第一种场景:
在UI线程中更新UI,这种是最简单的,直接更新UI即可。
代码如下
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private Button bt_click_me;
private TextView tv_text;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
bt_click_me = findViewById(R.id.bt_click_me);
tv_text = findViewById(R.id.tv_text);
bt_click_me.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
tv_text.setText("111111111111111");
}
});
}
}第二种场景:
从子线程中更新UI
代码如下
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private Button bt_click_me;
private TextView tv_text;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
bt_click_me = findViewById(R.id.bt_click_me);
tv_text = findViewById(R.id.tv_text);
bt_click_me.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Thread thread = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
tv_text.setText("111111111111111");
}
});
thread.start();
}
});
}
}当点击按钮更新UI的时候就会发现报了异常,异常如下
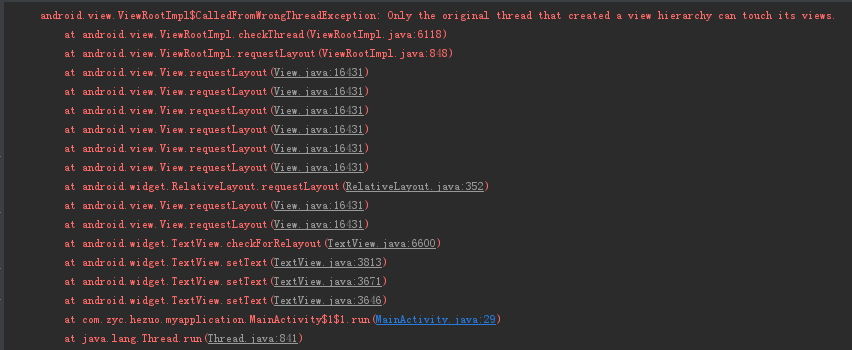
这个异常证明了子线程不能直接更新UI,解决方案如下
(1)通过Activity中的runOnUIThread方法
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private Button bt_click_me;
private TextView tv_text;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
bt_click_me = findViewById(R.id.bt_click_me);
tv_text = findViewById(R.id.tv_text);
bt_click_me.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Thread thread = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
runOnUiThread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
tv_text.setText("111111111111111");
}
});
}
});
thread.start();
}
});
}
}我们来深入源码
/**
* Runs the specified action on the UI thread. If the current thread is the UI
* thread, then the action is executed immediately. If the current thread is
* not the UI thread, the action is posted to the event queue of the UI thread.
*
* @param action the action to run on the UI thread
*/
public final void runOnUiThread(Runnable action) {
if (Thread.currentThread() != mUiThread) {
mHandler.post(action);
} else {
action.run();
}
}源码的意思是说, 如果当前线程不是UI线程, 那么执行
mHandler.post(action);否则直接执行run。
这个结论直接告诉了我们,Handler的post方法也能做到从子线程更新UI。
(2)通过Handler的post方法
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private Handler handler = new Handler();
private Button bt_click_me;
private TextView tv_text;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
bt_click_me = findViewById(R.id.bt_click_me);
tv_text = findViewById(R.id.tv_text);
bt_click_me.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Thread thread = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
handler.post(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
tv_text.setText("111111111111111");
}
});
}
});
thread.start();
}
});
}
}我在UI线程中new了一个Handler对象,在子线程中用这个对象来调用post方法。
我们来深入源码
/**
* Causes the Runnable r to be added to the message queue.
* The runnable will be run on the thread to which this handler is
* attached.
*
* @param r The Runnable that will be executed.
*
* @return Returns true if the Runnable was successfully placed in to the
* message queue. Returns false on failure, usually because the
* looper processing the message queue is exiting.
*/
public final boolean post(Runnable r)
{
return sendMessageDelayed(getPostMessage(r), 0);
}
private static Message getPostMessage(Runnable r) {
Message m = Message.obtain();
m.callback = r;
return m;
}在Handler对象中,有一个post方法,分析源码得知, 这个方法将形参r封装到一个消息里面, 再利用sendMessageDelayed方法将消息发送(添加)到消息队列。(注:理解这句话需要对Handler机制有一定的了解)
我们得出结论,通过handler发送消息也能实现子线程更新UI。
(3)通过handler发送消息来实现子线程更新UI
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private Handler handler = new Handler(){
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
super.handleMessage(msg);
switch (msg.what){
case 1:
tv_text.setText("111111111111111");
break;
}
}
};
private Button bt_click_me;
private TextView tv_text;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
bt_click_me = findViewById(R.id.bt_click_me);
tv_text = findViewById(R.id.tv_text);
bt_click_me.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Thread thread = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
Message message = Message.obtain();
message.what = 1;
handler.sendMessage(message);
}
});
thread.start();
}
});
}
}(4)通过view的post方法实现
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private Button bt_click_me;
private TextView tv_text;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
bt_click_me = findViewById(R.id.bt_click_me);
tv_text = findViewById(R.id.tv_text);
bt_click_me.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Thread thread = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
bt_click_me.post(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
tv_text.setText("111111111111111");
}
});
}
});
thread.start();
}
});
}
}我们来深入源码
/**
* <p>Causes the Runnable to be added to the message queue.
