参考
Android应用程序消息处理机制(Looper、Handler)分析
Handler 机制主要由四个部分组成:
- Looper
- MessageQueue
- Message
- Handler
典型用法
class LooperThread extends Thread {
public Handler mHandler;
public void run() {
Looper.prepare();
mHandler = new Handler() {
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
// process incoming messages here
}
};
Looper.loop();
}
}
Looper
不断循环执行 Looper.loop,按分发机制将消息分发给目标处理者
private static void prepare(boolean quitAllowed) {
if(sThreadLocal.get() != null) {
throw new RuntimeException("Only one Looper may be created per thread");
}
// 构建 Looper 存储到 ThreadLocal
sThreadLocal.set(new Looper(quitAllowed));
}
sThreadLocal 是一个 ThreadLocal 类型的静态变量
ThreadLocal:线程本地存储区(Thread Local Storage),每个线程都有自己的私有的本地存储区域,不同线程之间彼此不能访问对方的 TLS 区域
private Looper(boolean quitAllowed) {
// Looper 中创建 MessageQueue
mQueue = new MessageQueue(quitAllowed);
mThread = Thread.currentThread();
}
public static void loop() {
final Looper me = myLooper();
if (me == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("No Looper; Looper.prepare() wasn't called on this thread.");
}
final MessageQueue queue = me.mQueue;
// Make sure the identity of this thread is that of the local process,
// and keep track of what that identity token actually is.
Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
final long ident = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
for (;;) {
Message msg = queue.next(); // 获取下一条 Message,可能会阻塞
if (msg == null) {
// No message indicates that the message queue is quitting.
return;
}
// This must be in a local variable, in case a UI event sets the logger
final Printer logging = me.mLogging;
if (logging != null) {
logging.println(">>>>> Dispatching to " + msg.target + " " +
msg.callback + ": " + msg.what);
}
final long slowDispatchThresholdMs = me.mSlowDispatchThresholdMs;
//省略
final long start = (slowDispatchThresholdMs == 0) ? 0 : SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
final long end;
try {
// 分发 Message
msg.target.dispatchMessage(msg);
end = (slowDispatchThresholdMs == 0) ? 0 : SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
} finally {
if (traceTag != 0) {
Trace.traceEnd(traceTag);
}
}
if (slowDispatchThresholdMs > 0) {
final long time = end - start;
if (time > slowDispatchThresholdMs) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Dispatch took " + time + "ms on "
+ Thread.currentThread().getName() + ", h=" +
msg.target + " cb=" + msg.callback + " msg=" + msg.what);
}
}
if (logging != null) {
logging.println("<<<<< Finished to " + msg.target + " " + msg.callback);
}
// Make sure that during the course of dispatching the
// identity of the thread wasn't corrupted.
final long newIdent = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
if (ident != newIdent) {
Log.wtf(TAG, "Thread identity changed from 0x"
+ Long.toHexString(ident) + " to 0x"
+ Long.toHexString(newIdent) + " while dispatching to "
+ msg.target.getClass().getName() + " "
+ msg.callback + " what=" + msg.what);
}
// 释放 Message
msg.recycleUnchecked();
}
}
// Looper.quit 最终调用的都是 MessageQueue.quit
public void quit() {
mQueue.quit(false); // 移除消息
}
public void quitSafely() {
mQueue.quit(true); // 安全移除消息
}
MessageQueue 在构造方法中,会调用 native 方法 nativeInit 方法,在 NativeMessageQueue 的构造方法中,会构造一个 JNI 层的 Looper
// frameworks/base/libs
Looper::Looper(bool allowNonCallbacks) :
mAllowNonCallbacks(allowNonCallbacks),
mResponseIndex(0) {
// 管道机制
int wakeFds[2];
int result = pipe(wakeFds);
......
mWakeReadPipeFd = wakeFds[0];
mWakeWritePipeFd = wakeFds[1];
......
