认知
之前没有前后端分离的时候,路由几乎都是针对后台而言的,有人说掌控了路由就相当于占了主权地位,我觉得这句话是不为过的。因为路由才能决定你的页面从哪里来,到哪里去。现在的前后端分离项目,路由几乎都给了前端处理,比如你经常使用的vue-router,react-router,今天就react路由为基础,一起实现下React开发中常常使用的路由那些个东东。
选择
react-router-dom & react-router? #4648
HashRouter
本文依旧运用测试驱动开发的模式进行理顺思路。。。。。。Begin。。。。
- 根据不同的路由渲染三个不同的组件(Home,News,About)
let Home = () => <div>首页</div>;
let News = () => <div>新闻</div>;
let About = () => <div>关于我们</div>;
渲染方法:
ReactDOM.render(
<Router>
<Route path='/home' component={Home}></Route>
<Route path='/news' component={News}></Route>
<Route path='/about component={About}></Route>
</Router>,
document.querySelector('#app')
)
通过以下传递参数的方法,观察得到有用的参数(图1)
let Home = (props,context)=> {
console.log(props)
return <div>首页</div>;
}
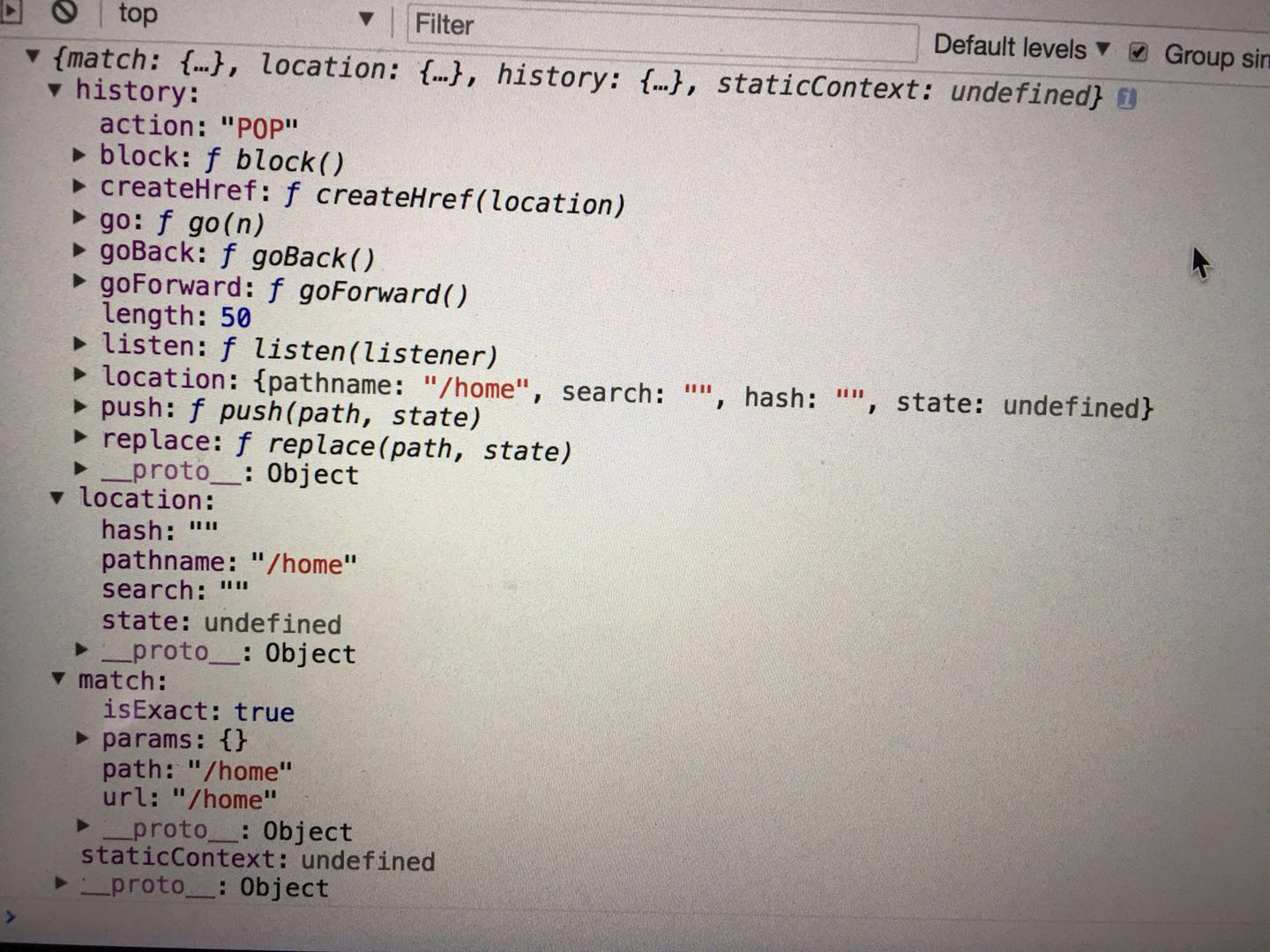
{
history:{
push()
},
location:{pathname:'/home'},
match{
params:{},
path:'/home',
url:'/home'
}
}
编写父组件HashRouter.js,以及单条路由Route.js
HashRouter.js:
在组件挂载的时候,监听hashchange事件,即重新渲染页面
componentWillMount(){
window.location.hash = window.location.hash || '/';
let render = ()=>{
this.setState({});
}
window.addEventListener('hashchange',render);
}
通过上下文context进行父子组件之间的通信,传递location.pathname值
static childContextTypes = {
location:PropTypes.object
}
constructor(props){
super(props);
this.state = {};
}
getChildContext(){
return {
location:{pathname:window.location.hash.slice(1)||'/'}
}
}
HashRouter具体render的对象为子组件,本身并没有东西需要render。
render(){
return this.props.children;
}
Route.js:
获取context中的pathname,跟组件传进来的path进行比较,看是否相等,相等则渲染传递进来的props中的component
static contextTypes = {
location: PropTypes.object
}
render(){
let {path,component:Component} = this.props;
let {location:{pathname}} = this.context;
if(path == pathname || pathname.startsWith(path)){
return <Component location={this.context.location} history={this.context.history}/>;
}
return null;
}
到此通过浏览器改变输入的hash值,就可以切换到不同的组件,显示不同的内容。
2. 通过导航的形式,点击页面的导航条,切换到不同的页面(Link组件)
本质为a标签。点击通过上下文的history改变hash。
HashRouter:
static childContextTypes = {
location:PropTypes.object
}
getChildContext(){
return {
location:{pathname:window.location.hash.slice(1)||'/'},
history:{
push(path){
window.location.hash = path;
}
}
}
}
Link.js
import React,{Component} from 'react';
import ProTypes from 'prop-types';
export default class Link extends Component{
static contextTypes = {
history:ProTypes.object
}
