作者: steins from 迅雷前端
随着 React Vue 等框架的流行,Virtual DOM 也越来越火,snabbdom 是其中一种实现,而且 Vue 2.x 版本的 Virtual DOM 部分也是基于 snabbdom 进行修改的。snabbdom 这个库核心代码只有 200 多行,非常适合想要深入了解 Virtual DOM 实现的读者阅读。如果您没听说过 snabbdom,可以先看看官方文档。
为什么选择 snabbdom
- 核心代码只有 200 行,丰富的测试用例
- 强大的插件系统、hook 系统
- vue 使用了 snabbdom,读懂 snabbdom 对理解 vue 的实现有帮助
什么是 Virtual DOM
snabbdom 是 Virtual DOM 的一种实现,所以在此之前,你需要先知道什么是 Virtual DOM。通俗的说,Virtual DOM 就是一个 js 对象,它是真实 DOM 的抽象,只保留一些有用的信息,更轻量地描述 DOM 树的结构。 比如在 snabbdom 中,是这样来定义一个 VNode 的:
export interface VNode {
sel: string | undefined;
data: VNodeData | undefined;
children: Array<VNode | string> | undefined;
elm: Node | undefined;
text: string | undefined;
key: Key | undefined;
}
export interface VNodeData {
props?: Props;
attrs?: Attrs;
class?: Classes;
style?: VNodeStyle;
dataset?: Dataset;
on?: On;
hero?: Hero;
attachData?: AttachData;
hook?: Hooks;
key?: Key;
ns?: string; // for SVGs
fn?: () => VNode; // for thunks
args?: Array<any>; // for thunks
[key: string]: any; // for any other 3rd party module
}
从上面的定义我们可以看到,我们可以用 js 对象来描述 dom 结构,那我们是不是可以对两个状态下的 js 对象进行对比,记录出它们的差异,然后把它应用到真正的 dom 树上呢?答案是可以的,这便是 diff 算法,算法的基本步骤如下:
- 用 js 对象来描述 dom 树结构,然后用这个 js 对象来创建一棵真正的 dom 树,插入到文档中
- 当状态更新时,将新的 js 对象和旧的 js 对象进行比较,得到两个对象之间的差异
- 将差异应用到真正的 dom 上
接下来我们来分析这整个过程的实现。
源码分析
首先从一个简单的例子入手,一步一步分析整个代码的执行过程,下面是官方的一个简单示例:
var snabbdom = require('snabbdom');
var patch = snabbdom.init([
// Init patch function with chosen modules
require('snabbdom/modules/class').default, // makes it easy to toggle classes
require('snabbdom/modules/props').default, // for setting properties on DOM elements
require('snabbdom/modules/style').default, // handles styling on elements with support for animations
require('snabbdom/modules/eventlisteners').default // attaches event listeners
]);
var h = require('snabbdom/h').default; // helper function for creating vnodes
var container = document.getElementById('container');
var vnode = h('div#container.two.classes', { on: { click: someFn } }, [
h('span', { style: { fontWeight: 'bold' } }, 'This is bold'),
' and this is just normal text',
h('a', { props: { href: '/foo' } }, "I'll take you places!")
]);
// Patch into empty DOM element – this modifies the DOM as a side effect
patch(container, vnode);
var newVnode = h('div#container.two.classes', { on: { click: anotherEventHandler } }, [
h('span', { style: { fontWeight: 'normal', fontStyle: 'italic' } }, 'This is now italic type'),
' and this is still just normal text',
h('a', { props: { href: '/bar' } }, "I'll take you places!")
]);
// Second `patch` invocation
patch(vnode, newVnode); // Snabbdom efficiently updates the old view to the new state
首先 snabbdom 模块提供一个 init 方法,它接收一个数组,数组中是各种 module,这样的设计使得这个库更具扩展性,我们也可以实现自己的 module,而且可以根据自己的需要引入相应的 module,比如如果不需要写入 class,那你可以直接把 class 的模块移除。
调用 init 方法会返回一个 patch 函数,这个函数接受两个参数,第一个是旧的 vnode 节点或是 dom 节点,第二个参数是新的 vnode 节点,调用 patch 函数会对 dom 进行更新。vnode 可以通过使用h函数来生成。使用起来相当简单,这也是本文接下来要分析的内容。
init 函数
export interface Module {
pre: PreHook;
create: CreateHook;
update: UpdateHook;
destroy: DestroyHook;
remove: RemoveHook;
post: PostHook;
}
export function init(modules: Array<Partial<Module>>, domApi?: DOMAPI) {
// cbs 用于收集 module 中的 hook
let i: number,
j: number,
cbs = {} as ModuleHooks;
const api: DOMAPI = domApi !== undefined ? domApi : htmlDomApi;
// 收集 module 中的 hook
for (i = 0; i < hooks.length; ++i) {
cbs[hooks[i]] = [];
for (j = 0; j < modules.length; ++j) {
const hook = modules[j][hooks[i]];
if (hook !== undefined) {
(cbs[hooks[i]] as Array<any>).push(hook);
}
}
}
function emptyNodeAt(elm: Element) {
// ...
}
function createRmCb(childElm: Node, listeners: number) {
// ...
}
// 创建真正的 dom 节点
function createElm(vnode: VNode, insertedVnodeQueue: VNodeQueue): Node {
// ...
}
function addVnodes(
parentElm: Node,
before: Node | null,
vnodes: Array<VNode>,
startIdx: number,
endIdx: number,
insertedVnodeQueue: VNodeQueue
) {
// ...
}
// 调用 destory hook
// 如果存在 children 递归调用
function invokeDestroyHook(vnode: VNode) {
// ...
}
function removeVnodes(parentElm: Node, vnodes: Array<VNode>, startIdx: number, endIdx: number): void {
// ...
}
function updateChildren(parentElm: Node, oldCh: Array<VNode>, newCh: Array<VNode>, insertedVnodeQueue: VNodeQueue) {
// ...
}
function patchVnode(oldVnode: VNode, vnode: VNode, insertedVnodeQueue: VNodeQueue) {
// ...
}
return function patch(oldVnode: VNode | Element, vnode: VNode): VNode {
// ...