* The runnable will be run on the user interface thread.</p>
*
* @param action The Runnable that will be executed.
*
* @return Returns true if the Runnable was successfully placed in to the
* message queue. Returns false on failure, usually because the
* looper processing the message queue is exiting.
*
* @see #postDelayed
* @see #removeCallbacks
*/
public boolean post(Runnable action) {
final AttachInfo attachInfo = mAttachInfo;
if (attachInfo != null) {
return attachInfo.mHandler.post(action);
}
// Postpone the runnable until we know on which thread it needs to run.
// Assume that the runnable will be successfully placed after attach.
getRunQueue().post(action);
return true;
}其实最终也调用了mHandler.post(action)方法。
第二种场景总结:
(1)Android从子线程更新UI就是通过Handler来实现的,官方发明Handler主要就是给我们更新UI用的。
其实吧, 一些脑洞大开的猿类动物偏不按照常理出牌:
(1)在子线程中他偏偏不用Handler更新UI?
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private TextView tv_text;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
tv_text = findViewById(R.id.tv_text);
tv_text.setText("1111111");
Thread thread = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i=0;i<500000;i++){
Log.e("aa", String.valueOf(i));//耗时操作
if(i==499999){
tv_text.setText("22222222");
}
}
}
});
thread.start();
}
}这个例子是从onCreate方法中的子线程更新UI, 其中有耗时操作
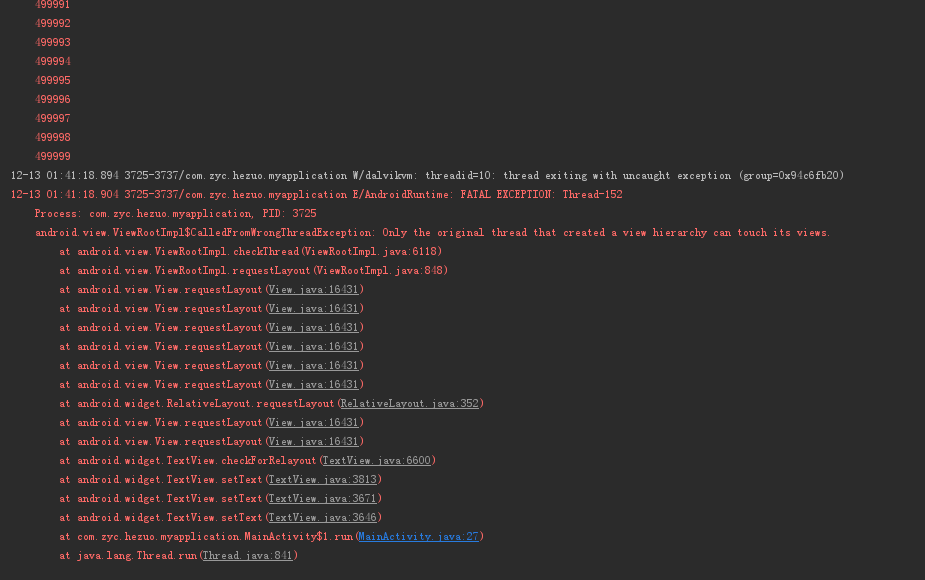
上述的例子依然报错, 那么怎么才能不让他报错呢,往下看
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private TextView tv_text;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
tv_text = findViewById(R.id.tv_text);
tv_text.setText("1111111");
Thread thread = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
tv_text.setText("22222222");
}
});
thread.start();
}
}当我去除耗时操作时,就不会报这个错误了,那么为什么呢?
我们来翻看源码
在ViewRootImpl类中找到了这个方法,这个方法就是之所以报错的根本
void checkThread() {
if (mThread != Thread.currentThread()) {
throw new CalledFromWrongThreadException(
"Only the original thread that created a view hierarchy can touch its views.");
}
}而ViewRootImpl对象是在执行到onResume才创建时的,所以得出结论,onCreate中的子线程如果不是耗时操作,基本都是可以更新UI的,但不能保证。因为一个是UI线程,一个是子线程,我们谁也不知道哪个线程更快一些。
(2)把消息从UI线程发送到子线程?
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private Button bt_click_me;
private Handler handler;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
bt_click_me = findViewById(R.id.bt_click_me);
bt_click_me.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Message message = Message.obtain();
message.what = 1;
handler.sendMessage(message);
}
});
Thread thread = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
Looper.prepare();
Looper looper = Looper.myLooper();
handler = new Handler(looper){
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
super.handleMessage(msg);
Log.d("aa", "11111");
}
};
Looper.loop();
}
});
thread.start();
}
}UI线程本身就有Looper,但是子线程是没有Looper的,所以必须新建Looper来轮询Looper中的消息队列。