MVVM模式
介绍
首先上一张MVVM的架构图
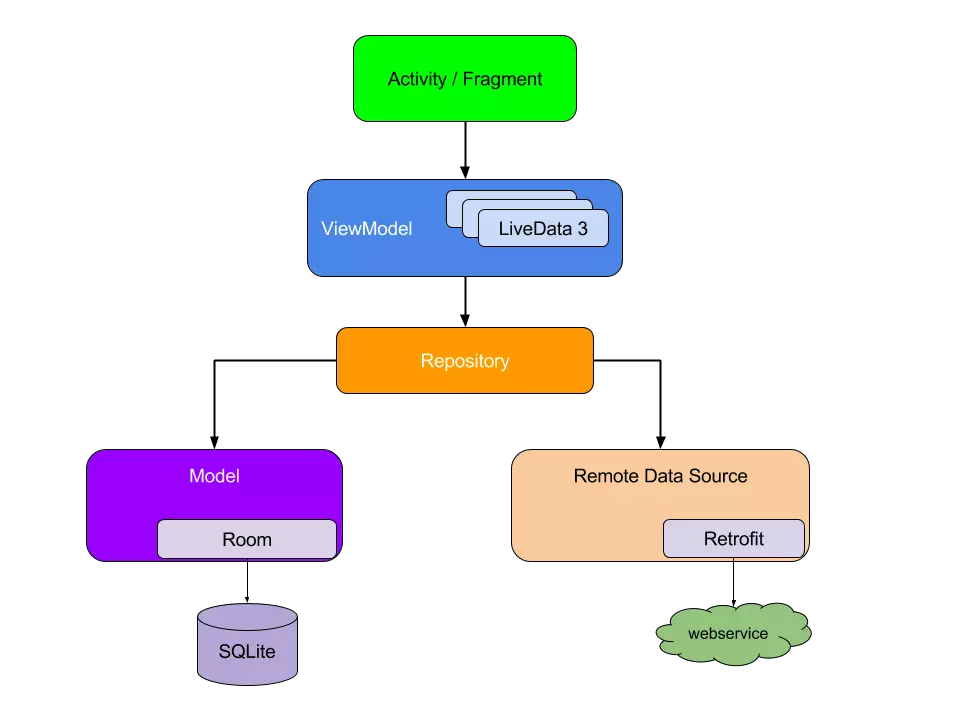
- View层即是图中绿色的Activity/Fragment,它的主要职责是负责UI中的绘制以及与用户交互,由ViewModel驱动,同时也监听UI事件及其生命周期,驱动ViewModel。
- ViewModel层即是图中蓝色的ViewModel,它创建关联,将model和view进行绑定,它只做业务逻辑的操作,不持有任何控件的引用。当model更改后,通过ViewModel传递给View来进行更新。
- Model层即是图中的橘色Repository并包括其下都是。Model层就是数据层,它的数据来源包括本地数据、缓存数据以及网络数据。
本文将以谷歌推出的MVVM框架DataBinding作为示例。
基本使用
- 启用DataBingding
在模块的build.gradle中添加以下代码。
dataBinding {
enabled = true
}
- 创建一个Bean类,这个bean类充当的就是Model。
public class StudentBean extends BaseObservable{
private String name;
private int age;
public StudentBean(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Bindable
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
notifyPropertyChanged(BR.name);
}
@Bindable
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
notifyPropertyChanged(BR.age);
}
}
- 修改Activity的xml布局文件,View层
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<layout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<data>
<variable
name="student"
type="cn.panf.mvvm_new.bean.StudentBean" />
</data>
<LinearLayout xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context="cn.panf.mvvm_new.MvvmActivity">
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@{student.name}"
android:textAlignment="center" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@{String.valueOf(student.age)}"
android:textAlignment="center" />
</LinearLayout>
</layout>
- 修改Activity类,ViewModel层
public class MvvmActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
// setContentView(R.layout.activity_mvvm);
ActivityMvvmBinding activityMvvmBinding =
DataBindingUtil.setContentView(this, R.layout.activity_mvvm);
StudentBean xiaoMing = new StudentBean("xiaoMing", 12);
activityMvvmBinding.setStudent(xiaoMing);
}
}
这样一个最简单的databinding就完成了,那么只要我们随意修改StudentBean中的任一对象,UI界面就会刷新。下面添加一个button按钮测试一下。
首先新建一个处理点击事件的类:
public interface HandleClick {
void buttonClick(View view);
}
在布局文件中添加:
<variable
name="clickhHandler"
type="cn.panf.mvvm_new.HandleClick" />
<Button
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:onClick="@{clickhHandler::buttonClick}" />
最后在Activity中:
//处理点击事件
activityMvvmBinding.setClickhHandler(new HandleClick() {
@Override
public void buttonClick(View view) {
xiaoMing.setAge(13);
}
});
这样你只要点击按钮,那么textView的数据就会自动刷新而不需要任何手动赋值,这就是所谓的数据驱动。
进阶使用
下面我们将databinding在RecyclerView中来进行使用。
首先修改布局文件
<layout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<LinearLayout xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context="cn.panf.mvvm_new.MvvmActivity">
<android.support.v7.widget.RecyclerView
android:id="@+id/rv"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" />
</LinearLayout>
</layout>
为RecyclerView的item新建一个布局layout_item_student.xml
