安装步骤:
1.npm install
2.数据库安装及连接
使用/graphql.sql安装数据库 修改conf/db.js中相关配置
3.启动步骤
npm start
4.访问:
localhost:3003
通过开发者工具查看相关的接口访问
5.访问调试工具:
http://localhost:3003/graphql
http://localhost:3003/article
6.官方的简单版本
/app_simple.js
7.schame 最小的实现版本
/graphql/user/userSchame.js
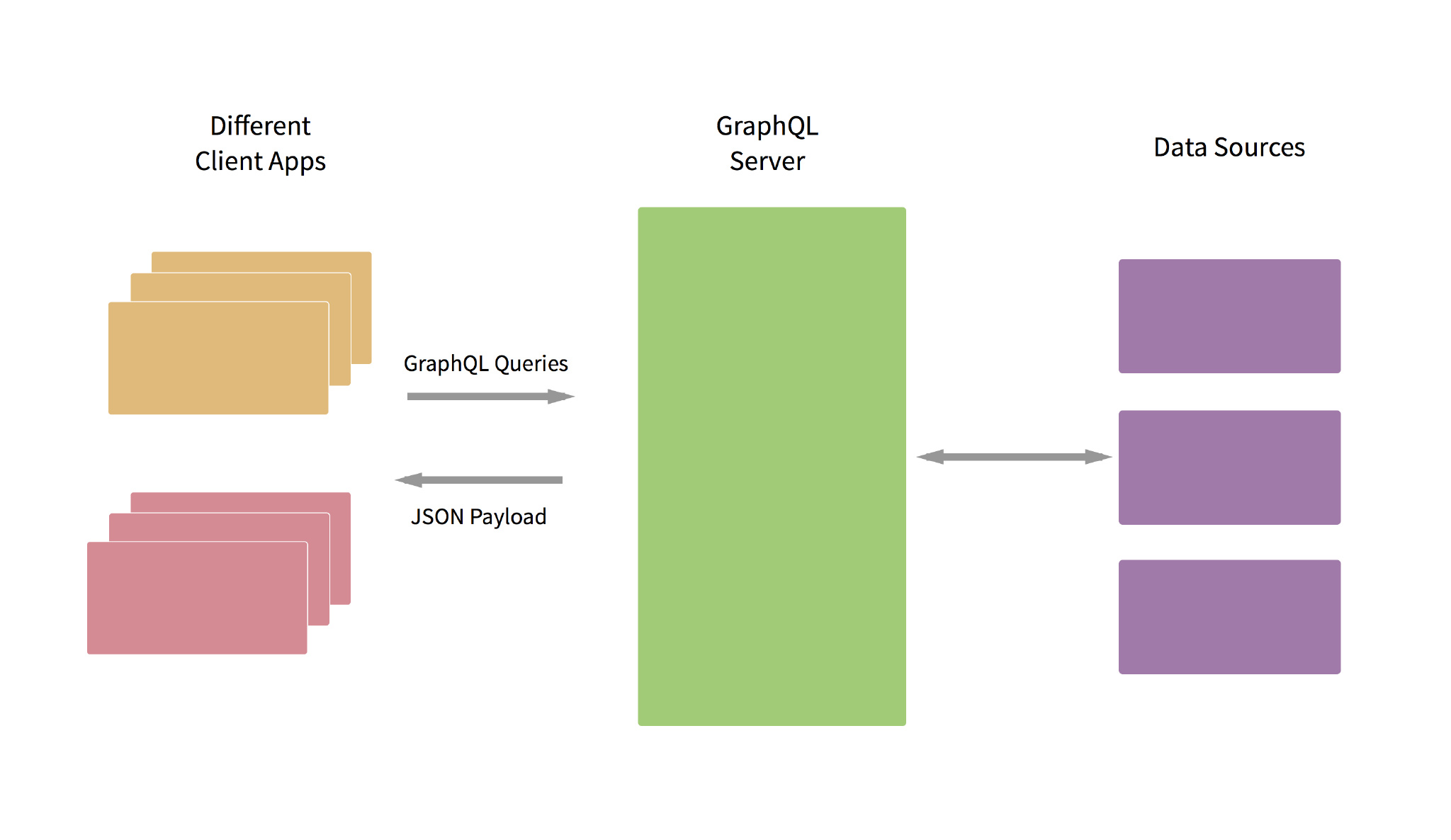
GraphQL是什么
GraphQL 是一个Facebook于2012开发出来且2015开源的应用层的查询语言,你需要在后台定义一个基于GraphQL的图形模式,然后你的客户端就可以查询他们想要的数据,而不需要后台重新定义一个接口返回你需要的数据.