};
}
上面是 init 方法的一些源码,为了阅读方便,暂时先把一些方法的具体实现给注释掉,等有用到的时候再具体分析。
通过参数可以知道,这里有接受一个 modules 数组,另外有一个可选的参数 domApi,如果没传递会使用浏览器中和 dom 相关的 api,具体可以看这里,这样的设计也很有好处,它可以让用户自定义平台相关的 api,比如可以看看weex 的相关实现
。首先这里会对 module 中的 hook 进行收集,保存到 cbs 中。然后定义了各种函数,这里可以先不管,接着就是返回一个 patch 函数了,这里也先不分析它的具体逻辑。这样 init 就结束了。
h 函数
根据例子的流程,接下来看看h方法的实现
export function h(sel: string): VNode;
export function h(sel: string, data: VNodeData): VNode;
export function h(sel: string, children: VNodeChildren): VNode;
export function h(sel: string, data: VNodeData, children: VNodeChildren): VNode;
export function h(sel: any, b?: any, c?: any): VNode {
var data: VNodeData = {},
children: any,
text: any,
i: number;
// 参数格式化
if (c !== undefined) {
data = b;
if (is.array(c)) {
children = c;
} else if (is.primitive(c)) {
text = c;
} else if (c && c.sel) {
children = [c];
}
} else if (b !== undefined) {
if (is.array(b)) {
children = b;
} else if (is.primitive(b)) {
text = b;
} else if (b && b.sel) {
children = [b];
} else {
data = b;
}
}
// 如果存在 children,将不是 vnode 的项转成 vnode
if (children !== undefined) {
for (i = 0; i < children.length; ++i) {
if (is.primitive(children[i])) children[i] = vnode(undefined, undefined, undefined, children[i], undefined);
}
}
// svg 元素添加 namespace
if (sel[0] === 's' && sel[1] === 'v' && sel[2] === 'g' && (sel.length === 3 || sel[3] === '.' || sel[3] === '#')) {
addNS(data, children, sel);
}
// 返回 vnode
return vnode(sel, data, children, text, undefined);
}
function addNS(data: any, children: VNodes | undefined, sel: string | undefined): void {
data.ns = 'http://www.w3.org/2000/svg';
if (sel !== 'foreignObject' && children !== undefined) {
for (let i = 0; i < children.length; ++i) {
let childData = children[i].data;
if (childData !== undefined) {
addNS(childData, (children[i] as VNode).children as VNodes, children[i].sel);
}
}
}
}
export function vnode(
sel: string | undefined,
data: any | undefined,
children: Array<VNode | string> | undefined,
text: string | undefined,
elm: Element | Text | undefined
): VNode {
let key = data === undefined ? undefined : data.key;
return {
sel: sel,
data: data,
children: children,
text: text,
elm: elm,
key: key
};
}
因为 h 函数后两个参数是可选的,而且有各种传递方式,所以这里首先会对参数进行格式化,然后对 children 属性做处理,将可能不是 vnode 的项转成 vnode,如果是 svg 元素,会做一个特殊处理,最后返回一个 vnode 对象。
patch 函数
patch 函数是 snabbdom 的核心,调用 init 会返回这个函数,用来做 dom 相关的更新,接下来看看它的具体实现。
function patch(oldVnode: VNode | Element, vnode: VNode): VNode {
let i: number, elm: Node, parent: Node;
const insertedVnodeQueue: VNodeQueue = [];
// 调用 module 中的 pre hook
for (i = 0; i < cbs.pre.length; ++i) cbs.pre[i]();
// 如果传入的是 Element 转成空的 vnode
if (!isVnode(oldVnode)) {
oldVnode = emptyNodeAt(oldVnode);
}
// sameVnode 时 (sel 和 key相同) 调用 patchVnode
if (sameVnode(oldVnode, vnode)) {
patchVnode(oldVnode, vnode, insertedVnodeQueue);
} else {
elm = oldVnode.elm as Node;
parent = api.parentNode(elm);
// 创建新的 dom 节点 vnode.elm
createElm(vnode, insertedVnodeQueue);
if (parent !== null) {
// 插入 dom
api.insertBefore(parent, vnode.elm as Node, api.nextSibling(elm));
// 移除旧 dom
removeVnodes(parent, [oldVnode], 0, 0);
}
}
// 调用元素上的 insert hook,注意 insert hook 在 module 上不支持
for (i = 0; i < insertedVnodeQueue.length; ++i) {
(((insertedVnodeQueue[i].data as VNodeData).hook as Hooks).insert as any)(insertedVnodeQueue[i]);
}
// 调用 module post hook
for (i = 0; i < cbs.post.length; ++i) cbs.post[i]();
return vnode;
}
function emptyNodeAt(elm: Element) {
const id = elm.id ? '#' + elm.id : '';
const c = elm.className ? '.' + elm.className.split(' ').join('.') : '';
return vnode(api.tagName(elm).toLowerCase() + id + c, {}, [], undefined, elm);
}
// key 和 selector 相同
function sameVnode(vnode1: VNode, vnode2: VNode): boolean {
return vnode1.key === vnode2.key && vnode1.sel === vnode2.sel;
}
首先会调用 module 的 pre hook,你可能会有疑惑,为什么没有调用来自各个元素的 pre hook,这是因为元素上不支持 pre hook,也有一些 hook 不支持在 module 中,具体可以查看这里的文档。然后会判断传入的第一个参数是否为 vnode 类型,如果不是,会调用 emptyNodeAt 然后将其转换成一个 vnode,emptyNodeAt 的具体实现也很简单,注意这里只是保留了 class 和 style,这个和 toVnode 的实现有些区别,因为这里并不需要保存很多信息,比如 prop attribute 等。接着调用 sameVnode 来判断是否为相同的 vnode 节点,具体实现也很简单,这里只是判断了 key 和 sel 是否相同。如果相同,调用 patchVnode,如果不相同,会调用 createElm 来创建一个新的 dom 节点,然后如果存在父节点,便将其插入到 dom 上,然后移除旧的 dom 节点来完成更新。最后调用元素上的 insert hook 和 module 上的 post hook。
这里的重点是 patchVnode 和 createElm 函数,我们先看 createElm 函数,看看是如何来创建 dom 节点的。
createElm 函数
// 创建真正的 dom 节点
function createElm(vnode: VNode, insertedVnodeQueue: VNodeQueue): Node {
let i: any, data = vnode.data;
// 调用元素的 init hook
if (data !== undefined) {
if (isDef(i = data.hook) && isDef(i = i.init)) {
i(vnode);
data = vnode.data;
}
}
let children = vnode.children, sel = vnode.sel;
// 注释节点
if (sel === '!') {
if (isUndef(vnode.text)) {
vnode.text = '';
}
// 创建注释节点
vnode.elm = api.createComment(vnode.text as string);
} else if (sel !== undefined) {
// Parse selector
const hashIdx = sel.indexOf('#');
const dotIdx = sel.indexOf('.', hashIdx);
const hash = hashIdx > 0 ? hashIdx : sel.length;
const dot = dotIdx > 0 ? dotIdx : sel.length;
const tag = hashIdx !== -1 || dotIdx !== -1 ? sel.slice(0, Math.min(hash, dot)) : sel;
const elm = vnode.elm = isDef(data) && isDef(i = (data as VNodeData).ns) ? api.createElementNS(i, tag)