<layout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<data>
<variable
name="student"
type="cn.panf.mvvm_new.bean.StudentBean" />
</data>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<TextView
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="@{student.name}" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="@{String.valueOf(student.age)}" />
</LinearLayout>
</layout>
新建Adapter类:
public class StudentAdapter extends RecyclerView.Adapter<StudentAdapter.StudentViewHolder> {
private List<StudentBean> mList;
private Context context;
public StudentAdapter(Context context, List<StudentBean> mList) {
this.mList = mList;
this.context = context;
}
@Override
public StudentViewHolder onCreateViewHolder(ViewGroup parent, int viewType) {
LayoutInflater inflater = (LayoutInflater) context.getSystemService(Context.LAYOUT_INFLATER_SERVICE);
LayoutItemStudentBinding layoutItemStudentBinding = DataBindingUtil
.inflate(inflater, R.layout.layout_item_student, parent, false);
return new StudentViewHolder(layoutItemStudentBinding);
}
@Override
public void onBindViewHolder(StudentViewHolder holder, int position) {
StudentBean studentBean = mList.get(position);
holder.getLayoutItemStudentBinding().setStudent(studentBean);
}
@Override
public int getItemCount() {
return mList == null ? 0 : mList.size();
}
class StudentViewHolder extends RecyclerView.ViewHolder {
private LayoutItemStudentBinding layoutItemStudentBinding;
LayoutItemStudentBinding getLayoutItemStudentBinding() {
return layoutItemStudentBinding;
}
StudentViewHolder(LayoutItemStudentBinding layoutItemStudentBinding) {
super(layoutItemStudentBinding.getRoot());
this.layoutItemStudentBinding = layoutItemStudentBinding;
}
}
}
注意,在上文的StudentViewHolder的构造函数中,我把item对应的布局的View对象改成了item对应布局的ViewDataBinding对象,然后提供一个get方法来给外部调用,这样做的好处是你不需要再去操作view去对数据进行修改,而是只需要把你获取到的数据直接传给Bean即可,因为你在item布局文件里已经把数据和View进行绑定了。
最后再来修改一下Activity:
public class MvvmActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private List<StudentBean> mList = new ArrayList<>();
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
// setContentView(R.layout.activity_mvvm);
ActivityMvvmBinding activityMvvmBinding =
DataBindingUtil.setContentView(this, R.layout.activity_mvvm);
// final StudentBean xiaoMing = new StudentBean("xiaoMing", 12);
addData();
StudentAdapter adapter = new StudentAdapter(this, mList);
LinearLayoutManager manager = new LinearLayoutManager(this, OrientationHelper.VERTICAL, false);
activityMvvmBinding.rv.setLayoutManager(manager);
activityMvvmBinding.rv.setAdapter(adapter);
}
private void addData() {
for (int i = 0; i < 15; i++) {
int age = new Random().nextInt(20);
StudentBean studentBean = new StudentBean("student" + i, age);
mList.add(studentBean);
}
}
}
OK, it works!