#ifdef LOOPER_USES_EPOLL
// 分配新的 epoll 实例同时注册唤醒管道
mEpollFd = epoll_create(EPOLL_SIZE_HINT);
......
struct epoll_event eventItem;
memset(& eventItem, 0, sizeof(epoll_event)); // zero out unused members of data field union
// 观察 EPOLLIN 事件
eventItem.events = EPOLLIN;
eventItem.data.fd = mWakeReadPipeFd;
result = epoll_ctl(mEpollFd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, mWakeReadPipeFd, & eventItem);
......
#else
......
#endif
......
}
管道:Linux 系统中的一种进程间通信机制。简单来说,管道就是一个文件,在管道的两端,分别是两个打开文件的文件描述符,这两个打开文件描述符都是对应同一个文件,其中一个是用来读的,别一个是用来写的,一般的使用方式就是,一个线程通过读文件描述符中来读管道的内容,当管道没有内容时,这个线程就会进入等待状态,而另外一个线程通过写文件描述符来向管道中写入内容,写入内容的时候,如果另一端正有线程正在等待管道中的内容,那么这个线程就会被唤醒。
epoll:Linux 系统中的 epoll 机制为处理大批量句柄而作了改进的 poll,是 Linux 下多路复用 IO 接口select/poll 的增强版本,它能显著减少程序在大量并发连接中只有少量活跃的情况下的系统 CPU 利用率。
pipe 是 Linux 系统中的管道机制,用于 IPC,在管道机制的实现中,又使用 epoll 机制来监听读写事件。
以上在 Android 上的应用为,当 Java 层的消息队列中没有消息时,就使 Android 应用程序主线程进入等待状态,而当 Java 层的消息队列中来了新的消息后,就唤醒 Android 应用程序的主线程来处理这个消息。
Handler
public Handler(Callback callback, boolean async) {
if (FIND_POTENTIAL_LEAKS) {
final Class<? extends Handler> klass = getClass();
if ((klass.isAnonymousClass() || klass.isMemberClass() || klass.isLocalClass()) &&
(klass.getModifiers() & Modifier.STATIC) == 0) {
// 匿名类、内部类或本地类都必须申明为 static,否则会警告出现内存泄漏
Log.w(TAG, "The following Handler class should be static or leaks might occur: " +
klass.getCanonicalName());
}
}
// 默认使用当前线程的 Looper
mLooper = Looper.myLooper();
if (mLooper == null) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Can't create handler inside thread that has not called Looper.prepare()");
}
mQueue = mLooper.mQueue;
mCallback = callback;
// 是否为异步处理
mAsynchronous = async;
}
在 Looper.loop 中,当存在 Message 需要处理时,会调用 dispatchMessage 来进行分发:
public void dispatchMessage(Message msg) {
if (msg.callback != null) {
// 先调用 callback
handleCallback(msg);
} else {
if (mCallback != null) {
// 接着检查通过构造方法传进来的 Callback
if (mCallback.handleMessage(msg)) {
return;
}
}
// 最后调用 handleMessage
handleMessage(msg);
}
}
通过 Handler 发送消息:
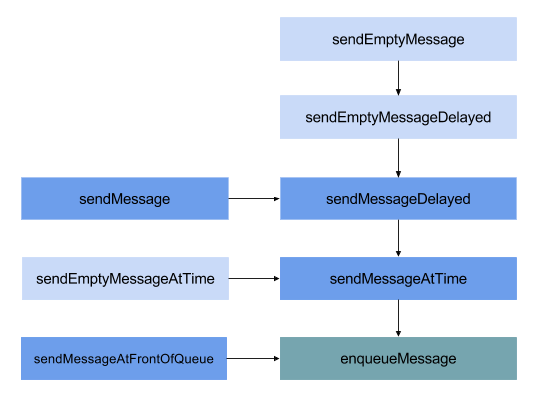 发送消息调用链
发送消息调用链 最终所有的方法都会调用到 MessageQueue.enqueueMessage
MessageQueue
消息机制中 Java 层和 C++ 层的连接纽带,大部分核心方法都交给 native 层来处理
MessageQueue(boolean quitAllowed) {
mQuitAllowed = quitAllowed;
// used by native code
mPtr = nativeInit();
}
MessageQueue 的初始化工作主要由 native 方法来执行
//frameworks/base/core/jni/android_os_MessageQueue.cpp
static void android_os_MessageQueue_nativeInit(JNIEnv* env, jobject obj) {