: api.createElement(tag);
if (hash < dot) elm.setAttribute('id', sel.slice(hash + 1, dot));
if (dotIdx > 0) elm.setAttribute('class', sel.slice(dot + 1).replace(/\./g, ' '));
// 调用 module 中的 create hook
for (i = 0; i < cbs.create.length; ++i) cbs.create[i](emptyNode, vnode);
// 挂载子节点
if (is.array(children)) {
for (i = 0; i < children.length; ++i) {
const ch = children[i];
if (ch != null) {
api.appendChild(elm, createElm(ch as VNode, insertedVnodeQueue));
}
}
} else if (is.primitive(vnode.text)) {
api.appendChild(elm, api.createTextNode(vnode.text));
}
i = (vnode.data as VNodeData).hook; // Reuse variable
// 调用 vnode 上的 hook
if (isDef(i)) {
// 调用 create hook
if (i.create) i.create(emptyNode, vnode);
// insert hook 存储起来 等 dom 插入后才会调用,这里用个数组来保存能避免调用时再次对 vnode 树做遍历
if (i.insert) insertedVnodeQueue.push(vnode);
}
} else {
// 文本节点
vnode.elm = api.createTextNode(vnode.text as string);
}
return vnode.elm;
}
这里的逻辑也很清晰,首先会调用元素的 init hook,接着这里会存在三种情况:
- 如果当前元素是注释节点,会调用
createComment来创建一个注释节点,然后挂载到vnode.elm - 如果不存在选择器,只是单纯的文本,调用
createTextNode来创建文本,然后挂载到vnode.elm - 如果存在选择器,会对这个选择器做解析,得到
tag、id和class,然后调用createElement或createElementNS来生成节点,并挂载到vnode.elm。接着调用module上的create hook,如果存在children,遍历所有子节点并递归调用createElm创建dom,通过appendChild挂载到当前的elm上,不存在children但存在text,便使用createTextNode来创建文本。最后调用调用元素上的create hook和保存存在insert hook的vnode,因为insert hook需要等dom真正挂载到document上才会调用,这里用个数组来保存可以避免真正需要调用时需要对vnode树做遍历。
接着我们来看看 snabbdom 是如何做 vnode 的 diff 的,这部分是 Virtual DOM 的核心。
patchVnode 函数
这个函数做的事情是对传入的两个 vnode 做 diff,如果存在更新,将其反馈到 dom 上。
function patchVnode(oldVnode: VNode, vnode: VNode, insertedVnodeQueue: VNodeQueue) {
let i: any, hook: any;
// 调用 prepatch hook
if (isDef((i = vnode.data)) && isDef((hook = i.hook)) && isDef((i = hook.prepatch))) {
i(oldVnode, vnode);
}
const elm = (vnode.elm = oldVnode.elm as Node);
let oldCh = oldVnode.children;
let ch = vnode.children;
if (oldVnode === vnode) return;
if (vnode.data !== undefined) {
// 调用 module 上的 update hook
for (i = 0; i < cbs.update.length; ++i) cbs.update[i](oldVnode, vnode);
i = vnode.data.hook;
// 调用 vnode 上的 update hook
if (isDef(i) && isDef((i = i.update))) i(oldVnode, vnode);
}
if (isUndef(vnode.text)) {
if (isDef(oldCh) && isDef(ch)) {
// 新旧节点均存在 children,且不一样时,对 children 进行 diff
// thunk 中会做相关优化和这个相关
if (oldCh !== ch) updateChildren(elm, oldCh as Array<VNode>, ch as Array<VNode>, insertedVnodeQueue);
} else if (isDef(ch)) {
// 旧节点不存在 children 新节点有 children
// 旧节点存在 text 置空
if (isDef(oldVnode.text)) api.setTextContent(elm, '');
// 加入新的 vnode
addVnodes(elm, null, ch as Array<VNode>, 0, (ch as Array<VNode>).length - 1, insertedVnodeQueue);
} else if (isDef(oldCh)) {
// 新节点不存在 children 旧节点存在 children 移除旧节点的 children
removeVnodes(elm, oldCh as Array<VNode>, 0, (oldCh as Array<VNode>).length - 1);
} else if (isDef(oldVnode.text)) {
// 旧节点存在 text 置空
api.setTextContent(elm, '');
}
} else if (oldVnode.text !== vnode.text) {
// 更新 text
api.setTextContent(elm, vnode.text as string);
}
// 调用 postpatch hook
if (isDef(hook) && isDef((i = hook.postpatch))) {
i(oldVnode, vnode);
}
}
首先调用 vnode 上的 prepatch hook,如果当前的两个 vnode 完全相同,直接返回。接着调用 module 和 vnode 上的 update hook。然后会分为以下几种情况做处理:
- 均存在
children且不相同,调用updateChildren - 新
vnode存在children,旧vnode不存在children,如果旧vnode存在text先清空,然后调用addVnodes - 新
vnode不存在children,旧vnode存在children,调用removeVnodes移除children - 均不存在
children,新vnode不存在text,移除旧vnode的text - 均存在
text,更新text
最后调用 postpatch hook。整个过程很清晰,我们需要关注的是 updateChildren addVnodes removeVnodes。
updateChildren
function updateChildren(parentElm: Node, oldCh: Array<VNode>, newCh: Array<VNode>, insertedVnodeQueue: VNodeQueue) {
let oldStartIdx = 0,
newStartIdx = 0;
let oldEndIdx = oldCh.length - 1;
let oldStartVnode = oldCh[0];
let oldEndVnode = oldCh[oldEndIdx];
let newEndIdx = newCh.length - 1;
let newStartVnode = newCh[0];
let newEndVnode = newCh[newEndIdx];
let oldKeyToIdx: any;
let idxInOld: number;
let elmToMove: VNode;
let before: any;
// 遍历 oldCh newCh,对节点进行比较和更新
// 每轮比较最多处理一个节点,算法复杂度 O(n)
while (oldStartIdx <= oldEndIdx && newStartIdx <= newEndIdx) {
// 如果进行比较的 4 个节点中存在空节点,为空的节点下标向中间推进,继续下个循环
if (oldStartVnode == null) {
oldStartVnode = oldCh[++oldStartIdx]; // Vnode might have been moved left
} else if (oldEndVnode == null) {
oldEndVnode = oldCh[--oldEndIdx];
} else if (newStartVnode == null) {
newStartVnode = newCh[++newStartIdx];
} else if (newEndVnode == null) {
newEndVnode = newCh[--newEndIdx];
// 新旧开始节点相同,直接调用 patchVnode 进行更新,下标向中间推进
} else if (sameVnode(oldStartVnode, newStartVnode)) {
patchVnode(oldStartVnode, newStartVnode, insertedVnodeQueue);
oldStartVnode = oldCh[++oldStartIdx];
newStartVnode = newCh[++newStartIdx];
// 新旧结束节点相同,逻辑同上
} else if (sameVnode(oldEndVnode, newEndVnode)) {
patchVnode(oldEndVnode, newEndVnode, insertedVnodeQueue);
oldEndVnode = oldCh[--oldEndIdx];
newEndVnode = newCh[--newEndIdx];
// 旧开始节点等于新的节点节点,说明节点向右移动了,调用 patchVnode 进行更新
} else if (sameVnode(oldStartVnode, newEndVnode)) {
// Vnode moved right
patchVnode(oldStartVnode, newEndVnode, insertedVnodeQueue);
// 旧开始节点等于新的结束节点,说明节点向右移动了
// 具体移动到哪,因为新节点处于末尾,所以添加到旧结束节点(会随着 updateChildren 左移)的后面
// 注意这里需要移动 dom,因为节点右移了,而为什么是插入 oldEndVnode 的后面呢?
