version = Number(Vue.version.split('.')[0])
if (version >= 2) {
// 如果是2.x.x以上版本,注入一个全局mixin, 执行vueInit方法
Vue.mixin({ beforeCreate: vuexInit })
} else {
// override init and inject vuex init procedure
// for 1.x backwards compatibility.
// 重写Vue原型上的_init方法, 注入vueinit方法 _init方法见 vue-dev/src/core/instance/init.js
const _init = Vue.prototype._init // 作为缓存变量
Vue.prototype._init = function (options = {}) {
options.init = options.init
? [vuexInit].concat(options.init)
: vuexInit
// 重新执行_init
_init.call(this, options)
}
}
/**
* Vuex init hook, injected into each instances init hooks list.
*/
// 注入store到Vue构造器
function vuexInit () {
// 这里的this. 指的是Vue构造器
/**
* new Vue({
* ...,
* store,
* route
* })
*/
// options: 就是new Vue(options)
// 源码见 vue-dev/src/core/instance/init.js initMixin方法
const options = this.$options
// store injection
// store是我们使用new Vuex.Store(options)的实例
// 注入store到Vue构造函数上的$store属性上, 所以我们在Vue组件里面使用this.$store来使用
if (options.store) {
// options.store为真说明是根节点root
this.$store = typeof options.store === 'function'
? options.store()
: options.store
} else if (options.parent && options.parent.$store) {
// 子组件直接从父组件中获取$store,这样就保证了所有组件都公用了全局的同一份store
this.$store = options.parent.$store
}
}
}
至于install方法Vuex是如果执行的?
export class Store {
constructor (options = {}) {
// 浏览器环境下安装vuex
if (!Vue && typeof window !== 'undefined' && window.Vue) {
install(window.Vue)
}
...
}
}