作者:Jerry
引言
前端是一个快速发展的领域,而在前端的技术栈当中,前端请求又是最见的一个领域,通过请求接口数据,才能将一个静态的页面动态化。本文将以前端发展的时间轴来逐一分析前端请求的技术演变及其优劣,针对这一课题,作者查阅了相关资料加以自己的理解,如有错误,烦请指出。
XMLHttpRequest
XMLHttpRequest是最早出现的与服务器交换数据的方案,有了XMLHttpRequest,开发者终于可以在不重新加载页面的情况下更新网页,可以在页面加载后请求接受以及发送数据。而所有浏览器均可以获取XMLHttpRequest对象:
var xhr = new XMLHttpRequest(); //获取xhr对象但是XMLHttpRequest是个比较粗燥的底层对象,各个浏览器对其的创建方法也不同,以下是兼容方法:
var xhr;
if (window.XMLHttpRequest) { // Mozilla, Safari...
xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
} else if (window.ActiveXObject) { // IE
try {
xhr = new ActiveXObject('Msxml2.XMLHTTP');
} catch (e) {
try {
xhr = new ActiveXObject('Microsoft.XMLHTTP'); //IE5,6
} catch (e) {}
}
}使用XMLHttpRequest发起一个get请求
//get请求
xhr.open("GET","test1.txt",true);
xhr.send();完整的post请求代码如下:
var xhr;
if (window.XMLHttpRequest) { // Mozilla, Safari...
xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
} else if (window.ActiveXObject) { // IE
try {
xhr = new ActiveXObject('Msxml2.XMLHTTP');
} catch (e) {
try {
xhr = new ActiveXObject('Microsoft.XMLHTTP');
} catch (e) {}
}
}
if (xhr) {
xhr.onreadystatechange = onReadyStateChange;
xhr.open('POST', '/api', true);
// 设置 Content-Type 为 application/x-www-form-urlencoded
// 以表单的形式传递数据
xhr.setRequestHeader('Content-Type', 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded');
xhr.send('username=admin&password=root');
}
// onreadystatechange 方法
function onReadyStateChange() {
// 该函数会被调用四次
if (xhr.readyState === 4 &&xhr.status === 200) {
console.log('执行成功');
} else {
console.log('执行出错');
}
}Jquery Ajax
说到Jquery,这是一个时代,几乎统治了前端10年有余,彻底解决了UI层与数据层交互的问题,直到三大框架(Angular/React/Vue)的出现,前端进入MVVM浪潮。而Ajax将XHR进行封装,让开发者可以更加便捷方便进行使用。
$.ajax({ //标准写法
type: 'POST',
url: url,
data: data,
dataType: dataType,
success: function () {},
error: function () {}
});
$.get(url,function(){}); //get请求
$.post(url,body,function(){}); //post请求
$.getJSON(url,function(){}); //get请求从服务器加载Json编码优点:
- 对原生XHR的封装
- 针对MVC的编程
- 完美的兼容性
- 支持jsonp
缺点:
- 不符合MVVM
- 异步模型不够现代,不支持链式,代码可读性差
- 整个Jquery太大,引入成本过高
Fetch
fetch其实是一个新世界,脱离的XHR,完全是基于Promise的异步处理机制,使用起来会比起ajax更加简单。
使用fetch的代码会相比xhr来说更具有条理性
fetch(url).then(function(response) {
return response.json();
}).then(function(data) {
console.log(data);
}).catch(function(e) {
console.log("Oops, error");
});在使用ES6的箭头函数后
fetch(url).then(response => response.json())
.then(data => console.log(data))
.catch(e => console.log("Oops, error", e))优点:
- 更加底层,提供的API丰富(request, response)
- 语法简单,脱离了XHR,基于ES新的Promise设计
看到以上,或许你会觉得fetch真的很美好,但是请了解,fetch本身是一个 low-level 的 API,它注定不会像你习惯的 $.ajax 或是 axios 等库帮你封装各种各样的功能或实现。
所以它是存在一定的缺点:
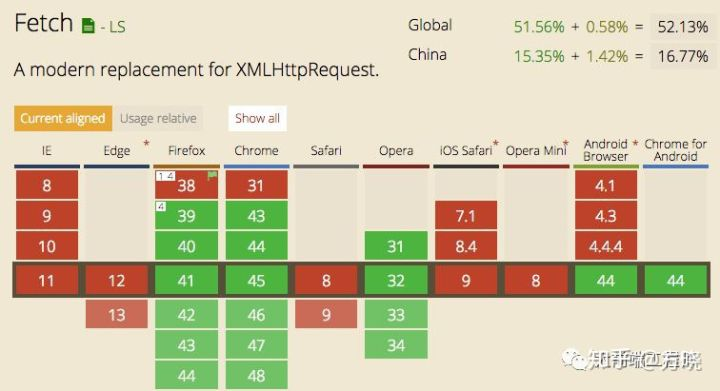
- 兼容性比较凄惨,低级别浏览器均不支持,需要实现fetch的polyfill了。思路其实很简单,就是判断浏览器是否支持原生的fetch,不支持的话,就仍然使用XMLHttpRequest的方式实现,同时结合Promise来进行封装。常见的polyfill就有:es6-promise,babel-polyfill,fetch-ie8等