// 可以分为两个情况来理解:
// 1. 当循环刚开始,下标都还没有移动,那移动到 oldEndVnode 的后面就相当于是最后面,是合理的
// 2. 循环已经执行过一部分了,因为每次比较结束后,下标都会向中间靠拢,而且每次都会处理一个节点,
// 这时下标左右两边已经处理完成,可以把下标开始到结束区域当成是并未开始循环的一个整体,
// 所以插入到 oldEndVnode 后面是合理的(在当前循环来说,也相当于是最后面,同 1)
api.insertBefore(parentElm, oldStartVnode.elm as Node, api.nextSibling(oldEndVnode.elm as Node));
oldStartVnode = oldCh[++oldStartIdx];
newEndVnode = newCh[--newEndIdx];
// 旧的结束节点等于新的开始节点,说明节点是向左移动了,逻辑同上
} else if (sameVnode(oldEndVnode, newStartVnode)) {
// Vnode moved left
patchVnode(oldEndVnode, newStartVnode, insertedVnodeQueue);
api.insertBefore(parentElm, oldEndVnode.elm as Node, oldStartVnode.elm as Node);
oldEndVnode = oldCh[--oldEndIdx];
newStartVnode = newCh[++newStartIdx];
// 如果以上 4 种情况都不匹配,可能存在下面 2 种情况
// 1. 这个节点是新创建的
// 2. 这个节点在原来的位置是处于中间的(oldStartIdx 和 endStartIdx之间)
} else {
// 如果 oldKeyToIdx 不存在,创建 key 到 index 的映射
// 而且也存在各种细微的优化,只会创建一次,并且已经完成的部分不需要映射
if (oldKeyToIdx === undefined) {
oldKeyToIdx = createKeyToOldIdx(oldCh, oldStartIdx, oldEndIdx);
}
// 拿到在 oldCh 下对应的下标
idxInOld = oldKeyToIdx[newStartVnode.key as string];
// 如果下标不存在,说明这个节点是新创建的
if (isUndef(idxInOld)) {
// New element
// 插入到 oldStartVnode 的前面(对于当前循环来说,相当于最前面)
api.insertBefore(parentElm, createElm(newStartVnode, insertedVnodeQueue), oldStartVnode.elm as Node);
newStartVnode = newCh[++newStartIdx];
} else {
// 如果是已经存在的节点 找到需要移动位置的节点
elmToMove = oldCh[idxInOld];
// 虽然 key 相同了,但是 seletor 不相同,需要调用 createElm 来创建新的 dom 节点
if (elmToMove.sel !== newStartVnode.sel) {
