界面更新本质上就是数据的变化。React把所有会动的东西收敛到状态(state),使得大部分的界面任务都可以用一个姿势搞定

没错,我说的是 setState()。本文会揭示setState()的内部实现,并通过改变在改变单一DOM元素属性来一探diffing算法的实现细节。
在开始前,我想先回应一下读者的反馈。其中最主要的一个疑问是:“为啥解析15.x,而不是最新的16.x(fiber)”
简单来说,是因为16.x本质还是同步渲染。所以我认为特意为同步渲染而设计的代码框架(stack reconciler)在现阶段是一个更好的学习对象。
我们先扩展一下{第四篇}中用到的例子
class App extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
desc: 'start',
color: 'blue'
};
this.timer = setTimeout(
() => this.tick(),
5000
);
}
tick() {
this.setState({
desc: 'end',
color: 'green'
});
}
render() {
return (
<div className="App">
<div className="App-header">
<img src="main.jpg" className="App-logo" alt="logo" />
<h1> "Welcom to React" </h1>
</div>
<p className="App-intro" style={{color: this.state.color}}>
{ this.state.desc }
</p>
</div>
);
}
}
export default App;
这个版本的 App 给 <p> 元素新增了 style ,然后在 App 构造完成以后5秒后用 setState() 将 desc 设置为 'end',并将 'color' 设置为 'green'。
App 的实例化是在{第四篇}讨论过。
ctl-f "setState"
在同一篇文章里我也提到了ReactInstanceMap,这个Map被用于从外部的ReactComponent,App反向引用内部的ReactCompositeComponent[ins]。
这里我也拷贝下它的数据结构图
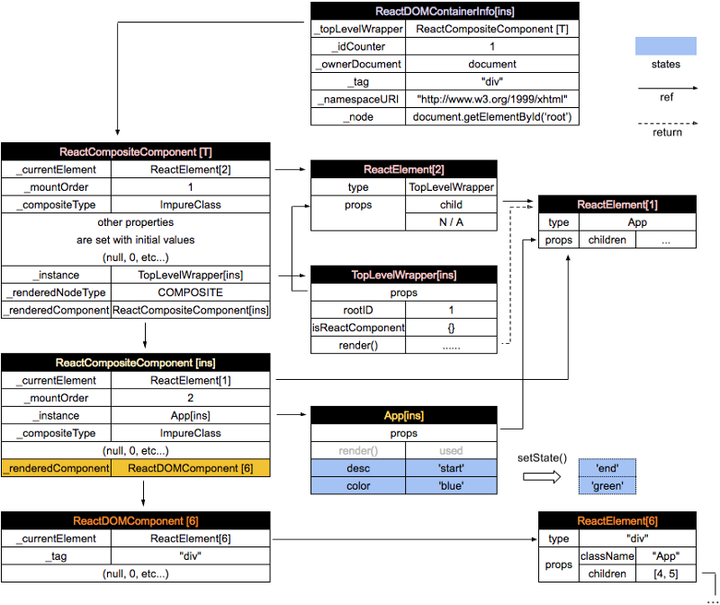
启动Transactions 之前的操作
我们从 setState() 的函数体开始:
ReactComponent.prototype.setState = function (
partialState,
callback
) {
// scr: ---> sanity check
this.updater.enqueueSetState(this, partialState);
if (callback) {
// scr: ---> no callbak
}
};
ReactComponent@isomorphic/modern/class/ReactBaseClasses.js
没错,这个 setState() 是从 ReactComponent 继承过来的。
等一下,这个 this.updater 又是啥?它不是被赋值为 ReactNoopUpdateQueue (空指令)了吗?其实理解了{上一篇} 里讲的Transaction,然后从{第四篇}的 App 实例化的部分往上看一点,这个
updater 的来源就很好找了。
这个问题就留给读者思考吧,我们加快点速度看核心的部分
enqueueSetState: function (publicInstance, partialState) {
// scr: DEV code
// scr: ------------------------------------------------------> 1)
var internalInstance = getInternalInstanceReadyForUpdate(publicInstance, 'setState');
if (!internalInstance) {
return;
}
// scr: ------------------------------------------------------> 2)
var queue = internalInstance._pendingStateQueue || (internalInstance._pendingStateQueue = []);
queue.push(partialState);
// scr: ------------------------------------------------------> 3)
enqueueUpdate(internalInstance);
},
ReactUpdateQueue@renderers/shared/stack/reconciler/ReactUpdateQueue.js
1) 这个方法会从反向链接 ReactInstanceMap 里取得内部操作类 ReactCompositeComponent[ins];
function getInternalInstanceReadyForUpdate(
publicInstance,
callerName
) {
var internalInstance = ReactInstanceMap.get(publicInstance);
... // scr: DEV code
return internalInstance;
}
getInternalInstanceReadyForUpdate@renderers/shared/stack/reconciler/ReactUpdateQueue.js
2)将 _pendingStateQueue 初始化成 ReactCompositeComponent[ins] 的成员变量,然后把 变化的状态 {desc:'end',color:'green'} 加入到这个列表中;
...