// 构建一个 NativeMessageQueue,在它的构造方法中,也会创建一个 Looper,不过这个 Looper 对象实现是在 JNI 层
NativeMessageQueue* nativeMessageQueue = new NativeMessageQueue();
if (! nativeMessageQueue) {
jniThrowRuntimeException(env, "Unable to allocate native queue");
return;
}
// 在这里,会 NativeMessageQueue 保存到 Java 层 MessageQueue 的 mPtr 变量中,这里保存的是一个偏移量
android_os_MessageQueue_setNativeMessageQueue(env, obj, nativeMessageQueue);
}
nativeInit 中主要是在 JNI 层创建一个 NativeMessageQueue 并将偏移量保存在 MessageQueue 中的 mPtr,关联了 NativeMessageQueue 和 MessageQueue
Message next() {
// messsage loop has already quit
final long ptr = mPtr;
if (ptr == 0) {
return null;
}
int pendingIdleHandlerCount = -1; // -1 only during first iteration
int nextPollTimeoutMillis = 0;
for (;;) {
if (nextPollTimeoutMillis != 0) {
Binder.flushPendingCommands();
}
// 阻塞操作,当等待nextPollTimeoutMillis时长,或者消息队列被唤醒,都会返回
// ptr 是在 JNI 层创建的 NativeMessageQueue
nativePollOnce(ptr, nextPollTimeoutMillis);
// 当前 nativePollOnce 返回后,查看消息队列中是否存在消息
synchronized (this) {
// 尝试检索下一条消息,如果找到则返回
final long now = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
Message prevMsg = null;
Message msg = mMessages;
if (msg != null && msg.target == null) {
// 找到下一条异步消息或者没有消息了,则退出循环
do {
prevMsg = msg;
msg = msg.next;
} while (msg != null && !msg.isAsynchronous());
}
if (msg != null) {
if (now < msg.when) {
// 下一个消息还没准备好,重新设置唤醒超时时间
nextPollTimeoutMillis = (int) Math.min(msg.when - now, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
} else {
// 获取一条消息
mBlocked = false;
if (prevMsg != null) {
prevMsg.next = msg.next;
} else {
mMessages = msg.next;
}
msg.next = null;
if (DEBUG) Log.v(TAG, "Returning message: " + msg);
// 标记当前消息已使用
msg.markInUse();
return msg;
}
} else {
// 当前还没有消息,设置为 -1,无限等待中
nextPollTimeoutMillis = -1;
}
// Process the quit message now that all pending messages have been handled.
if (mQuitting) {
dispose();
return null;
}
// queue is empty or if the first message
// get pending idle handler count
if (pendingIdleHandlerCount < 0
&& (mMessages == null || now < mMessages.when)) {
pendingIdleHandlerCount = mIdleHandlers.size();
}
if (pendingIdleHandlerCount <= 0) {
// 没有 idle handlers 需要运行,循环继续等待
mBlocked = true;
continue;
}
if (mPendingIdleHandlers == null) {
mPendingIdleHandlers = new IdleHandler[Math.max(pendingIdleHandlerCount, 4)];
}
mPendingIdleHandlers = mIdleHandlers.toArray(mPendingIdleHandlers);
}
// Run the idle handlers.