api.insertBefore(parentElm, createElm(newStartVnode, insertedVnodeQueue), oldStartVnode.elm as Node);
} else {
// 否则调用 patchVnode 对旧 vnode 做更新
patchVnode(elmToMove, newStartVnode, insertedVnodeQueue);
// 在 oldCh 中将当前已经处理的 vnode 置空,等下次循环到这个下标的时候直接跳过
oldCh[idxInOld] = undefined as any;
// 插入到 oldStartVnode 的前面(对于当前循环来说,相当于最前面)
api.insertBefore(parentElm, elmToMove.elm as Node, oldStartVnode.elm as Node);
}
newStartVnode = newCh[++newStartIdx];
}
}
}
// 循环结束后,可能会存在两种情况
// 1. oldCh 已经全部处理完成,而 newCh 还有新的节点,需要对剩下的每个项都创建新的 dom
if (oldStartIdx <= oldEndIdx || newStartIdx <= newEndIdx) {
if (oldStartIdx > oldEndIdx) {
before = newCh[newEndIdx + 1] == null ? null : newCh[newEndIdx + 1].elm;
addVnodes(parentElm, before, newCh, newStartIdx, newEndIdx, insertedVnodeQueue);
// 2. newCh 已经全部处理完成,而 oldCh 还有旧的节点,需要将多余的节点移除
} else {
removeVnodes(parentElm, oldCh, oldStartIdx, oldEndIdx);
}
}
}
整个过程简单来说,对两个数组进行对比,找到相同的部分进行复用,并更新。整个逻辑可能看起来有点懵,可以结合下面这个例子理解下:
- 假设旧节点顺序为[A, B, C, D],新节点为[B, A, C, D, E]
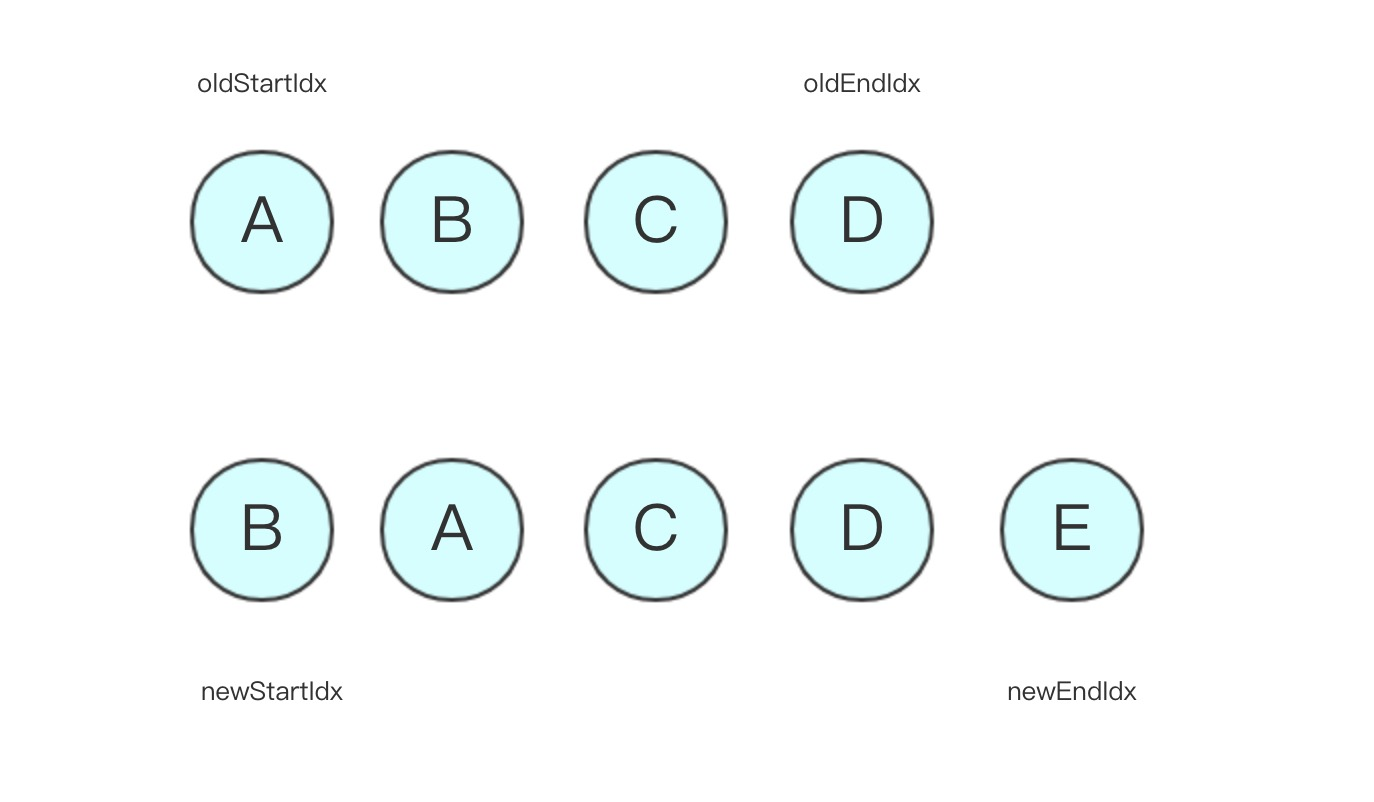
- 第一轮比较:开始结束节点两两并不相等,于是看 newStartVnode 在旧节点中是否存在,最后找到了在第二个位置,调用 patchVnode 进行更新,将 oldCh[1] 至空,将 dom 插入到 oldStartVnode 前面,newStartIdx 向中间移动,状态更新如下
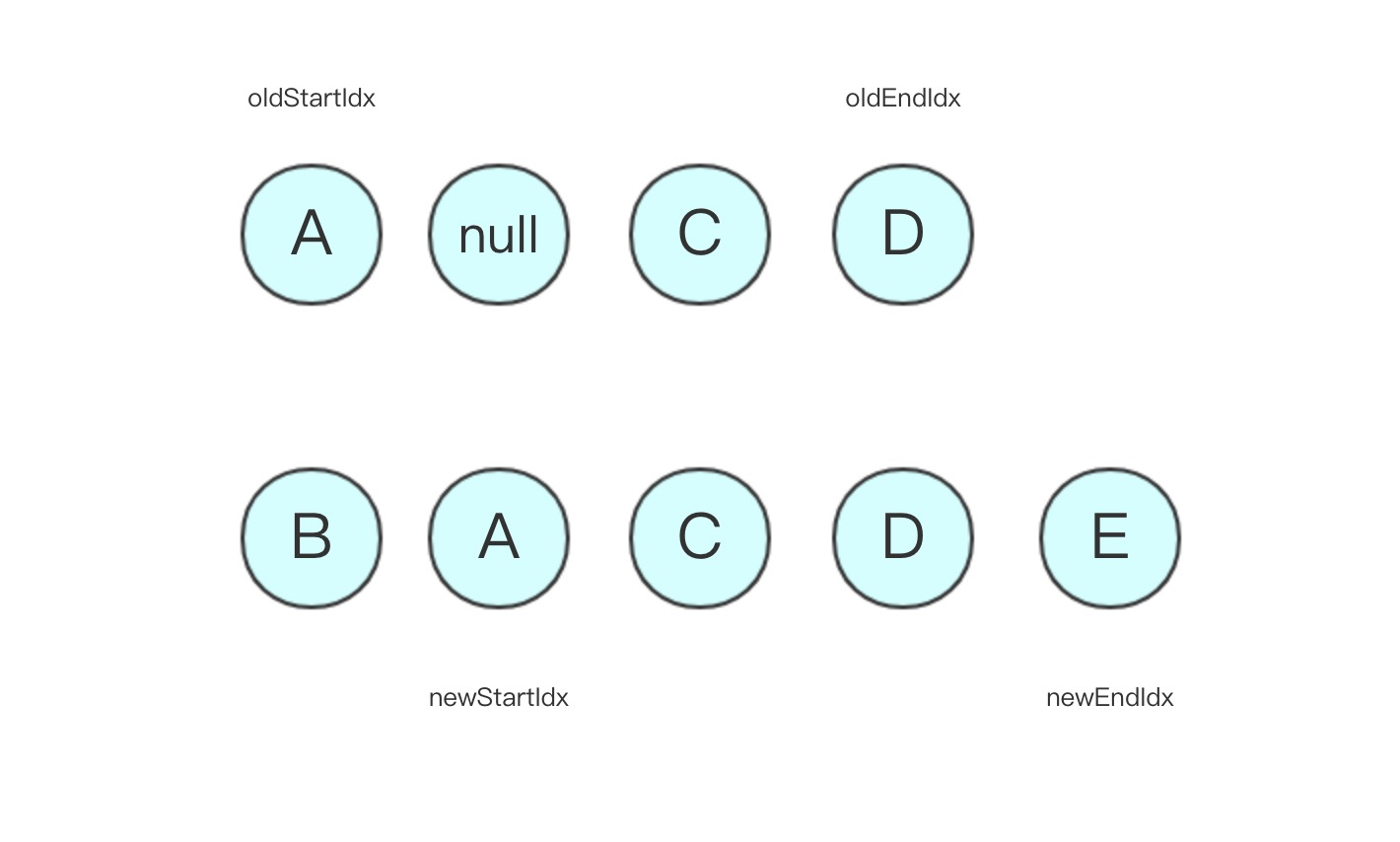
- 第二轮比较:oldStartVnode 和 newStartVnode 相等,直接 patchVnode,newStartIdx 和 oldStartIdx 向中间移动,状态更新如下
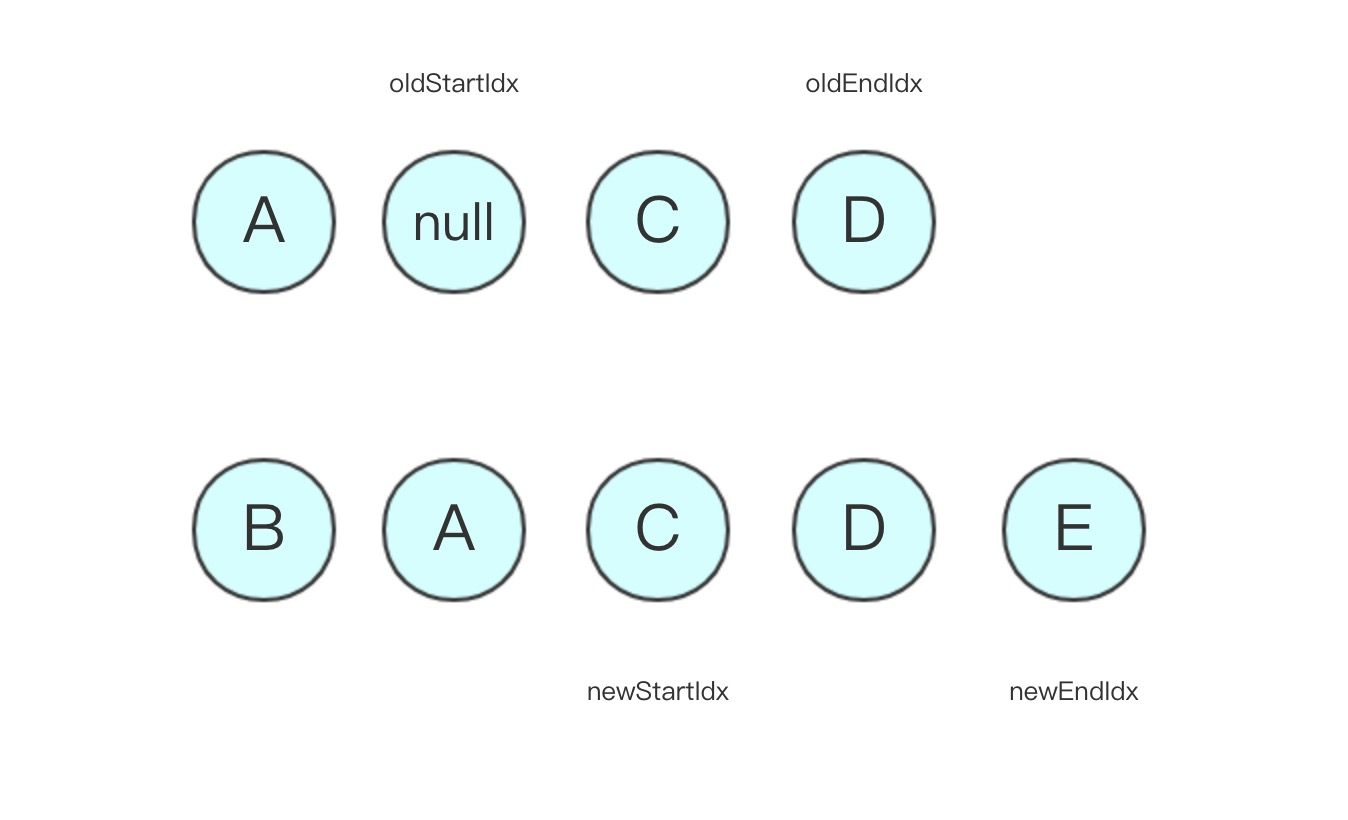
- 第三轮比较:oldStartVnode 为空,oldStartIdx 向中间移动,进入下轮比较,状态更新如下
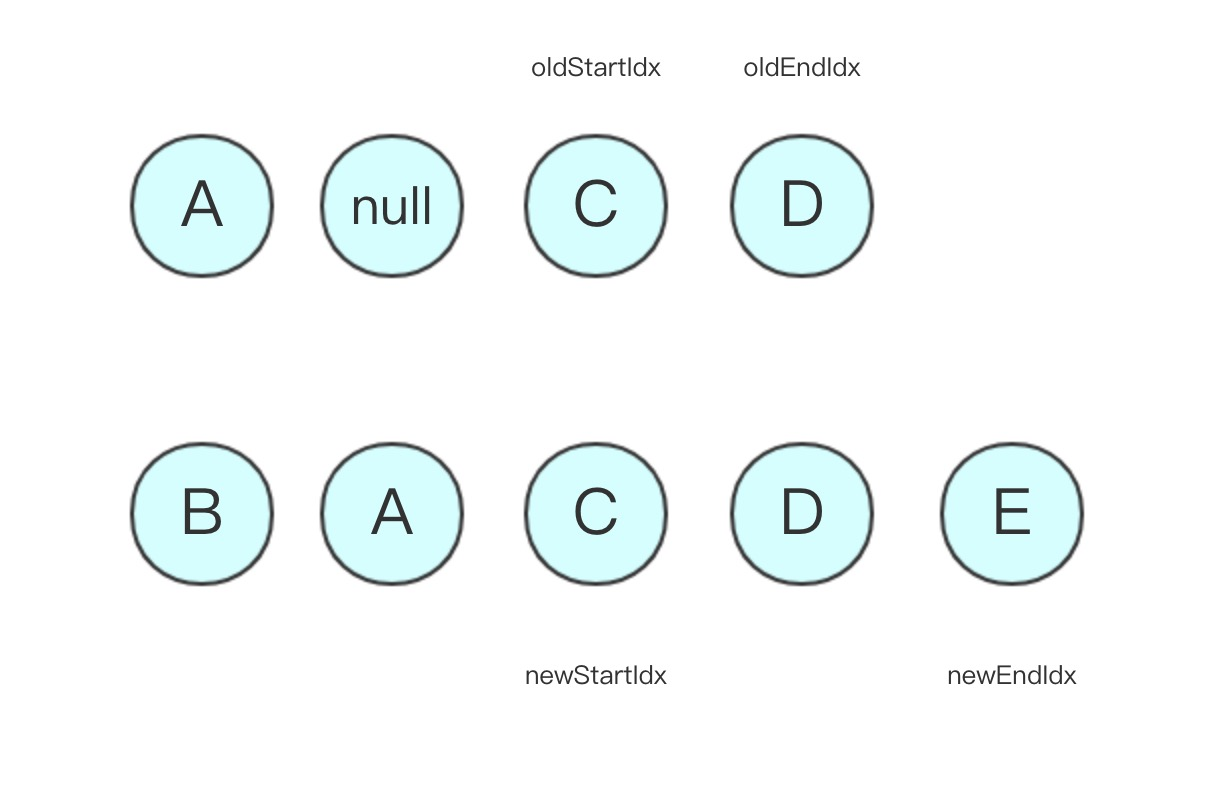