function enqueueUpdate(internalInstance) {
ReactUpdates.enqueueUpdate(internalInstance);
}
...
enqueueUpdate@renderers/shared/stack/reconciler/ReactUpdateQueue.js
至此的调用栈一览:
|-ReactComponent.setState()
|-ReactUpdateQueue.enqueueSetState()
|-getInternalInstanceReadyForUpdate()
|-enqueueUpdate()
|-ReactUpdates.enqueueUpdate()
|~~~
这里我也拷贝一下 Transaction(s) 相关的调用关系。
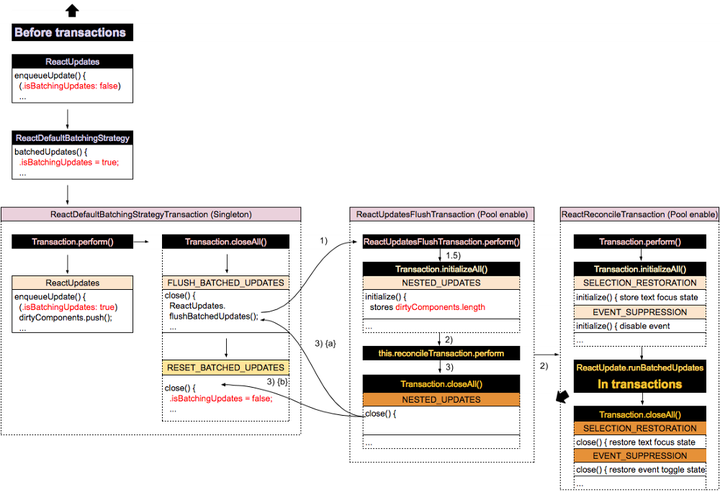
启动Transaction之后的操作
function runBatchedUpdates(transaction) {
var len = transaction.dirtyComponentsLength;
// scr: -----------------------------------> sanity check
...
dirtyComponents.sort(mountOrderComparator);
updateBatchNumber++;
for (var i = 0; i < len; i++) {
var component = dirtyComponents[i];
var callbacks = component._pendingCallbacks;
component._pendingCallbacks = null;
// scr: ------------------------------> logging
...
ReactReconciler.performUpdateIfNecessary(component, transaction.reconcileTransaction, updateBatchNumber);
// scr: ------------------------------> logging
if (callbacks) { // scr: -------------> no callbacks
...
}
}
}
ReactUpdates@renderers/shared/stack/reconciler/ReactUpdates.js
这次我们只有一个 dirtyComponents,ReactCompositeComponent[ins]。 它也是ReactReconciler.performUpdateIfNecessary() 的第一个参数。
performUpdateIfNecessary: function (
internalInstance,
transaction,
updateBatchNumber
) {
// scr: DEV code
...
internalInstance.performUpdateIfNecessary(transaction);
// scr: DEV code
...
}
ReactReconciler@renderers/shared/stack/reconciler/ReactUpdates.js
和 ReactReconciler 里的其它函数一样,ReactReconciler.performUpdateIfNecessary() 直接调用 component 的同名函数, ReactCompositeComponent.performUpdateIfNecessary()
你也可以把这个 ReactReconciler 理解为显式多态
performUpdateIfNecessary: function (transaction) {
if (this._pendingElement != null) {
// scr: -----------> condition not applied
...
} else if (
this._pendingStateQueue !== null ||
this._pendingForceUpdate
) {
this.updateComponent(transaction, this._currentElement, this._currentElement, this._context, this._context);
} else {
// scr: -----------> condition not applied
...
