一、前言
上一节内容我们简单回顾了Mybatis的整体架构和相关概念知识点,并简述了本系列所用框架的版本。Mybatis功能强大,花样繁多。我们不会太关心所有的技术点,而是重点剖析常用的功能点。同Spring相比,Mybatis多以应用为主。从本节开始,我们正式开始源码的分析。
二、环境配置
每个基于 MyBatis 的应用都是以一个 SqlSessionFactory 的实例为中心的,SqlSessionFactory 的实例可以通过 SqlSessionFactoryBuilder 获得。而 SqlSessionFactoryBuilder 则可以从 XML 配置文件或一个预先定制的 Configuration 的实例构建出 SqlSessionFactory 的实例。例如:
String resource = "org/mybatis/example/mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory =
new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
当然,上面这些是Mybatis官方的样例。不过,我们日常开发中Mybatis都是与Spring一起使用的,交给Spring去搞定这些岂不更好。
<bean id="sqlSessionFactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" />
<property name="mapperLocations" value="classpath:com/viewscenes/netsupervisor/mapping/*.xml"></property>
<property name="typeAliasesPackage">
<array>
<value>com.viewscenes.netsupervisor.entity</value>
</array>
</property>
</bean>
三、初始化
我们来到org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean,看到它实现了InitializingBean接口。这说明,在这个类被实例化之后会调用到afterPropertiesSet()。它只有一个方法
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
this.sqlSessionFactory = buildSqlSessionFactory();
}
四、两个接口
1、SqlSessionFactory
SqlSessionFactory是一个接口,它里面其实就两个方法:openSession、getConfiguration。
package org.apache.ibatis.session;
public interface SqlSessionFactory {
SqlSession openSession();
SqlSession openSession(boolean autoCommit);
SqlSession openSession(Connection connection);
SqlSession openSession(TransactionIsolationLevel level);
SqlSession openSession(ExecutorType execType);
SqlSession openSession(ExecutorType execType, boolean autoCommit);
SqlSession openSession(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level);
SqlSession openSession(ExecutorType execType, Connection connection);
Configuration getConfiguration();
}
我们知道,可以通过openSession方法获取一个SqlSession对象,完成必要数据库增删改查功能。但是,SqlSessionFactory属性也太少了,那些mapper映射文件、SQL参数、返回值类型、缓存等属性都在哪呢?
2、Configuration
Configuration,你可以把它当成一个数据的大管家。MyBatis所有的配置信息都维持在Configuration对象之中,基本每个对象都会持有它的引用。正是应了那句话我是革命一块砖,哪里需要往哪搬。下面是部分属性
public class Configuration {
//环境
protected Environment environment;
protected boolean safeRowBoundsEnabled;
protected boolean safeResultHandlerEnabled = true;
protected boolean mapUnderscoreToCamelCase;
protected boolean aggressiveLazyLoading;
protected boolean multipleResultSetsEnabled = true;
protected boolean useGeneratedKeys;
protected boolean useColumnLabel = true;
protected boolean cacheEnabled = true;
protected boolean callSettersOnNulls;
protected boolean useActualParamName = true;
protected boolean returnInstanceForEmptyRow;
//日志信息的前缀
protected String logPrefix;
//日志接口
protected Class<? extends Log> logImpl;
//文件系统接口
protected Class<? extends VFS> vfsImpl;
//本地Session范围
protected LocalCacheScope localCacheScope = LocalCacheScope.SESSION;
//数据库类型
protected JdbcType jdbcTypeForNull = JdbcType.OTHER;
//延迟加载的方法
protected Set<String> lazyLoadTriggerMethods = new HashSet<String>(
Arrays.asList(new String[] { "equals", "clone", "hashCode", "toString" }));
//默认执行语句超时
protected Integer defaultStatementTimeout;
//默认的执行器
protected ExecutorType defaultExecutorType = ExecutorType.SIMPLE;
//数据库ID
protected String databaseId;
//mapper注册表
protected final MapperRegistry mapperRegistry = new MapperRegistry(this);
//拦截器链
protected final InterceptorChain interceptorChain = new InterceptorChain();
//类型处理器
protected final TypeHandlerRegistry typeHandlerRegistry = new TypeHandlerRegistry();
//类型别名
protected final TypeAliasRegistry typeAliasRegistry = new TypeAliasRegistry();
//语言驱动
protected final LanguageDriverRegistry languageRegistry = new LanguageDriverRegistry();
//mapper_id 和 mapper文件的映射
protected final Map<String, MappedStatement> mappedStatements = new StrictMap<MappedStatement>(
"Mapped Statements collection");
//mapper_id和缓存的映射
protected final Map<String, Cache> caches = new StrictMap<Cache>("Caches collection");
//mapper_id和返回值的映射
protected final Map<String, ResultMap> resultMaps = new StrictMap<ResultMap>("Result Maps collection");
//mapper_id和参数的映射
protected final Map<String, ParameterMap> parameterMaps = new StrictMap<ParameterMap>("Parameter Maps collection");
//资源列表
protected final Set<String> loadedResources = new HashSet<String>();
未完.......