总结
通过介绍了MVVM的相关定义以及提供了两个实例来帮助理解,相信理解了本文的两个例子,必然会理解MVVM这种数据驱动的魅力所在,所有代码没有一处对控件进行赋值即可让数据进行自动刷新。但是,没有最好,只有最合适。目前在android中最广泛使用的还是MVP,而且在2017年谷歌推出了新的MVVM框架LiveData。
note: 目的在于以DataBinding来介绍MVVM,对DataBinding的更多用法并未详细介绍,有兴趣的可以去查阅更多相关资料。
更新
宫影让我看看能不能把databinding针对recyclerView在多布局上应用,我进行了尝试发现确实可行。
- 首先是要对不同的viewType进行区分,在上面我们已经将对于数据完全和Bean进行绑定了,所以最好在绑定数据时在Bean中进行区分。那么可以定义一个接口,使所有的Bean来实现它。
public interface IBaseItem {
int getItemViewType();
}
修改StudentBean类,并添加TeacherBean类。
//只放一张图片,仅为了做区分
public class TeacherBean extends BaseObservable implements IBaseItem {
private int resId;
public TeacherBean(int resId) {
this.resId = resId;
}
@Bindable
public int getResId() {
return resId;
}
public void setResId(int resId) {
this.resId = resId;
notifyPropertyChanged(BR.resId);
}
@Override
public int getItemViewType() {
return R.layout.layout_item_teacher;
}
}
public class StudentBean extends BaseObservable implements IBaseItem{
......
@Override
public int getItemViewType() {
return R.layout.layout_item_student;
}
}
layout_item_teacher.xml
<layout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto">
<data>
<variable
name="teacher"
type="cn.panf.mvvm_new.bean.TeacherBean" />
</data>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<ImageView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:scaleType="center"
app:imgUrl="@{teacher.resId}"/>
</LinearLayout>
</layout>
显示图片时由于dataBinding不支持直接写int类型,这里需要额外提供显示image的方法。 可以新建一个类页可以直接写在Adapter里面,看喜好。
public class ImgUtil {
@BindingAdapter("imgUrl")
public static void showImgByUrl(ImageView iv, int resId) {
iv.setImageResource(resId);
}
}
- 修改原本的StudentAdapter类,因为添加了Teacher,这里修改名称为SchoolAdapter。
package cn.panf.mvvm_new;
import android.content.Context;
import android.databinding.DataBindingUtil;
import android.support.v7.widget.RecyclerView;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import java.util.List;
import cn.panf.androidknowledge.R;
import cn.panf.androidknowledge.databinding.LayoutItemStudentBinding;
import cn.panf.androidknowledge.databinding.LayoutItemTeacherBinding;
import cn.panf.mvvm_new.bean.IBaseItem;
import cn.panf.mvvm_new.bean.StudentBean;
import cn.panf.mvvm_new.bean.TeacherBean;
/**
* author: aaron.pf
* date: 2019/4/17 19:49.