- 不支持jsonp,可以引入fetch-jsonp
//安装
npm install fetch-jsonp --save-dev
//使用
fetchJsonp(url, {
timeout: 3000,
jsonpCallback: 'callback'
}).then(function(response) {
console.log(response.json());
}).catch(function(e) {
console.log(e)
});- 没有拦截器,需要额外再封装一层或者fetch-interceptor
- 默认不带cookie,需要添加配置
fetch(url,{
credentials: 'include' //include表示cookie既可同域,也可跨域,‘same-origin’表示只可同域
});- 没有abort,不支持timeout超时处理
可以用Promise.race()实现,Promise.race(iterable) 方法返回一个Promise对象,只要 iterable 中任意一个Promise 被 resolve 或者 reject 后,外部的Promise 就会以相同的值被 resolve 或者 reject。
- 无法获取progress状态
fetch中的Response.body 中实现了getReader()方法用于读取原始字节流, 该字节流可以循环读取。参考javascript - Progress indicators for fetch? - Stack Overflow2016 - the year of web streams
Axios
axios也是比较新的网络请求的类库,并且被尤雨溪尤大推荐,已成为VUE的网络请求标配,也是十分的火爆。它本身也是对原生XHR的封装。
- 支持node,创建http请求
- 支持Promise API
- 客户端防止CSRF:每个请求带一个cookie拿到的key
- 拦截请求和响应
- 可取消请求
兼容性上虽然axios本质上也是对原生XHR的封装,但是它也依赖原生ES6 Promise的实现,和fetch一样需要polyfill的兼容。

安装
//npm
npm install axios
//cdn
<script src="https://unpkg.com/axios/dist/axios.min.js"></script>基本使用如下:
axios({
method: 'GET',
url: url,
})
.then(res => {console.log(res)})
.catch(err => {console.log(err)})
// get请求
axios.get(url)
.then(function (response) {
console.log(response);
})
.catch(function (error) {
console.log(error);
});
// post请求
axios.post(‘/user’, {
name: 'Jerry',
lastName: 'Liang'
})
.then(function (response) {
console.log(response);
})
.catch(function (error) {
console.log(error);
});特殊场景的处理
在开发过程中,经常会遇到比较尴尬的场景就是多请求的串行与并发,并发比较容易解决,不存在回调地狱,但是代码可读性就会容易变得很渣,而串行问题对于前端是绝望的,最好的办法是后端来做合并,如果后端不做这块的处理,前端就必须来面对回调地狱。
多请求串行
// ajax
$.ajax({
url: '',
data: '',
success: function (data) {
$.ajax({
url: '',
data: '',
success: function (data) {
$.ajax({
// 如此一层嵌套一层
})
}
})
}
})
//axios
axios.get(url)
.then(res => {
return axios.get(url,{
{name:result.name}
});
}).then(res => {
//如此一层层嵌套
});多请求并行
//ajax 通过计数器实现(虽然Jquery支持$.when的方式,但此处不做案例)
var num = 0;
function all(){
num++;
if(n>=3)console.log('三个请求全部完成');
}
$.ajax({
url: '',
data: '',
success: function (data) {
console.log("ajax请求1 完成");
all();
}
})
$.ajax({
url: '',
data: '',
success: function (data) {
console.log("ajax请求2 完成");
all();
}
})
$.ajax({
url: '',
data: '',
success: function (data) {
console.log("ajax请求3 完成");
all();
}
})
//axios
function getInfo() {
return axios.get(url);
}
function getUser() {
return axios.get(url);
}
axios.all([getInfo(), getUser()])
.then(axios.spread(function (info, user) {
// 两个请求现在都执行完成
}));如何选择(个人理解,仅供参考)
- 首先可以肯定的是,如果你的代码依旧是基于Jquery,那毫无疑问,ajax就是你最好的选择。
- 如果你使用的是任意MVVM框架,建议无脑使用axios,fetch在实际项目使用中,需要各种的封装和异常处理,并非开箱即用,而axios可以做到直接替换$.ajax。
- 如果就是要使用fetch,那相信你也一定能封装成自己的一套最佳实践。