}
五、构建SqlSessionFactory
在afterPropertiesSet方法只有一个动作,就是buildSqlSessionFactory。它可以分为两部分来看,先从配置文件的property属性中加载各种组件,解析配置到configuration中,然后加载mapper文件,解析SQL语句,封装成MappedStatement对象,配置到configuration中。
1、配置property属性
- typeAliases
这是一个类型的别名,很好用。比如在user_mapper的方法中,resultType和parameterType想使用实体类映射,而不用写全限定类名。
//这里的resultType就是别名
//它对应的是com.viewscenes.netsupervisor.entity.User
<select id="getUserById" resultType="user">
select * from user where uid=#{uid}
</select>
它有两种配置方式,指定包路径或者指定类文件的路径。
<property name="typeAliasesPackage">
<array>
<value>com.viewscenes.netsupervisor.entity</value>
</array>
</property>
或者
<property name="typeAliases">
<array>
<value>com.viewscenes.netsupervisor.entity.User</value>
</array>
</property>
它的解析很简单,就是拿到类路径的反射对象,key为默认类名小写,value为Class对象,注册到容器中。当然了,你也可以使用@Alias注解来设置别名的名称。
public void registerAlias(Class<?> type) {
String alias = type.getSimpleName();
Alias aliasAnnotation = type.getAnnotation(Alias.class);
if (aliasAnnotation != null) {
alias = aliasAnnotation.value();
}
String key = alias.toLowerCase(Locale.ENGLISH);
TYPE_ALIASES.put(key, type);
}
TYPE_ALIASES容器就是一个HashMap,里面已经默认添加了很多的类型别名。
registerAlias("string", String.class);
registerAlias("byte", Byte.class);
registerAlias("long", Long.class);
registerAlias("short", Short.class);
registerAlias("int", Integer.class);
registerAlias("integer", Integer.class);
registerAlias("double", Double.class);
registerAlias("float", Float.class);
registerAlias("boolean", Boolean.class);
......未完
- typeHandlers
它是一个类型的处理器。在数据库查询出结果后,应该转换成Java中的什么类型?由它来决定。如果Mybatis里面没有你想要的,就可以在这里自定义一个处理器。 这块内容,在后续章节我将通过一个实例独立讲解。现在,先来看下它的默认处理器。
register(JdbcType.BOOLEAN, new BooleanTypeHandler());
register(JdbcType.TINYINT, new ByteTypeHandler());
register(JdbcType.SMALLINT, new ShortTypeHandler());
register(Integer.class, new IntegerTypeHandler());
register(JdbcType.INTEGER, new IntegerTypeHandler());
register(JdbcType.FLOAT, new FloatTypeHandler());
register(JdbcType.DOUBLE, new DoubleTypeHandler());
register(String.class, new StringTypeHandler());
register(String.class, JdbcType.CHAR, new StringTypeHandler());
register(String.class, JdbcType.CLOB, new ClobTypeHandler());
register(String.class, JdbcType.VARCHAR, new StringTypeHandler());
register(String.class, JdbcType.LONGVARCHAR, new ClobTypeHandler());
register(String.class, JdbcType.NVARCHAR, new NStringTypeHandler());
register(String.class, JdbcType.NCHAR, new NStringTypeHandler());
register(String.class, JdbcType.NCLOB, new NClobTypeHandler());
register(JdbcType.CHAR, new StringTypeHandler());
register(JdbcType.VARCHAR, new StringTypeHandler());
register(JdbcType.CLOB, new ClobTypeHandler());
register(JdbcType.LONGVARCHAR, new ClobTypeHandler());
.....未完
- plugins