* desc:
*/
public class SchoolAdapter extends RecyclerView.Adapter {
private List<IBaseItem> mList;
private LayoutInflater inflater;
public SchoolAdapter(Context context, List<IBaseItem> mList) {
this.mList = mList;
inflater = (LayoutInflater) context.getSystemService(Context.LAYOUT_INFLATER_SERVICE);
}
@Override
public RecyclerView.ViewHolder onCreateViewHolder(ViewGroup parent, int viewType) {
switch (viewType) {
case R.layout.layout_item_student:
LayoutItemStudentBinding layoutItemStudentBinding = DataBindingUtil
.inflate(inflater, R.layout.layout_item_student, parent, false);
return new StudentViewHolder(layoutItemStudentBinding);
case R.layout.layout_item_teacher:
LayoutItemTeacherBinding layoutItemTeacherBinding = DataBindingUtil
.inflate(inflater, R.layout.layout_item_teacher, parent, false);
return new TeacherViewHolder(layoutItemTeacherBinding);
default:
LayoutItemTeacherBinding layoutItemTeacherBinding1 = DataBindingUtil
.inflate(inflater, R.layout.layout_item_teacher, parent, false);
return new TeacherViewHolder(layoutItemTeacherBinding1);
}
}
@Override
public void onBindViewHolder(RecyclerView.ViewHolder holder, int position) {
if (holder instanceof StudentViewHolder) {
StudentBean studentBean = (StudentBean) mList.get(position);
((StudentViewHolder) holder).getLayoutItemStudentBinding().setStudent(studentBean);
//防止数据刷新闪烁
((StudentViewHolder) holder).getLayoutItemStudentBinding().executePendingBindings();
} else if (holder instanceof TeacherViewHolder) {
TeacherBean teacherBean = (TeacherBean) mList.get(position);
((TeacherViewHolder) holder).getLayoutItemTeacherBinding().setTeacher(teacherBean);
((TeacherViewHolder) holder).getLayoutItemTeacherBinding().executePendingBindings();
}
}
@Override
public int getItemViewType(int position) {
return mList.get(position).getItemViewType();
}
@Override
public int getItemCount() {
return mList == null ? 0 : mList.size();
}
class StudentViewHolder extends RecyclerView.ViewHolder {
private LayoutItemStudentBinding layoutItemStudentBinding;
LayoutItemStudentBinding getLayoutItemStudentBinding() {
return layoutItemStudentBinding;
}
StudentViewHolder(LayoutItemStudentBinding layoutItemStudentBinding) {
super(layoutItemStudentBinding.getRoot());
this.layoutItemStudentBinding = layoutItemStudentBinding;
}
}
class TeacherViewHolder extends RecyclerView.ViewHolder {
private LayoutItemTeacherBinding layoutItemTeacherBinding;
public LayoutItemTeacherBinding getLayoutItemTeacherBinding() {
return layoutItemTeacherBinding;
}
public TeacherViewHolder(LayoutItemTeacherBinding layoutItemTeacherBinding) {
super(layoutItemTeacherBinding.getRoot());
this.layoutItemTeacherBinding = layoutItemTeacherBinding;
}
}
}
- 最后在Activity中来测试一下
public class MvvmActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private List<IBaseItem> mList = new ArrayList<>();
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
// setContentView(R.layout.activity_mvvm);
ActivityMvvmBinding activityMvvmBinding =
DataBindingUtil.setContentView(this, R.layout.activity_mvvm);
// final StudentBean xiaoMing = new StudentBean("xiaoMing", 12);
addData();
SchoolAdapter adapter = new SchoolAdapter(this, mList);
LinearLayoutManager manager = new LinearLayoutManager(this, OrientationHelper.VERTICAL, false);
activityMvvmBinding.rv.setLayoutManager(manager);
activityMvvmBinding.rv.setAdapter(adapter);
}
private void addData() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
mList.add(new StudentBean("stu1", 12));
mList.add(new StudentBean("stu2", 15));
mList.add(new TeacherBean(R.mipmap.ic_launcher));
mList.add(new StudentBean("stu3", 16));
mList.add(new TeacherBean(R.mipmap.ic_launcher));
mList.add(new StudentBean("stu4", 18));
mList.add(new TeacherBean(R.mipmap.ic_launcher));
}
}
}
OK, it works again!
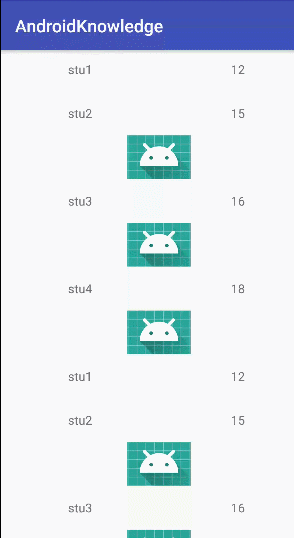
思考
这里虽然实现了功能,但是能否更进一步将Adapter抽取成通用的呢?能否将ViewHolder抽取一下呢?毕竟这两个ViewHolder重复的代码略多呀。