// We only ever reach this code block during the first iteration
for (int i = 0; i < pendingIdleHandlerCount; i++) {
final IdleHandler idler = mPendingIdleHandlers[i];
mPendingIdleHandlers[i] = null;
boolean keep = false;
try {
keep = idler.queueIdle();
} catch (Throwable t) {
Log.wtf(TAG, "IdleHandler threw exception", t);
}
if (!keep) {
synchronized (this) {
mIdleHandlers.remove(idler);
}
}
}
// Reset the idle handler count to 0 so we do not run them again.
pendingIdleHandlerCount = 0;
//不设置超时时间,因为可能在处理 IdleHandler 时可能有新的消息加入
nextPollTimeoutMillis = 0;
}
}
在 next 方法中,nativePollOnce 是阻塞操作,其中 nextPollTimeoutMillis 代表下一个消息到来之前,还需要等待的时长;nextPollTimeoutMillis == -1 表示当前没有更多消息。nativePollOnce 调用结束后,从 mMessages 中提取一个消息
当处于空闲时,执行 IdleHandler 中的回调方法。
// frameworks/base/core/jni/android_os_MessageQueue.cpp
static void android_os_MessageQueue_nativePollOnce(JNIEnv* env, jobject obj,
jint ptr, jint timeoutMillis) {
// 通过前面设置的 mPrt 获取 NativeMessageQueue
NativeMessageQueue* nativeMessageQueue = reinterpret_cast<NativeMessageQueue*>(ptr);
// 调用 NativeMessageQueue.pollOnce 进行轮询
nativeMessageQueue->pollOnce(timeoutMillis);
}
void NativeMessageQueue::pollOnce(int timeoutMillis) {
// 将调用转发给了 JNI 层的 Looper
mLooper->pollOnce(timeoutMillis);
}
pollOnce 会调用 pollnner 来进一步操作,如果 pollnner 返回值不等于 0,则返回
// frameworks/base/libs/utils/Looper.cpp
int Looper::pollInner(int timeoutMillis) {
......
int result = ALOOPER_POLL_WAKE;
......
#ifdef LOOPER_USES_EPOLL
struct epoll_event eventItems[EPOLL_MAX_EVENTS];
// 调用 epoll_wait 检查 epoll 专用文件描述符 mEpollFd 所监控的文件描述符是否有 IO 事件,超时时间为 timeoutMillis
// 在 JNI 层的 Looper 构造函数中,设置了要监控 mWakeReadPipeFd 文件描述符的 EPOLLIN 事件
// 如果检查成功或者超时,则结束等待
// 处于 Idle 状态
int eventCount = epoll_wait(mEpollFd, eventItems, EPOLL_MAX_EVENTS, timeoutMillis);
bool acquiredLock = false;
#else
......
#endif
// eventCount < 0 可能出错了
if (eventCount < 0) {
if (errno == EINTR) {
goto Done;
}
LOGW("Poll failed with an unexpected error, errno=%d", errno);
result = ALOOPER_POLL_ERROR;
goto Done;
}
// eventCount == 0 超时
if (eventCount == 0) {
......
result = ALOOPER_POLL_TIMEOUT;
goto Done;
}
......
#ifdef LOOPER_USES_EPOLL
// eventCount > 0 存在事件
for (int i = 0; i < eventCount; i++) {
int fd = eventItems[i].data.fd;
uint32_t epollEvents = eventItems[i].events;
if (fd == mWakeReadPipeFd) {
if (epollEvents & EPOLLIN) {
// Looper 中使用 epoll 监听的 EPOLLIN 事件
awoken();
} else {
LOGW("Ignoring unexpected epoll events 0x%x on wake read pipe.", epollEvents);
}
} else {
......
}
}
if (acquiredLock) {
mLock.unlock();
}
Done: ;
#else
......
#endif
......
return result;
}
void Looper::awoken() {
......