可以配置一个或多个插件。插件功能很强大,在执行SQL之前,在返回结果之后,在插入数据时...都可以让你有机会插手数据的处理。这个部分最常用的是分页,在后续章节,笔者将通过分页和数据同步的实例单独讲解。
<property name="plugins">
<array>
<bean class="com.viewscenes.netsupervisor.interceptor.xxxInterceptor"></bean>
<bean class="com.viewscenes.netsupervisor.interceptor.xxxInterceptor"></bean>
</array>
</property>
2、解析mapperLocations
mapperLocations配置的是应用中mapper文件的路径,获取所有的mapper文件。通过解析里面的select/insert/update/delete节点,每一个节点生成一个MappedStatement对象。最后注册到Configuration对象的mappedStatements。key为mapper的namespace+节点id。
先来看一下方法的整体。
public class XMLMapperBuilder extends BaseBuilder {
private void configurationElement(XNode context) {
//命名空间 即mapper接口的路径
String namespace = context.getStringAttribute("namespace");
if (namespace == null || namespace.equals("")) {
throw new BuilderException("Mapper's namespace cannot be empty");
}
//设置当前mapper文件的命名空间
builderAssistant.setCurrentNamespace(namespace);
//引用缓存
cacheRefElement(context.evalNode("cache-ref"));
//是否开启二级缓存
cacheElement(context.evalNode("cache"));
//参数
parameterMapElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/parameterMap"));
//返回值
resultMapElements(context.evalNodes("/mapper/resultMap"));
//解析sql节点
sqlElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/sql"));
//SQL语句解析
buildStatementFromContext(context.evalNodes("select|insert|update|delete"));
}
}
- 缓存
通过在mapper文件中声明</cache>来开启二级缓存。通过获取缓存的配置信息来构建Cache的实例,最后注册到configuration。
private void cacheElement(XNode context) throws Exception {
//获取缓存的实例类型,在configuration初始化的时候注册
// typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("PERPETUAL", PerpetualCache.class);
//typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("FIFO", FifoCache.class);
//typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("LRU", LruCache.class);
String type = context.getStringAttribute("type", "PERPETUAL");
Class<? extends Cache> typeClass = typeAliasRegistry.resolveAlias(type);
//LRU回收算法
String eviction = context.getStringAttribute("eviction", "LRU");
Class<? extends Cache> evictionClass = typeAliasRegistry.resolveAlias(eviction);
//刷新间隔
Long flushInterval = context.getLongAttribute("flushInterval");
//大小
Integer size = context.getIntAttribute("size");
//是否只读
boolean readWrite = !context.getBooleanAttribute("readOnly", false);
//是否阻塞
boolean blocking = context.getBooleanAttribute("blocking", false);
Properties props = context.getChildrenAsProperties();
builderAssistant.useNewCache(typeClass, evictionClass, flushInterval, size, readWrite, blocking, props);
}
拿到这些属性后,将缓存设置到configuration。
//二级缓存是和mapper绑定的
//所以,这里的id就是mapper的命名空间
public void addCache(Cache cache) {
caches.put(cache.getId(), cache);
}
- resultMap、parameterMap