- 第四轮比较:oldStartVnode 和 newStartVnode 相等,直接 patchVnode,newStartIdx 和 oldStartIdx 向中间移动,状态更新如下
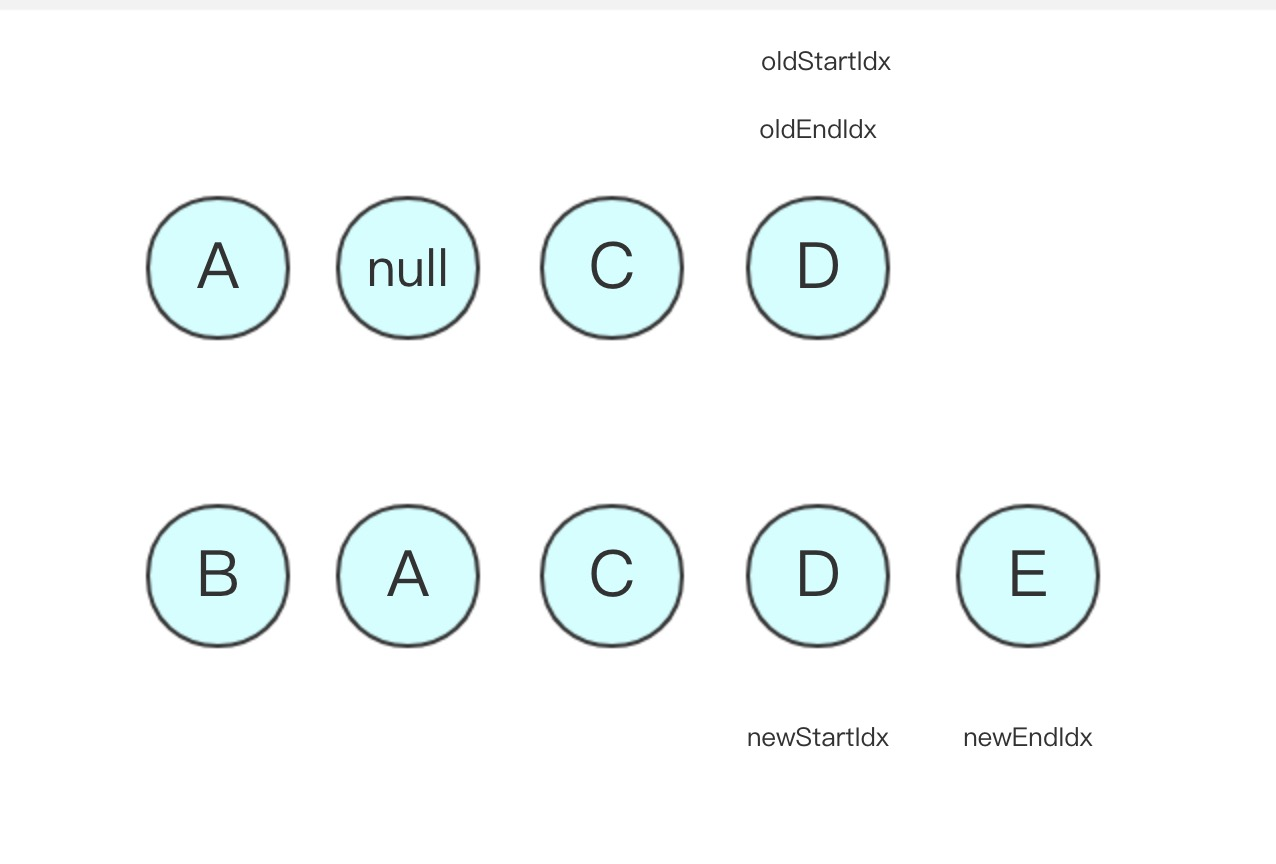
- oldStartVnode 和 newStartVnode 相等,直接 patchVnode,newStartIdx 和 oldStartIdx 向中间移动,状态更新如下
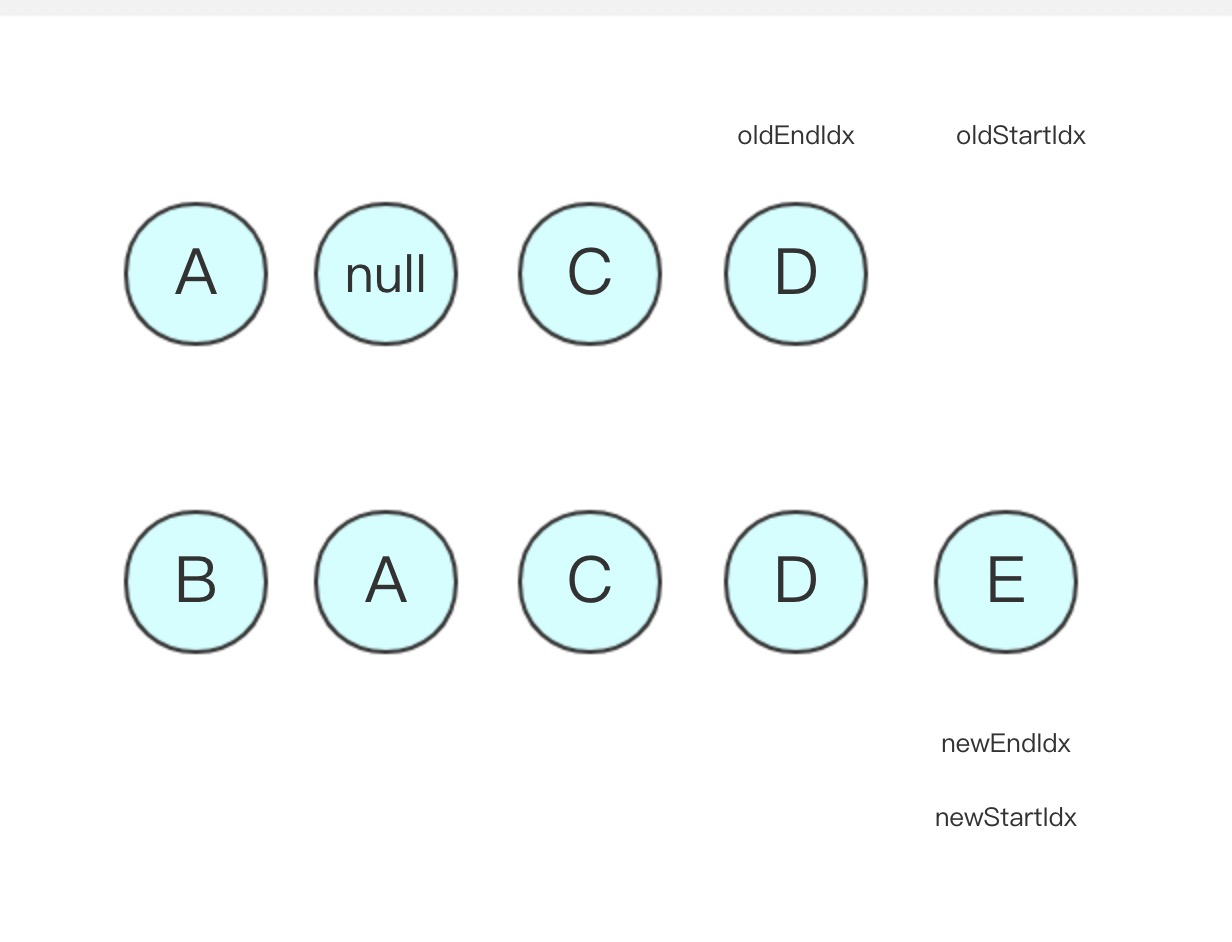
- oldStartIdx 已经大于 oldEndIdx,循环结束,由于是旧节点先结束循环而且还有没处理的新节点,调用 addVnodes 处理剩下的新节点
addVnodes 和 removeVnodes 函数
function addVnodes(parentElm: Node, before: Node | null, vnodes: Array<VNode>, startIdx: number, endIdx: number, insertedVnodeQueue: VNodeQueue) {
for (; startIdx <= endIdx; ++startIdx) {
const ch = vnodes[startIdx];
if (ch != null) {
api.insertBefore(parentElm, createElm(ch, insertedVnodeQueue), before);
}
}
}
function removeVnodes(parentElm: Node, vnodes: Array<VNode>, startIdx: number, endIdx: number): void {
for (; startIdx <= endIdx; ++startIdx) {
let i: any, listeners: number, rm: () => void, ch = vnodes[startIdx];
if (ch != null) {
if (isDef(ch.sel)) {
// 调用 destory hook
invokeDestroyHook(ch);
// 计算需要调用 removecallback 的次数 只有全部调用了才会移除 dom
listeners = cbs.remove.length + 1;
rm = createRmCb(ch.elm as Node, listeners);
// 调用 module 中是 remove hook
for (i = 0; i < cbs.remove.length; ++i) cbs.remove[i](ch, rm);
// 调用 vnode 的 remove hook
if (isDef(i = ch.data) && isDef(i = i.hook) && isDef(i = i.remove)) {
i(ch, rm);
} else {
rm();
}
} else { // Text node
api.removeChild(parentElm, ch.elm as Node);
}
}
}
}
// 调用 destory hook
// 如果存在 children 递归调用
function invokeDestroyHook(vnode: VNode) {
let i: any, j: number, data = vnode.data;