因为不需要更改你后台,所以这种方式比 REST API 方式更好,让我们可以在不同的客户端上灵活改变数据显示.
GraphQL 是一个规范.这意味着你可以在任何语言上实现 GraphQL.点击这里你可以查看更多关于 GraphQL 的介绍.Facebook 有一个对于JavaScript的 GraphQL 实现.
为什么要用
GraphQL对你的API中的数据提供了一套易于理解的完整描述,使得客户端能够准确地获得它需要的数据,而且没有任何冗余,也让 API 更容易地随着时间推移而演进,还能用于构建强大的开发者工具。 获取多个资源只用一个请求
-
声明式。描述所有的可能类型系统 查询的结果格式由请求方(即客户端)决定而非响应方(即服务器端)决定。你不需要编写很多额外的接口来适配客户端请求
-
减少开发文档的维护工作量,相对应的减少沟通成本
-
强类型。每个 GraphQL 查询必须遵循其设定的类型才会被执行。
-
请求合并 多个接口可以通过组合为一个
-
请求你所要的数据不多不少
如何使用
自省
GraphQL是可自省的,也就是说你可以通过查询一个GraphQL知道它自己的schema细节。
查询__schema以列出所有该schema中定义的类型,并获取每一个的细节:
query {
__schema {
types {
name
kind
description
fields {
name
}
}
}
}
查询__type以获取任意类型的细节:
query {
__type(name: "Repository") {
name
kind
description
fields {
name
}
}
}
提示:自省查询可能是你在GraphQL中唯一的GET请求。不管是query还是mutation,如果你要传递请求体,GraphQL请求方式都应该是POST
查询
列表查询(无参数)
{
courses {
id
score
course
}
}
结果:
{
"data": {
"courses": [
{
"id": 1,
"score": 33,
"course": "数学"
},
{
"id": 2,
"score": 55,
"course": "语文"
},
{
"id": 3,
"score": 55,
"course": "数学"
}
]
}
}###单独查询(有参数)
{
course(id:1) {
score
course
}
}
结果:
{
"data": {
"course": {
"score": 33,
"course": "数学"
}
}
}变更
mutation {
addUser (name:"nk",sex:"22",intro:"sdfasdfasdf"){
id
}
}
结果:
{
"data": {
"addUser": {
"id": 26
}
}
}组合查询
{
courses {
id
score
course
}
users {
id
name
}
}
结果
{
"data": {
"courses": [
{
"id": 1,
"score": 33,
"course": "数学"
},
{
"id": 2,
"score": 55,
"course": "语文"
}
],
"users": [
{
"id": 1,
"name": "xiaoming"
},
{
"id": 2,
"name": "2"
},
{
"id": 3,
"name": "2333"
}
]
}
}查询别名
有时候我们想这样查找使数据分开,方便自己各个地方调用:
{
postsnoargs{
title
},
postsnoargs{
_id
}
}我们设想得到的数据是这样的:
{
"data": {
"postsnoargs": {
"title":[
"title": "Sharing the Meteor Login State Between Subdomains",
],
"_id":[
"_id": "0176413761b289e6d64c2c14a758c1c7"
]
}
}
}但其实服务器返回的是这样的:
{
"data": {
"postsnoargs": [
{
"title": "Sharing the Meteor Login State Between Subdomains",
"_id": "0176413761b289e6d64c2c14a758c1c7"
}
]
}
}这时候我们就需要设置别名了,否则服务器返回的时候会合并你的数据:
{
posttitle:postsnoargs{
title
},
postid:postsnoargs{
_id
}
}服务器返回:
{
"data": {
"posttitle": [
{
"title": "Sharing the Meteor Login State Between Subdomains"
}
],
"postid": [
{
"_id": "0176413761b289e6d64c2c14a758c1c7"
}
]
}
} query {
corsesssssss:courses {
id
score
course
}
users {
id
}
}用户输入类型查询
mutation {
addUserByInput (userInfo:{
name:"222222",
intro:"33",
sex:"2"
}) {
id
}
}
结果:
{
"data": {
"addUserByInput": {
"id": 27
}
}
}如何传参数(argument)来调用GraphQL api
// (unit:cm)
{
user(id: 0) {
name
stature(unit: MM)
intro
id
}
}嵌套查询
有时候我们需要对查询到的数据进行筛选,比如限制大小,这时候就需要一个嵌套查询来实现这个功能了.