它们表示的是查询结果集中的列与Java对象中属性的对应关系。其实,只有在数据库字段与JavaBean不匹配的情况下才用到,通常情况下推荐使用resultType/parameterType,也就是直接利用实体类即可。这种方式很简便,同时遵循约定大于配置,代码出错的可能较小。
中间过程不看了,最后他们也都是注册到configuration。
public void addParameterMap(ParameterMap pm) {
parameterMaps.put(pm.getId(), pm);
}
public void addResultMap(ResultMap rm) {
resultMaps.put(rm.getId(), rm);
}
- SQL标签
SQL标签可将重复的sql提取出来,使用时用include引用即可,最终达到sql重用的目的。它的解析很简单,就是把内容放入sqlFragments容器。id为命名空间+节点ID
- SELECT、INSERT、UPDATE、DELETE
动态SQL的解析是Mybatis的核心所在。之所以是动态SQL,源自它不同的动态标签,比如Choose、ForEach、If、Set等,而Mybatis把它们都封装成不同的类对象,它们共同的接口是SqlNode。

每一种标签又对应一种处理器。
private void initNodeHandlerMap() {
nodeHandlerMap.put("trim", new TrimHandler());
nodeHandlerMap.put("where", new WhereHandler());
nodeHandlerMap.put("set", new SetHandler());
nodeHandlerMap.put("foreach", new ForEachHandler());
nodeHandlerMap.put("if", new IfHandler());
nodeHandlerMap.put("choose", new ChooseHandler());
nodeHandlerMap.put("when", new IfHandler());
nodeHandlerMap.put("otherwise", new OtherwiseHandler());
nodeHandlerMap.put("bind", new BindHandler());
}
- 静态SQL
静态SQL,就是不带上面那些标签的节点。它比较简单,最后就是将SQL内容封装到MixedSqlNode对象。MixedSqlNode对象里面有个List,封装的就是StaticTextSqlNode对象,而StaticTextSqlNode对象只有一个属性text,即SQL内容。
protected MixedSqlNode parseDynamicTags(XNode node) {
//SQL内容
String data = child.getStringBody("");
//生成TextSqlNode判断是否为动态SQL
TextSqlNode textSqlNode = new TextSqlNode(data);
if (textSqlNode.isDynamic()) {
contents.add(textSqlNode);
isDynamic = true;
} else {
contents.add(new StaticTextSqlNode(data));
}
return new MixedSqlNode(contents);
}
如果是静态SQL,将SQL语句中的#{}转为?,返回StaticSqlSource对象 。
public StaticSqlSource(Configuration configuration, String sql, List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings) {
this.sql = sql;
this.parameterMappings = parameterMappings;
this.configuration = configuration;
}
- 动态SQL
一个动态SQL会分为不同的子节点,我们以一个UPDATE语句为例,尝试跟踪下它的解析过程。比如下面的UPDATE节点会分为三个子节点。两个静态节点和一个SET动态节点,而SET节点又分为两个IF动态节点。
<update id="updateUser" parameterType="user">
update user
<set>
<if test="username!=null">
username = #{username},
</if>
<if test="password!=null">
password = #{password},
</if>
</set>
where uid = #{uid}
</update>
[
[#text: update user ],
[set: null],
[#text: where uid = #{uid}]
]
首先,获得当前的节点的内容,即updateUser。调用parseDynamicTags
public class XMLScriptBuilder extends BaseBuilder {
//参数node即为当前UDATE节点的内容
protected MixedSqlNode parseDynamicTags(XNode node) {
List<SqlNode> contents = new ArrayList<SqlNode>();
//children分为3个子节点
//2个静态节点(update user和where id=#{id})
//1个动态节点set
NodeList children = node.getNode().getChildNodes();
for (int i = 0; i < children.getLength(); i++) {
XNode child = node.newXNode(children.item(i));
//如果是静态节点,将内容封装成StaticTextSqlNode对象
if (child.getNode().getNodeType() == Node.CDATA_SECTION_NODE || child.getNode().getNodeType() == Node.TEXT_NODE) {