}
},
ReactCompositeComponent@renderers/shared/stack/reconciler/ReactCompositeComponent.js
随即这个函数会调用 ReactCompositeComponent[ins].updateComponent(),这里要注意 _pendingStateQueue 这个之前初始化的队列。
updateComponent: function(
transaction,
prevParentElement,
nextParentElement,
prevUnmaskedContext,
nextUnmaskedContext,
) {
var inst = this._instance; // scr: ---------------------------> 1)
// scr: sanity check and code that is not applicable this time
...
// scr: ------------------------------------------------------> 2)
var nextState = this._processPendingState(nextProps, nextContext);
var shouldUpdate = true;
if (!this._pendingForceUpdate) {
if (inst.shouldComponentUpdate) { // scr: ------------------> 3)
shouldUpdate = inst.shouldComponentUpdate(
nextProps,
nextState,
nextContext,
);
} else {
if (this._compositeType === CompositeTypes.PureClass) {
// scr: ---------------> it is ImpureClass, not applicable
...
}
}
}
this._updateBatchNumber = null;
if (shouldUpdate) {
this._pendingForceUpdate = false;
// Will set `this.props`, `this.state` and `this.context`.
this._performComponentUpdate( // scr: --------------------> 4)
nextParentElement,
nextProps,
nextState,
nextContext,
transaction,
nextUnmaskedContext,
);
} else {
// scr: code that is not applicable this time
...
}
},
ReactCompositeComponent@renderers/shared/stack/reconciler/ReactCompositeComponent.js
1)从ReactCompositeComponent[ins]._instance 获取 外部的 ReactComponent 实例 (App);
2)用 Object.assign() 将存在 ReactCompositeComponent[ins]._pendingStateQueue 里的状态变更列表{desc:'end',color:'green'} 合并;
_processPendingState: function(props, context) {
// scr: -------> obtain the App {Figure-I}
var inst = this._instance;
var queue = this._pendingStateQueue;
// scr: code that is not applicable this time
...
var nextState =
Object.assign({}, replace ? queue[0] : inst.state);
for (var i = replace ? 1 : 0; i < queue.length; i++) {
var partial = queue[i];
Object.assign(
nextState,
typeof partial === 'function'
? partial.call(inst, nextState, props, context)
: partial,
);
}
return nextState;
},
ReactCompositeComponent@renderers/shared/stack/reconciler/ReactCompositeComponent.js
3)是一个用于性能调优的回调函数,它可以在 setState() 没有改变关键状态的情况下直接返回,从而避免后面的逻辑被执行;
其实大部分时候用不上
4)进入下一步。
_performComponentUpdate: function(
nextElement,
nextProps,
nextState,
nextContext,
transaction,
unmaskedContext,
) {
var inst = this._instance; // scr: {Figure-I}
// scr: code that is not applicable this time
...
// scr: invoke App's life cycle method if defined
if (inst.componentWillUpdate) {
inst.componentWillUpdate(nextProps, nextState, nextContext);
}
// scr: code that is not applicable this time
...
inst.state = nextState;
...
this._updateRenderedComponent(transaction, unmaskedContext);
// scr: queue App's life cycle method if defined
if (hasComponentDidUpdate) {
...
}
},
ReactCompositeComponent@renderers/shared/stack/reconciler/ReactCompositeComponent.js
这个函数仅仅将新近合并的状态赋值给 App,然后调用 this._updateRenderedComponent() 开始diffing。
至此的调用栈,
...
