接上一篇history源码解析-管理会话历史记录,本篇教你手写history,重在理解其原理。
history是一个JavaScript库,可让你在JavaScript运行的任何地方轻松管理会话历史记录
1.前言
history是由Facebook维护的,react-router依赖于history,区别于浏览器的window.history,history是包含window.history的,让开发者可以在任何环境都能使用history的api(例如Node、React Native等)。本文中history指仓库的对象,window.history指浏览器的对象。
本篇读后感分为五部分,分别为前言、使用、原理、上手、总结,推荐顺序阅读哈哈。
附上地址
2.使用
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<script src="history.js"></script>
<script>
var createHistory = History.createBrowserHistory
var page = 0
// createHistory创建所需要的history对象
var h = createHistory()
// h.block触发在地址栏改变之前,用于告知用户地址栏即将改变
h.block(function (location, action) {
return 'Are you sure you want to go to ' + location.path + '?'
})
// h.listen监听当前地址栏的改变
h.listen(function (location) {
console.log(location, 'lis-1')
})
</script>
</head>
<body>
<p>Use the two buttons below to test normal transitions.</p>
<p>
<!-- h.push用于跳转 -->
<button onclick="page++; h.push('/' + page, { page: page })">history.push</button>
<button onclick="h.goBack()">history.goBack</button>
</p>
</body>
</html>
history用法:
block用于地址改变之前的截取;listener用于监听地址栏的改变;push添加新历史记录;replace替换当前历史记录;go(n)跳转到某条历史记录;goBack返回上一条历史记录。
3.原理
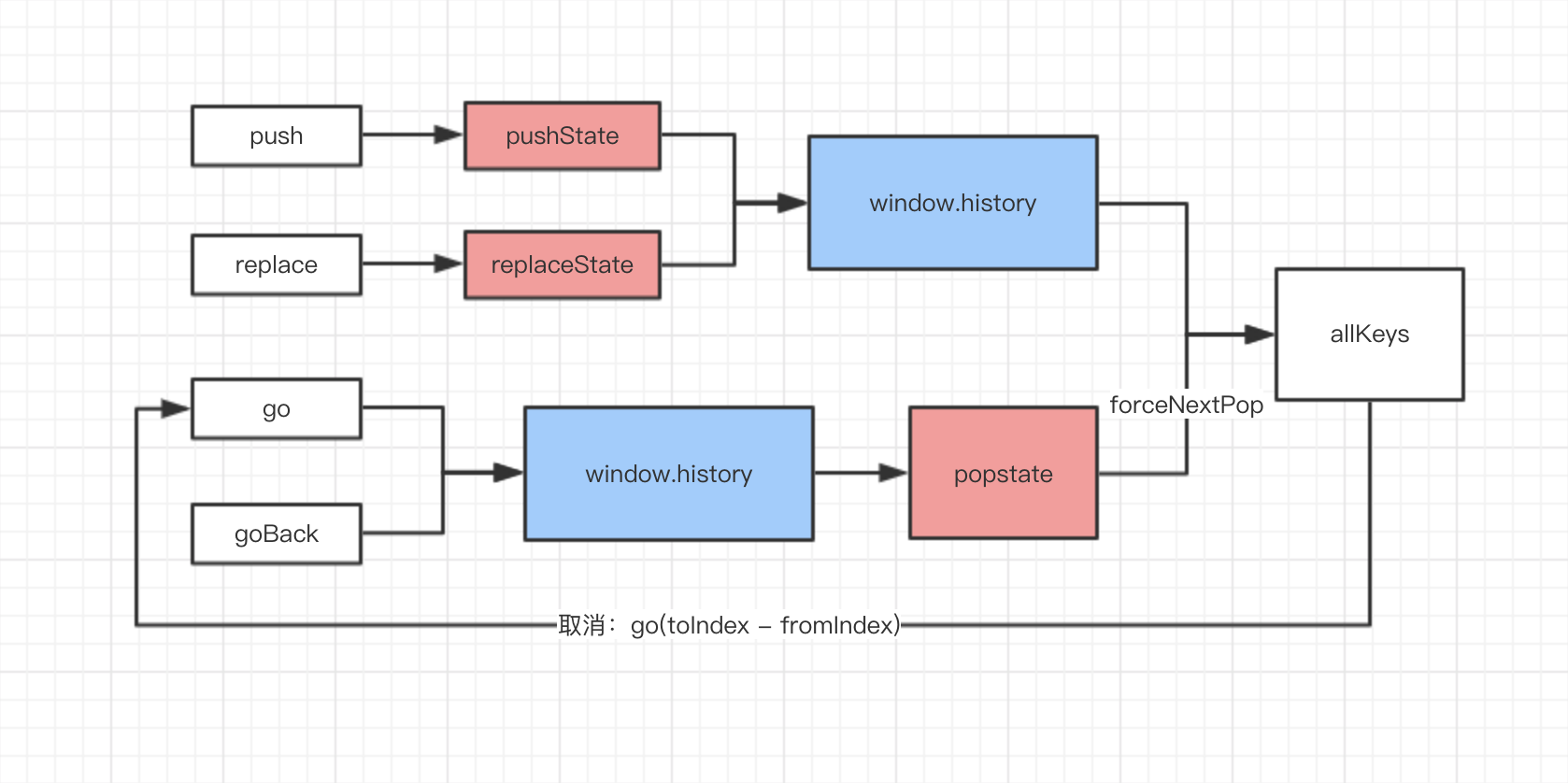
解释:
push、replace、go、goBack:仓库history的方法pushState、replaceState:window.history的方法,用于修改window.history历史记录popstate:监听历史记录的改变window.addEventListener('popstate', callback)forceNextPop:自定义变量,用于判断是否跳过弹出框allKeys:自定义变量,它跟历史记录是同步的。每当修改历史记录,都会维护这个数组,用于当弹出框点击取消时,可以返回到上次历史记录go(toIndex - fromIndex):弹出框取消时,返回上一次历史记录
当活动历史记录条目更改时,将触发popstate事件。需要注意的是调用history.pushState()或history.replaceState()不会触发popstate事件。只有在做出浏览器动作时,才会触发该事件,如用户点击浏览器的回退按钮(或者在Javascript代码中调用history.back())
路线1(push和replace):
- 用户调用
push; - 弹出弹出框;
- 点确定按钮:
- 调用
window.history.pushState添加历史记录,把key存储到window.history中(注意这个时候不会触发popstate监听函数); - 地址改变;
- 维护自定义变量
allKeys,添加key到allKeys数组。
- 调用
- 点取消按钮:不操作。
- 点确定按钮:
线路2(go和goBack):
- 用户调用
go; - 修改历史记录
window.history,地址改变; - 触发
popstate历史记录监听函数(如果绑定了popstate监听函数); - 弹出弹出框;
- 点确定按钮:
- 更新
history(保证history是最新的信息,例如history.location是当前地址信息)。
- 更新
- 点取消按钮(因为在第二步的时候地址已经跳转了,点弹出框的取消意图就需要回到之前的记录):
- 计算
toIndex:跳转前的地址(取history.location的值,因为此时的history.location尚未更新是旧值); - 计算
fromIndex:当前地址的key; - 计算两者的差值,调用
go方法跳回去上次历史记录。
- 计算
- 点确定按钮:
这基本是history的原理了,应该会有些同学存在疑惑,调用弹出框这个可以放在调用go之前,同样能达到效果,而且代码会更加简洁且不需要维护allKeys这个数组。我之前也有这个疑问,但仔细想想,go函数并不包含所有历史记录改变的操作,如果用户左滑动返回上一个页面呢,那样就达不到效果了。所以必须在监听历史记录改变后,才能触发弹出框,当点击弹出框的取消按钮后,只能采用维护allKeys数组的方式来返回上一页。
4.demo
代码都有注释,100多行代码模仿history写了个简易阉割版,目的是为了了解history的原理,应该很容易就看懂的。
(function(w){
let History = {
createBrowserHistory
}
function createBrowserHistory(){
// key
function createKey() {
return Math.random().toString(36).substr(2, 6);
}
// 获取地址信息
function getDOMLocation(historyState = {}) {
const { key, state } = historyState || {};
const { pathname, search, hash } = window.location;
return {pathname, search, hash, key};
}
// location地址信息
let initialLocation = getDOMLocation()
// 初始化allKeys
let allKeys = [initialLocation.key]
// listen数组
let listener = []
// 监听
function listen(fn){
listener.push(fn)
checkDOMListeners()
}
// 只能添加一个监听历史条目改变的函数
let isListener = false
function checkDOMListeners(){
if (!isListener) {
isListener = true
window.addEventListener('popstate', handlePop)
}
}
// 跳过block。因为当点击弹出框的取消后,会执行go,然后会再一次执行handlePop函数,此次要跳过
let forceNextPop = false
// 监听历史条目改变
function handlePop(event){
let location = getDOMLocation(event.state)
if (forceNextPop) {
forceNextPop = false
} else {
// 弹出框
let isComfirm = prompt && window.confirm(prompt(window.location)) && true
if (isComfirm) {
// 确定
// 更新history
Object.assign(history, {location, length: history.length})
} else {
// 取消
// 获取当前的history.key和上一次的location.key比较,然后进行回跳
let toIndex = allKeys.indexOf(history.location.key)
toIndex = toIndex === -1 ? 0 : toIndex
let fromIndex = allKeys.indexOf(location.key)
fromIndex = fromIndex === -1 ? 0 : fromIndex
// 差值
let delta = toIndex - fromIndex
// 差值为0不跳
if (delta) {
forceNextPop = true;
go(delta);
}
}
}
}
// 截取函数
let prompt = null
function block(fn){
prompt = fn
}
// push
function push(href){
let isComfirm = prompt && window.confirm(prompt(window.location)) && true
if (isComfirm) {
let key = createKey()
// 更新allKeys数组
allKeys.push(key)
// 更新历史条目
w.history.pushState({key}, null, href)
// 获取当前最新的location信息
let location = getDOMLocation({key})
// 更新history
Object.assign(history, {location, length: history.length})
}
}
// go
function go(n){
w.history.go(n)
}
// goBack
function goBack(){
go(-1);
}
let history = {
length: w.history.length,
listen,
block,
push,
go,
goBack,
location: initialLocation
}
return history
}
w.History = History
})(window)
5.总结
学代码必须手写,学英语必须开口,学习必须主动!