String data = child.getStringBody("");
TextSqlNode textSqlNode = new TextSqlNode(data);
if (textSqlNode.isDynamic()) {
contents.add(textSqlNode);
isDynamic = true;
} else {
contents.add(new StaticTextSqlNode(data));
}
}
//动态节点
else if (child.getNode().getNodeType() == Node.ELEMENT_NODE) { // issue #628
//获取节点名称 比如SET/IF
String nodeName = child.getNode().getNodeName();
//获取节点标签对应的处理类 比如SetHandler
NodeHandler handler = nodeHandlerMap.get(nodeName);
handler.handleNode(child, contents);
isDynamic = true;
}
}
return new MixedSqlNode(contents);
}
}
第一个是静态节点update user。根据上面的源码,它将被封装成StaticTextSqlNode对象,加入contents集合。
第二个是动态节点SET,他将调用到SetHandler.handleNode()。
private class SetHandler implements NodeHandler {
//nodeToHandle为SET节点的内容,targetContents为已解析完成的Node集合
public void handleNode(XNode nodeToHandle, List<SqlNode> targetContents) {
//回调parseDynamicTags
MixedSqlNode mixedSqlNode = parseDynamicTags(nodeToHandle);
//最终将SET节点封装成SetSqlNode,放入Node集合
SetSqlNode set = new SetSqlNode(configuration, mixedSqlNode);
targetContents.add(set);
}
}
在第二次回调到parseDynamicTags方法时,这时候的参数为SET节点里的2个IF子节点。同样,它们会将当做动态节点解析,调用到IfHandler.handleNode()。
private class IfHandler implements NodeHandler {
//nodeToHandle为IF节点的内容, targetContents为已解析完成的Node集合
public void handleNode(XNode nodeToHandle, List<SqlNode> targetContents) {
//回调parseDynamicTags
MixedSqlNode mixedSqlNode = parseDynamicTags(nodeToHandle);
//获取IF标签的test属性,即条件表达式
String test = nodeToHandle.getStringAttribute("test");
//将IF节点封装成IfSqlNode对象,放入Node集合。
IfSqlNode ifSqlNode = new IfSqlNode(mixedSqlNode, test);
targetContents.add(ifSqlNode);
}
}
就这样,递归的调用parseDynamicTags方法,直到传进来的参数Node为一个静态节点,返回StaticTextSqlNode对象,并加入集合中。 第三个是静态节点where id=#{id},封装成StaticTextSqlNode对象,加入contents集合。
最后,contents集合就是UPDATE节点对应的各种sqlNode。
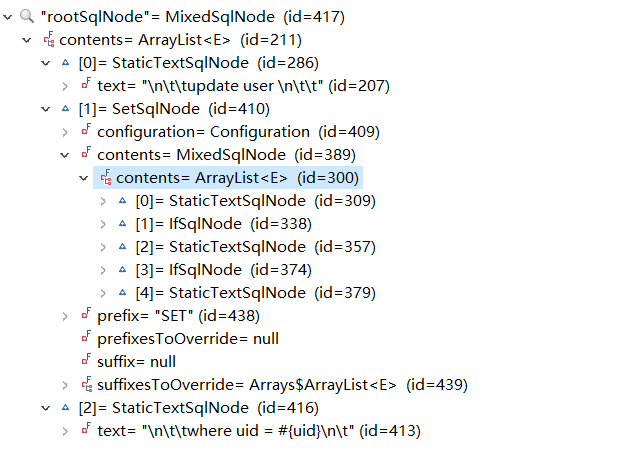
如果是动态SQL,返回DynamicSqlSource对象。
public DynamicSqlSource(Configuration configuration, SqlNode rootSqlNode) {
this.configuration = configuration;
this.rootSqlNode = rootSqlNode;
}
3、生成MappedStatement对象
mapper文件中的每一个SELECT/INSERT/UPDATE/DELETE节点对应一个MappedStatement对象。
public MappedStatement addMappedStatement() {
//全限定类名+方法名
id = applyCurrentNamespace(id, false);
//是否为查询语句
boolean isSelect = sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.SELECT;
//配置各种属性
MappedStatement.Builder statementBuilder = new MappedStatement.Builder(configuration, id, sqlSource, sqlCommandType)
.resource(resource)
.fetchSize(fetchSize)
.timeout(timeout)
.statementType(statementType)
.keyGenerator(keyGenerator)
.keyProperty(keyProperty)
.keyColumn(keyColumn)
.databaseId(databaseId)
.lang(lang)
.resultOrdered(resultOrdered)
.resultSets(resultSets)