char buffer[16];
ssize_t nRead;
do {
nRead = read(mWakeReadPipeFd, buffer, sizeof(buffer));
} while ((nRead == -1 && errno == EINTR) || nRead == sizeof(buffer));
}
总结上面的代码,Looper 通过 loop 调用 MessageQueue 的 next,next 中又会调用到 native 方法 nativePollOnce,在这个方法中,会调用到 NativeMessageQueue 的 pollInner,这里会通过在 JNI 层 Looper 的构造方法中,使用 epoll 监听管道 EPOLLIN 事件,如果存在调用
awoken,清空管道中的内容,以便下次再调用pollInner函数时,知道自从上次处理完消息队列中的消息后,有没有新的消息加进来。
boolean enqueueMessage(Message msg, long when) {
if (msg.target == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Message must have a target.");
}
if (msg.isInUse()) {
throw new IllegalStateException(msg + " This message is already in use.");
}
synchronized (this) {
if (mQuitting) {
IllegalStateException e = new IllegalStateException(
msg.target + " sending message to a Handler on a dead thread");
Log.w(TAG, e.getMessage(), e);
msg.recycle();
return false;
}
msg.markInUse();
msg.when = when;
Message p = mMessages;
boolean needWake;
if (p == null || when == 0 || when < p.when) {
// 不存在头部消息或立即执行或执行时机快于头部消息
// 将处理的消息作为新的头部消息
msg.next = p;
mMessages = msg;
needWake = mBlocked;
} else {
// 将处理的消息插入到队列的尾部
// 一般不需要唤醒事件队列,除非消息头存在 barrier,并且当前处理的消息是队列中最早的异步消息
needWake = mBlocked && p.target == null && msg.isAsynchronous();
Message prev;
for (;;) {
prev = p;
p = p.next;
if (p == null || when < p.when) {
break;
}
if (needWake && p.isAsynchronous()) {
needWake = false;
}
}
msg.next = p; // invariant: p == prev.next
prev.next = msg;
}
// We can assume mPtr != 0 because mQuitting is false.
if (needWake) {
nativeWake(mPtr);
}
}
return true;
}
MessageQueue 是按照消息触发时间的先后顺序排列的,队列头部的消息是最早触发的。当有消息加入,会从队列头部开始遍历,插入到合适的位置,以保证所有消息的时间顺序。
如果当前线程处于空闲等待状态,那么还需要调用 nativeWake 来唤醒:
// frameworks/base/core/jni/android_os_MessageQueue.cpp
static void android_os_MessageQueue_nativeWake(JNIEnv* env, jobject obj, jint ptr) {
// ptr 获取 NativeMessageQueue
NativeMessageQueue* nativeMessageQueue = reinterpret_cast<NativeMessageQueue*>(ptr);
return nativeMessageQueue->wake();
}
这里将唤醒请求转发到 Looper wake:
// frameworks/base/libs/utils/Looper.cpp
void Looper::wake() {
......
ssize_t nWrite;
do {
// 先管道中写入 "W
nWrite = write(mWakeWritePipeFd, "W", 1);
} while (nWrite == -1 && errno == EINTR);
.......
}
往管道写入内容,从而唤醒线程,因为当消息队列中没有消息处理时,线程会进入空闲等待状态,具体是通过 Looper 的 polllnner 中调用 epoll_wait 进入
void removeMessages(Handler h, int what, Object object) {
if (h == null) {
return;
}
synchronized (this) {
Message p = mMessages;
// 从队列头部开始,移除连续的所有符合条件的消息
while (p != null && p.target == h && p.what == what
&& (object == null || p.obj == object)) {
Message n = p.next;
mMessages = n;
// 找到对应的消息,释放它
p.recycleUnchecked();
p = n;
}
// 从新的队列头部开始,移除全部符合条件的消息
while (p != null) {
Message n = p.next;
if (n != null) {
if (n.target == h && n.what == what
&& (object == null || n.obj == object)) {
Message nn = n.next;
n.recycleUnchecked();
p.next = nn;
continue;
}
}
p = n;
}
}
}
postSyncBarrier 提交一个同步屏障,这将会阻止队列中消息的执行,直到手动调用 removeSyncBarrier
当 MessageQueue 退出时,需要 dispose:
// Disposes of the underlying message queue.