if (data !== undefined) {
if (isDef(i = data.hook) && isDef(i = i.destroy)) i(vnode);
for (i = 0; i < cbs.destroy.length; ++i) cbs.destroy[i](vnode);
if (vnode.children !== undefined) {
for (j = 0; j < vnode.children.length; ++j) {
i = vnode.children[j];
if (i != null && typeof i !== "string") {
invokeDestroyHook(i);
}
}
}
}
}
// 只有当所有的 remove hook 都调用了 remove callback 才会移除 dom
function createRmCb(childElm: Node, listeners: number) {
return function rmCb() {
if (--listeners === 0) {
const parent = api.parentNode(childElm);
api.removeChild(parent, childElm);
}
};
}
这两个函数主要用来添加 vnode 和移除 vnode,代码逻辑基本都能看懂。
thunk 函数
一般我们的应用是根据 js 状态来更新的,比如下面这个例子
function renderNumber(num) {
return h('span', num);
}
这里意味着如果 num 没有改变的话,那对 vnode 进行 patch 就是没有意义的,
对于这种情况,snabbdom 提供了一种优化手段,也就是 thunk,该函数同样返回一个 vnode 节点,但是在 patchVnode 开始时,会对参数进行一次比较,如果相同,将结束对比,这个有点类似于 React 的 pureComponent,pureComponent 的实现上会做一次浅比较 shadowEqual,结合 immutable 数据进行使用效果更加。上面的例子可以变成这样。
function renderNumber(num) {
return h('span', num);
}
function render(num) {
return thunk('div', renderNumber, [num]);
}
var vnode = patch(container, render(1))
// 由于num 相同,renderNumber 不会执行
patch(vnode, render(1))
它的具体实现如下:
export interface ThunkFn {
(sel: string, fn: Function, args: Array<any>): Thunk;
(sel: string, key: any, fn: Function, args: Array<any>): Thunk;
}
// 使用 h 函数返回 vnode,为其添加 init 和 prepatch 钩子
export const thunk = function thunk(sel: string, key?: any, fn?: any, args?: any): VNode {
if (args === undefined) {
args = fn;