.resultMaps(getStatementResultMaps(resultMap, resultType, id))
.resultSetType(resultSetType)
.flushCacheRequired(valueOrDefault(flushCache, !isSelect))
.useCache(valueOrDefault(useCache, isSelect))
.cache(currentCache);
//参数类型
ParameterMap statementParameterMap = getStatementParameterMap(parameterMap, parameterType, id);
if (statementParameterMap != null) {
statementBuilder.parameterMap(statementParameterMap);
}
//将MappedStatement对象注册到configuration
//注册其实就是往Map中添加。mappedStatements.put(ms.getId(), ms);
MappedStatement statement = statementBuilder.build();
configuration.addMappedStatement(statement);
return statement;
}
六、Annotation的支持
1、注解式的SQL定义
除了在mapper文件中配置SQL,Mybatis还支持注解方式的SQL。通过@Select,标注在Mapper接口的方法上。
public interface UserMapper {
@Select("select * from user ")
List<User> AnnotationGetUserList();
}
或者你想要的是动态SQL,那么就加上<script>。
public interface UserMapper {
@Select("select * from user ")
List<User> AnnotationGetUserList();
@Select("<script>"
+ "select * from user "
+ "<if test='id!=null'>"
+ "where id=#{id}"
+ "</if>"
+ "</script>")
List<User> AnnotationGetUserById(@Param("id")String id);
}
以上这两种方式都不常用,如果你真的不想用mapper.xml文件来定义SQL,那么以下方式可能适合你。你可以通过@SelectProvider来声明一个类的方法,此方法负责返回一个SQL的字符串。
public interface UserMapper {
@SelectProvider(type=SqlProvider.class,method="getUserById")
List<User> AnnotationProviderGetUserById(String id);
}
types指定了类的Class,method就是类的方法。其实这种方式也很不错,动态SQL的生成不仅仅依靠Mybatis的动态标签,在程序中可以随便搞。
public class SqlProvider {
public String getUserById(String id) {
String sql = "select * from user ";
if (id!=null) {
sql += " where id="+id;
}
return sql;
}
}
除了上面的@Select,当然还有对应其它几种的注解。
sqlAnnotationTypes.add(Select.class);
sqlAnnotationTypes.add(Insert.class);
sqlAnnotationTypes.add(Update.class);
sqlAnnotationTypes.add(Delete.class);
sqlProviderAnnotationTypes.add(SelectProvider.class);
sqlProviderAnnotationTypes.add(InsertProvider.class);
sqlProviderAnnotationTypes.add(UpdateProvider.class);
sqlProviderAnnotationTypes.add(DeleteProvider.class);
2、注解的扫描
上面我们看完了mapper文件中SQL的解析,下面来看注解是在哪里被扫描到的呢?
public class MapperRegistry {
public <T> void addMapper(Class<T> type) {
if (type.isInterface()) {
try {
MapperAnnotationBuilder parser = new MapperAnnotationBuilder(config, type);
parser.parse();
}
}
}
}
type就是当前mapper接口的Class对象。获取Class对象的所有Method[]。
Method[] methods = type.getMethods();
for (Method method : methods) {
if (!method.isBridge()) {
parseStatement(method);
}
}
parseStatement方法最终就生成MappedStatement对象,注册到configuration中,这个流程是与XML的方式一样,不会变的。
void parseStatement(Method method) {
//判断方法上是否包含那几种注解
//如果有,就根据注解的内容创建SqlSource对象。创建过程与XML创建过程一样
SqlSource sqlSource = getSqlSourceFromAnnotations(method, parameterTypeClass, languageDriver);
if (sqlSource != null) {
//获取各种属性,过程略过
......