比如下面这个查询A开头的全国省市信息:
{
address(nameKey:"A"){
ShortKey,
Content(limit:5) {
Id,
Code,
Name,
FirstStr
}
}
}服务器返回:
{
"data": {
"address": [
{
"ShortKey": "A",
"Content": [
{
"Id": 36,
"Code": "152900",
"Name": "阿拉善盟",
"FirstStr": "A"
},
{
"Id": 39,
"Code": "210300",
"Name": "鞍山市",
"FirstStr": "A"
},
{
"Id": 105,
"Code": "340800",
"Name": "安庆市",
"FirstStr": "A"
},
{
"Id": 155,
"Code": "410500",
"Name": "安阳市",
"FirstStr": "A"
},
{
"Id": 293,
"Code": "513200",
"Name": "阿坝藏族羌族自治州 ",
"FirstStr": "A"
}
]
}
]
}
}其中的Content字段加上了限制返回前五个市的信息,注意其中的limit是服务器设置的,并不是Graphql的关键字.
后端解析查询
graphql(schema, ' query HeroNameAndFriends{\n' +
'\tcourses {\n' +
' id\n' +
'\t score\n' +
'\t course\n' +
'\t}\n' +
'}', root).then((response) => {
console.log(response);
});
分片
在 GraphQL 中,分片是一段能够复用的片段.
如果我们需要查询三个不同文章的信息,那么我们可能会做如下的查询:
{
first:posts(index:1){
title,
category,
layout
},
second:posts(index:2){
title,
category,
layout
},
third:posts(index:3){
title,
category,
layout
}
}我们将上面的posts查询进行了一遍又一遍,开始你可能觉得没什么,但是当需要查询的数据有几十个字段的时候你会开始头疼(相信我).
那么我们有什么方法可以复用这一块经常用到的片段呢?
接下来我来给你答案:
fragment post on Post{
title,
category,
layout
}上面的就是一个分片,Post是一个已经服务器定义好的类型,你可以看右上角的文档,每个操作名称的后面都会有一个返回的类型.
下面我们就开始使用这个分片:
{
first:posts(index:1){
...post
},
second:posts(index:2){
...post
},
third:posts(index:3){
...post
}
}
fragment post on Post{
title,
category,
layout
}使用了对象展开符...,如果你了解ES6的话你肯定对这个特别的熟悉,那么我们是不是可以试试ES6类似的特性?
那我们来试试:
{
first:posts(index:1){
...post
},
second:posts(index:2){
...post,
category
},
third:posts(index:3){
...post,
layout
}
}
fragment post on Post{
title,
category,
}看起来一点问题都没有,服务器返回了正确的信息,这些我就不解释了,都是一些ES6的东西,如果你不懂ES6那么要抓紧时间了.
分片总结
分片也可以嵌套分片,所以只要是服务器定义过的数据类型,你都可以写成一个个的分片,这种模式能大量减少你写重复代码的时间.
查询变量
正如上面所说的,分片可以减少大量的时间,那么现在我准备说的查询变量就可以增加你生命(好吧我承认我在瞎扯).