|~~~
|-runBatchedUpdates()
|-performUpdateIfNecessary()
|-ReactCompositeComponent[ins].performUpdateIfNecessary()
|-this.updateComponent()
|-this._processPendingState()
|-this._performComponentUpdate() ___
|-this._updateRenderedComponent() |
... diffing
Virtual DOM
在开始描述deffing之前,我们先统一下具体啥是Virtual DOM。
我先复制一下{第五篇}里的一张图:
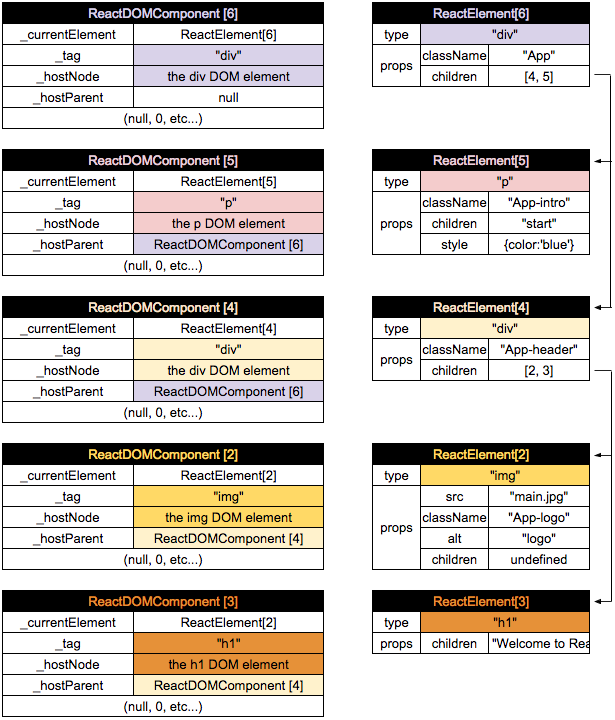
这个ReactElements 就是我们说的Virtual DOM了。{第五篇}也讨论了这个Virtual DOM树的构建过程。
用MVC的术语来说,Virtual DOM是用于存数据的modal,而ReactDOMComponents则是提供各种操作的controller
Diffing
上面那张是{第四篇}中构建的Virtual DOM树。
ctl-f “in _renderValidatedComponent()”
这次我们要基于已经变化的状态构建一个新的DOM树用于Diffing
_updateRenderedComponent: function (transaction, context) {
var prevComponentInstance = this._renderedComponent; // scr: -> 1)
// scr: ------------------------------------------------------> 2)
var prevRenderedElement = prevComponentInstance._currentElement;
// scr: create a new DOM tree
var nextRenderedElement = this._renderValidatedComponent();
var debugID = 0;
// scr: DEV code
...
if (shouldUpdateReactComponent( // scr: ----------------------> 3)
prevRenderedElement,
nextRenderedElement)
) {
ReactReconciler.receiveComponent( // scr: ------------------> 5)
prevComponentInstance,
nextRenderedElement,
transaction,
this._processChildContext(context)
);
} else { // scr: ---------------------------------------------> 4)
// scr: code that is not applicable this time
...
}
},
ReactCompositeComponent@renderers/shared/stack/reconciler/ReactCompositeComponent.js
1)从 ReactCompositeComponent[ins] 获取 ReactDOMComponent[6]{Figure-I};
2)调用 App[ins].render() 从而级连调用 React.createElement() 来创建 新的 DOM 树 {第四篇},这里唯一有区别的节点是:
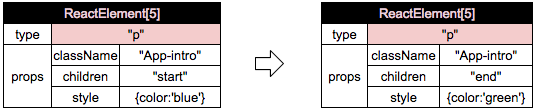
3)Diffing算法是从比较根节点类型开始的;
4)如果类型就不一样,则从头开始构建整棵树-构建过程和{第五篇}一样;
whenever the root elements have different types, React will tear down the old tree and build the new tree from scratchreactjs.org
5)如果一样,则开始DOM更新。
updateComponent: function(
transaction,
prevElement,
nextElement,
context
) {
var lastProps = prevElement.props;
var nextProps = this._currentElement.props;
// scr: code that is not applicable this time
...
// scr: ------------------------------------------------------> 1)
this._updateDOMProperties(lastProps, nextProps, transaction);
// scr: ------------------------------------------------------> 2)
this._updateDOMChildren(lastProps, nextProps, transaction, context);
// scr: code that is not applicable this time
...
},
ReactDOMComponent@renderers/dom/shared/ReactDOMComponent.js
1)从新,旧Virtual Dom中取得props(nextProps,lastProps);
2)ReactDOMComponent._updateDOMProperties() 检查新,旧props,如果不同会调用CSSPropertyOperations.setValueForStyles() 来更新DOM;
3)ReactDOMComponent._updateDOMChildren() 检查新,旧 DOM的content (text, inner HTML),如果不一样会调用ReactDOMComponent.updateTextContent() 来更新DOM;
静态调用栈:
... ___
ReactReconciler.receiveComponent() <----------------| |
|-ReactDOMComponent.receiveComponent() | |
|-this.updateComponent() | |
|-this._updateDOMProperties() | diffing
|-CSSPropertyOperations.setValueForStyles() | |
|-this._updateDOMChildren() | |
|-this.updateTextContent() | |
|-recursing children (not the focus this time) --| |
---
简单观察一下这个调用栈,不难发现这个递归的规律,
1)每一次递归会更新一个Virtual DOM;
2)ReactDOMComponent.updateDOMChildren() 也负责遍历当前Virtual DOM的所有子节点,并且会对每个节点重启这个递归。
但是子DOM遍历并不在本文讨论范围内
把上面的几个函数压缩下,
|-ReactReconciler.receiveComponent()
|-ReactDOMComponent[n].receiveComponent()
|-this.updateComponent()
=>
|-ReactDOMComponent[n].updateComponent()
则可以得到如下的调用栈:
...