// Must only be called on the looper thread or the finalizer.
private void dispose() {
if (mPtr != 0) {
// native 方法
nativeDestroy(mPtr);
// mPtr 是记录 JNI 层的 NativeMessageQueue 的偏移量
mPtr = 0;
}
}
nativeDestroy 最终会调用 RefBase 的 decStrong:
void RefBase::decStrong(const void* id) const
{
weakref_impl* const refs = mRefs;
refs->removeStrongRef(id); //移除强引用
const int32_t c = android_atomic_dec(&refs->mStrong);
if (c == 1) {
refs->mBase->onLastStrongRef(id);
if ((refs->mFlags&OBJECT_LIFETIME_MASK) == OBJECT_LIFETIME_STRONG) {
delete this;
}
}
refs->decWeak(id); // 移除弱引用
}
Message
void recycleUnchecked() {
// 标记为使用状态,清除其他状态
flags = FLAG_IN_USE;
what = 0;
arg1 = 0;
arg2 = 0;
obj = null;
replyTo = null;
sendingUid = -1;
when = 0;
target = null;
callback = null;
data = null;
synchronized (sPoolSync) {
// 消息缓存
if (sPoolSize < MAX_POOL_SIZE) {
next = sPool;
sPool = this;
sPoolSize++;
}
}
}
public static Message obtain() {
synchronized (sPoolSync) {
if (sPool != null) {
// 从缓存中获取
Message m = sPool;
sPool = m.next;
m.next = null;
m.flags = 0; // clear in-use flag
sPoolSize--;
return m;
}
}
return new Message();
}
总结
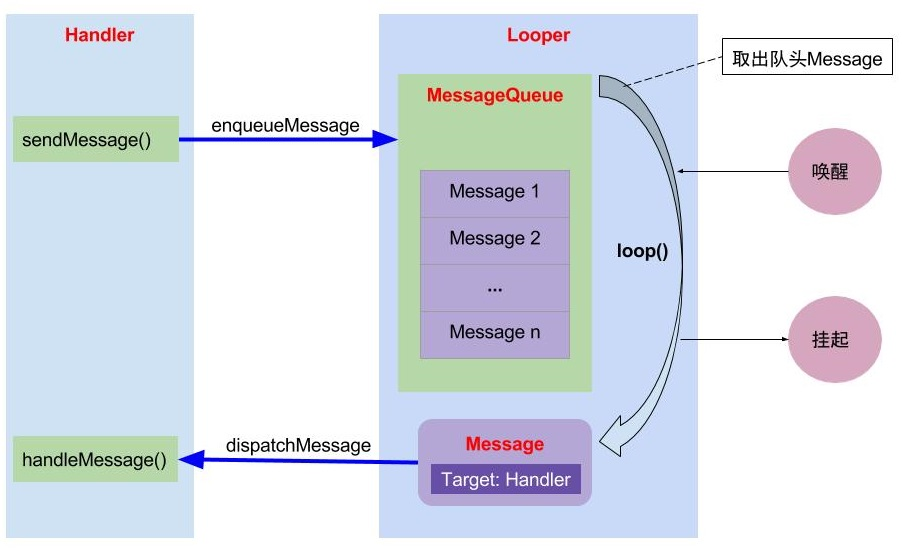 消息机制
消息机制 Java 层:
- Handler 通过
sendMessage,将 Message 通过MessageQueue.enqueueMessage添加到队列中 - Looper 通过
loop提取需要执行的 Message,并交与Message.target的 Handler 进行dispatchMessage分发 - 将 Message 添加到 MessageQueue 时,会唤醒 Looper 线程;如果 MessageQueue 中没有 Message 时,并处于 Idle 状态,则会执行 IdelHandler
JNI 层:
- 线程在进入循环之前,会在 JNI 创建管道(Pipe) ,当消息队列为空时,线程处于空闲等待状态
- 通过 epoll 机制监听
EPOLLIN事件,当有新事件进入消息队列时,并且当前线程处于空闲状态,通过向管道写入数据,来唤醒线程
消息分发的优先级:
Message.callback.run()Handler.mCallback.handleMessage()Handler.handleMessage()
EPOLL:Linux 内核的可扩展 I/O 事件通知机制
PIPE:管道是一系列将标准输入输出链接起来的进程,其中每个进程的输出被直接作为下一个进程的输入
文件描述符(File descriptor):用于表述指向文件的引用的抽象化概念