对于上面的那个带参数的查询操作,我们查询了index等于1,2,3时候的数据,分片减少了你输入相同字段的时间,而查询变量减少了你写分片的时间...
废话补多少,先看代码:
query getFewPosts($index: Int!) {
first:posts(index:$index){
...post
}
}
fragment post on Post{
title,
category,
}然后在查询窗口中输入:
{
"index":1
}这就是一个简单的变量查询,也可以和分片一起使用,你可以增加几个变量增加使用分片:
query getFewPosts($index: Int!,
$index1: Int!,
$index2: Int!) {
first:posts(index:$index){
...post
},
second:posts(index:$index1){
...post,
category
},
third:posts(index:$index2){
...post,
layout
}
}
fragment post on Post{
title,
category,
}然后在查询窗口中输入:
{
"index": 1,
"index1": 2,
"index2": 3
}前端查询:
var xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhr.responseType = 'json';
xhr.open("POST", "/article");
xhr.setRequestHeader("Content-Type", "application/json");
xhr.setRequestHeader("Accept", "application/json");
xhr.onload = function () {
console.log('data returned:', xhr.response);
}
xhr.send(JSON.stringify({
query: `
query getFewPosts($index: Int!,
$index1: Int!,
$index2: Int!) {
first:posts(index:$index){
...post
},
second:posts(index:$index1){
...post,
category
},
third:posts(index:$index2){
...post,
layout
}
}
fragment post on Post{
title,
category,
}
`,
variables:{
"index": 1,
"index1": 2,
"index2": 3
}
}));服务端是如何实现的
简单方式(app_simple.js)
var express = require('express');
var graphqlHTTP = require('express-graphql');
var {
GraphQLList,
GraphQLObjectType,
GraphQLSchema,
GraphQLString,
GraphQLInt,
GraphQLFloat,
GraphQLEnumType,
GraphQLNonNull,
GraphQLInterfaceType,
GraphQLInputObjectType,
GraphQLUnionType
} = require('graphql');
//服务端示例数据
var animals=[
{
chinaName: '狗狗',
legs: 4
},
{
englishName: 'fish',
tailColor:'red'
},
];
//定义schema及resolver
const Dog = new GraphQLObjectType({
name: 'Dog',
description: '狗狗实体',
fields: () => ({
chinaName: {type: new GraphQLNonNull(GraphQLString)},
legs: {type: new GraphQLNonNull(GraphQLInt)},
}),
isTypeOf:obj=>obj.legs,
});
const Fish=new GraphQLObjectType({
name:'Fish',
description:"鱼儿实体",
fields: () => {
return ({
englishName: {type: new GraphQLNonNull(GraphQLString)},
tailColor: {type: new GraphQLNonNull(GraphQLString)},
});
},
isTypeOf:obj=>obj.tailColor,
});
const Animal = new GraphQLUnionType({
name: 'Animal',
description: 'Union',
types:[Dog,Fish],
resolveType:function (obj) {
if(obj.legs) {
return Dog;
}else if(obj.tailColor){
return Fish;
}else{
return null;
}
}
});
const Query=new GraphQLObjectType({
name:'AnimalQuery',
description:'动物信息查询',
fields:()=>({
animals:{
type:new GraphQLList(Animal),
description:'查询全部动物列表',
resolve:function () {
return animals;
}
}
}),
});
const schema = new GraphQLSchema({
types: [Dog, Fish,Animal],
query: Query
});
var app = express();
app.use('/graphql', graphqlHTTP({
schema: schema,
graphiql: true, //启用GraphiQL
}));
app.listen(4000, () => console.log('请在浏览器中打开地址:localhost:4000/graphql'));
GraphQL中有对应JavaScript的类型:
GraphQLObjectType,//自定义类型
GraphQLSchema,//定义视图
GraphQLInterfaceType,//描述多个类型的通用字段
GraphQLList,//其他类型的封装
GraphQLString,//字符串类型
GraphQLInt,//整型
GraphQLFloat,//浮点型
GraphQLEnumType,//可迭代类型
GraphQLNonNull,//不允许为空类型,接受一个graphql类型定义查询
const Post = new GraphQLObjectType({
name:"Post",
description:"一篇文章",
fields:()=>({
_id:{
type:new GraphQLNonNull(GraphQLString),//不允许为空
},
title:{
type:new GraphQLNonNull(GraphQLString),//不允许为空
},
category:{
type:GraphQLString
},
layout:{
type:GraphQLString
},
content:{
type:GraphQLString
},
})
});一篇文章包含了id,title,category,layout,content这些信息,其中id和title是不允许空的字符串,如果查询到的数据没有这两个就会报错.