render(){
return (
// <a href={"#"+this.props.to}>{this.props.children}</a>
<a onClick={()=>this.context.history.push(this.props.to)}>{this.props.children}</a>
)
}
}
调用:
<ul className='nav navbar-nav'>
<li>
<Link to='/home'>首页</Link>
</li>
<li>
<Link to='/news'>新闻管理</Link>
</li>
<li>
<Link to='/about'>关于我们</Link>
</li>
</ul>
-
二级路由
我们创建一个新闻管理的类News.js,在这里进行二级路由的分发,有一个新闻列表(路由为/news/list,组件为NewsList),和一个添加新闻(路由为/news/add,组件为NewsAdd),点击添加新闻和新闻列表 可以跳转到相对应的路由 此项功能通过之前的实现是支持的,无须对我们自己的HashRouter等进行改写 -
路径参数实现之params
express中,vue中都有类似于'/news/datail/:id'这样的路径,后面的id是动态匹配的,即为路径参数。而且相似的是这些实现都用到了path-to-regxp这个库。这里我们也重点使用这个库实现路径参数的功能。 在News.js中添加一条路由信息,可以跳转到NewsDetail详情页。
<Route path='/news/datail/:id' component={NewsDetail}></Route>
然后在Route.js添加constructor,通过path-to-regexp获取到正则匹配路径信息,并且修改render中路径匹配的方法如下:
constructor(props) {
super(props);
let { path } = props;
this.keys = [];
this.regxp = pathToRegexp(path, this.keys, { end: false });
this.keys = this.keys.map(key => key.name);
}
let { location } = this.context;
let result = location.pathname.match(this.regxp);
let props = {
location,
history: this.context.history
}
if (result) {
let [url, ...values] = result;
props.match = {
url,
path,
params: this.keys.reduce((memo, key, idx) => {
memo[key] = values[idx];
return memo;
}, {})
}
return <Component {...props}></Component>
} else {
return null;
}
上述props.match是很重要的一部,拿到match的信息 图1中也有显示
- Switch组件 有的时候在我们写路由信息的时候,会手误写成两个,比如
<Route path='/home' component={Home}></Route>
<Route path='/home' component={Home}></Route>
<Route path='/news' component={News}></Route>
<Route path='/about' component={About}></Route>
这里有两个/home,那么页面就会显示两次,这时候我们需要些一个Switch组件,套在最外层,那么原理就是依次匹配,匹配到了直接返回,不再往下匹配。由此得出Switch.js的逻辑:
<Switch>
<Route path='/home' component={Home}></Route>
<Route path='/home' component={Home}></Route>
<Route path='/news' component={News}></Route>
<Route path='/about' component={About}></Route>
</Switch>
export default class Switch extends Component {
static contextTypes = {
location: ProTypes.object
}
render() {
let { pathname } = this.context.location;
let children = this.props.children;
for (let i = 0; i < children.length; i++) {
let child = children[i];
let { path } = child.props;
if (pathToRegexp(path, [], { end: false }).test(pathname)) {
return child;
}
}
return null;
}
}
小结
未完待续。。。。