fn = key;
key = undefined;
}
return h(sel, {
key: key,
hook: {init: init, prepatch: prepatch},
fn: fn,
args: args
});
} as ThunkFn;
// 将 vnode 上的数据拷贝到 thunk 上,在 patchVnode 中会进行判断,如果相同会结束 patchVnode
// 并将 thunk 的 fn 和 args 属性保存到 vnode 上,在 prepatch 时需要进行比较
function copyToThunk(vnode: VNode, thunk: VNode): void {
thunk.elm = vnode.elm;
(vnode.data as VNodeData).fn = (thunk.data as VNodeData).fn;
(vnode.data as VNodeData).args = (thunk.data as VNodeData).args;
thunk.data = vnode.data;
thunk.children = vnode.children;
thunk.text = vnode.text;
thunk.elm = vnode.elm;
}
function init(thunk: VNode): void {
const cur = thunk.data as VNodeData;
const vnode = (cur.fn as any).apply(undefined, cur.args);
copyToThunk(vnode, thunk);
}
function prepatch(oldVnode: VNode, thunk: VNode): void {
let i: number, old = oldVnode.data as VNodeData, cur = thunk.data as VNodeData;
const oldArgs = old.args, args = cur.args;
if (old.fn !== cur.fn || (oldArgs as any).length !== (args as any).length) {
// 如果 fn 不同或 args 长度不同,说明发生了变化,调用 fn 生成新的 vnode 并返回
copyToThunk((cur.fn as any).apply(undefined, args), thunk);
return;
}
for (i = 0; i < (args as any).length; ++i) {
if ((oldArgs as any)[i] !== (args as any)[i]) {
// 如果每个参数发生变化,逻辑同上
copyToThunk((cur.fn as any).apply(undefined, args), thunk);
return;
}
}
copyToThunk(oldVnode, thunk);
}
可以回顾下 patchVnode 的实现,在 prepatch 后,会对 vnode 的数据做比较,比如当 children 相同、text 相同都会结束 patchVnode。
结语
到这里 snabbdom 的核心源码已经阅读完毕,剩下的还有一些内置的 module,有兴趣的可以自行阅读。
扫一扫关注迅雷前端公众号