定义好后我们就需要在根查询里面建立一个引用,否则定义的就没法使用:
// 查询根目录(关于查询的动作都需要在这里声明)
const Query = new GraphQLObjectType({
name: 'BlogSchema',
description: 'Root of the Blog Schema',
fields: () => ({
// 回应查询
echo: {
// ...
},
// 文章查询
posts:{
type:new GraphQLList(Post),
args:{
index:{type:GraphQLInt}
},
resolve:(source,args)=>{
return [PostsList[args.index]],//返回数组(虽然只有一个)
}
}
});
})文章查询posts接收一个index参数,这个参数是一个整型.
resolve返回存储在PostsList数组里的对应文章信息,因为posts返回的是一个数组(数组里的数据全是Post对象),而我们查询到的数据是一个Post对象,所以需要用一个数组号括起来.
有时候你需要嵌套几个GraphQLObjectType来得到自己想要的数据格式,比如项目中的schema.js定义了一个地址查询,定义了三层查询.
Mutation
客户端查询数据的时候有时候是也伴随着修改数据和创建数据,所以这里也要介绍一下如果操作更新数据.
我们来看看一个Mutation操作:
mutation CREATE{
createAddress(Id:1,Code:"13156",Name:"信息价",FirstStr:"S"){
Id,
Name,
Code,
}
}增加一个地级市的信息,这个地级市有以下字段:Id,Code,Name,FirstStr.
CREATE是一个mutation名,并不是关键字,你可以随便取其他名字.
createAddress是服务器定义好的一个关键字,接收四个字段,大括号里返回的是创建好的信息.
我们再来看看服务器这边:
// 操作根目录(关于操作的动作都需要在这里声明)
const Mutation = new GraphQLObjectType({
name:"Mutation",
description:"增删改数据",
fields:()=>({
createAddress:{
type:AddressContent,
args:{
Id:{
type:new GraphQLNonNull(GraphQLInt)
},
Code:{
type:new GraphQLNonNull(GraphQLString)
},
Name:{
type:new GraphQLNonNull(GraphQLString)
},
FirstStr:{
type:new GraphQLNonNull(GraphQLString)
}
},
resolve:(source,args)=>{
let address = Object.assign({},args);//获取数据
//改为大写
address.FirstStr = address.FirstStr.toUpperCase();
let queryData = _.find(AddressList,item=>item.ShortKey===address.FirstStr);//查找的数据
//检测是否存在FirstStr开头的
if(queryData){
// 有这个数据
//存储数据
queryData.Content.push(address);
// console.log(address)
return address;//返回新存储的数据
}
else{
return null;
}
}
}
})
})todoList
-
学习使用 DataLoader 来获取列表数据
-
高级用法 接口 联合 等
#相关文档:
该系列比较好
基本一整套的实现,但是没有数据库,没法跑通
GraphQL初探:从REST到GraphQL,更完善的数据查询定义
可参考github: github.com/zhaiqianfen… github.com/proYang/Gra… koa实现 文档不错 封装很好.比较不错 ###坑
node支持 import
下面在项目文件夹新建一个start.js,然后在里面写上以下代码:
require('babel-core/register')({
'presets': [
'stage-3',
["latest-node", { "target": "current" }]
]
})
require('babel-polyfill')
require('./server')
然后 在命令行,运行npm install babel-core babel-polyfill babel-preset-latest-node babel-preset-stage-3 --save-dev安装几个开发模块。
安装完毕之后,在命令行运行 node start.js
mysql
1.graphQL 与mysql数据库查询的异步问题 : async awit