//创建MappedStatement对象,注册到configuration
assistant.addMappedStatement();
}
}
所以,我们看到。getSqlSourceFromAnnotations才是重点,拿到注解及注解上的值,创建SqlSource对象。
private SqlSource getSqlSourceFromAnnotations(Method method,
Class<?> parameterType, LanguageDriver languageDriver) {
//注解就分为两大类,sqlAnnotation和sqlProviderAnnotation
//循环注解列表,判断Method包含哪一种,就返回哪种类型注解的实例
Class<? extends Annotation> sqlAnnotationType = getSqlAnnotationType(method);
Class<? extends Annotation> sqlProviderAnnotationType = getSqlProviderAnnotationType(method);
//不能两种类型都配置哦
if (sqlAnnotationType != null) {
if (sqlProviderAnnotationType != null) {
throw new BindingException("You cannot supply both a static SQL and SqlProvider to method named " + method.getName());
}
Annotation sqlAnnotation = method.getAnnotation(sqlAnnotationType);
final String[] strings = (String[]) sqlAnnotation.getClass().getMethod("value").invoke(sqlAnnotation);
return buildSqlSourceFromStrings(strings, parameterType, languageDriver);
}else if (sqlProviderAnnotationType != null) {
Annotation sqlProviderAnnotation = method.getAnnotation(sqlProviderAnnotationType);
return new ProviderSqlSource(assistant.getConfiguration(), sqlProviderAnnotation, type, method);
}
return null;
}
3、创建SqlSource对象
扫描到注解后,就要根据注解类型的不同,创建SqlSource对象。
- SELECT
我们以AnnotationGetUserList为例,它的注解是这样:@Select("select * from user ")。最后创建SqlSource对象的过程与XML创建过程是一样的。
public SqlSource createSqlSource(Configuration configuration, String script, Class<?> parameterType) {
//如果是带script标签的内容,最终调用到parseDynamicTags方法。
//parseDynamicTags方法会递归调用,直到节点属性为静态节点。
if (script.startsWith("<script>")) {
XPathParser parser = new XPathParser(script, false, configuration.getVariables(), new XMLMapperEntityResolver());
return createSqlSource(configuration, parser.evalNode("/script"), parameterType);
}else {
script = PropertyParser.parse(script, configuration.getVariables());
TextSqlNode textSqlNode = new TextSqlNode(script);
if (textSqlNode.isDynamic()) {
return new DynamicSqlSource(configuration, textSqlNode);
}else {
//把#{}换成?,生成StaticSqlSource对象
return new RawSqlSource(configuration, script, parameterType);
}
}
}
- SelectProvider
调用到ProviderSqlSource类的构造器,过程比较简单,就是拿到SqlProvider类上的方法,将方法名、方法参数和参数类型设置一下。
public ProviderSqlSource(Configuration configuration, Object provider, Class<?> mapperType, Method mapperMethod) {
String providerMethodName;
this.configuration = configuration;
this.sqlSourceParser = new SqlSourceBuilder(configuration);
this.providerType = (Class<?>) provider.getClass().getMethod("type").invoke(provider);
providerMethodName = (String) provider.getClass().getMethod("method").invoke(provider);
for (Method m : this.providerType.getMethods()) {
if (providerMethodName.equals(m.getName()) && CharSequence.class.isAssignableFrom(m.getReturnType())) {
this.providerMethod = m;
this.providerMethodArgumentNames = new ParamNameResolver(configuration, m).getNames();
this.providerMethodParameterTypes = m.getParameterTypes();
}
}
}
4、注册
注册过程也同XML方式一样,生成MappedStatement对象,然后设置到configuration中。configuration.addMappedStatement(statement);
七、总结
本章节主要阐述了Mybatis的启动过程之一,加载配置信息,解析SQL。最后生成SqlSessionFactory对象。
1、配置信息
Mybatis的配置信息较多,但也并非都需要。常用的就是缓存、类型转换器、类型别名、插件等。
2、解析SQL
生成SQL的方式大致有mapper.xml和Annotation两种。Annotation又分为SqlAnnotation和SqlProviderAnnotation,如果真的想要注解式的SQL,还是比较推荐SqlProviderAnnotation。