|-ReactDOMComponent[6].updateComponent()
|-this._updateDOMProperties() // scr: ----> same
|-this._updateDOMChildren
|-recursing children (not the focus this time...)
|-ReactDOMComponent[4].updateComponent()
|-this._updateDOMProperties() // scr: ----> same
|-this._updateDOMChildren
|-recursing children (not the focus this time...)
|-ReactDOMComponent[2].updateComponent()
|-this._updateDOMProperties() // scr: ----> same
|-this._updateDOMChildren // scr: ----> same
|-ReactDOMComponent[3].updateComponent()
|-this._updateDOMProperties() // scr: ----> same
|-this._updateDOMChildren // scr: ----> same
|-ReactDOMComponent[5].updateComponent()
|-this._updateDOMProperties()
|-CSSPropertyOperations.setValueForStyles()
|-this._updateDOMChildren
|-this.updateTextContent()
ReactDOMComponent._updateDOMProperties() —检查props有没有变
这个也是我们在{第三篇 *6}中有意遗漏的一个函数
本篇中,我们重点看STYLE相关的操作。
_updateDOMProperties: function(lastProps, nextProps, transaction) {
var propKey;
var styleName;
var styleUpdates;
// scr: --------------------------------------------------------> 1)
for (propKey in lastProps) {
if (
nextProps.hasOwnProperty(propKey) ||
!lastProps.hasOwnProperty(propKey) ||
lastProps[propKey] == null
) {
continue;
}
if (propKey === STYLE) {
var lastStyle = this._previousStyleCopy;
for (styleName in lastStyle) {
if (lastStyle.hasOwnProperty(styleName)) {
styleUpdates = styleUpdates || {};
styleUpdates[styleName] = '';
}
}
this._previousStyleCopy = null;
} else if ... {
// scr: not the focus this time
...
}
}
// scr: ----------------------------------------------------> end 1)
for (propKey in nextProps) {
var nextProp = nextProps[propKey];
var lastProp = propKey === STYLE
? this._previousStyleCopy
: lastProps != null ? lastProps[propKey] : undefined;
if (
!nextProps.hasOwnProperty(propKey) ||
nextProp === lastProp ||
(nextProp == null && lastProp == null)
) {
continue;
}
if (propKey === STYLE) {
if (nextProp) {
// scr: DEV code
...
// scr: -------------------------------------------------> 2)
nextProp = this._previousStyleCopy = Object.assign({}, nextProp);
} else {
this._previousStyleCopy = null;
}
if (lastProp) { // scr: ----------------------------------> 3)
// scr: the comment applies here -----------------------> a)
// Unset styles on `lastProp` but not on `nextProp`.
for (styleName in lastProp) {
if (
lastProp.hasOwnProperty(styleName) &&
(!nextProp || !nextProp.hasOwnProperty(styleName))
) {
styleUpdates = styleUpdates || {};
styleUpdates[styleName] = '';
}
}
// scr: the comment applies here -----------------------> b)
// Update styles that changed since `lastProp`.
for (styleName in nextProp) {
if (
nextProp.hasOwnProperty(styleName) &&
lastProp[styleName] !== nextProp[styleName]
) {
styleUpdates = styleUpdates || {};
styleUpdates[styleName] = nextProp[styleName];
}
}
} else { // scr: -----------------------------------------> 4)
// Relies on `updateStylesByID` not mutating `styleUpdates`.
styleUpdates = nextProp;
}
} else if (...) {
// scr: DEV code
...
}
}
if (styleUpdates) { // scr: ----------------------------------> 5)
CSSPropertyOperations.setValueForStyles(
getNode(this),
styleUpdates,
this,
);
}
},
ReactDOMComponent@renderers/dom/shared/ReactDOMComponent.js
1)如果新props中不存在“style”,
...
if (nextProps.hasOwnProperty(propKey) ||...) {
continue;
} // scr: else, do something
...
将所有的既存style条目标记为‘删除’,注意既存的style条目是在第2)步存在this._previousStyleCopy 里的;
2)将 nextProp (当前的styles)拷贝至 this._previousStyleCopy;
3)如果有既存的styles,
var lastProp = propKey === STYLE
? this._previousStyleCopy
...
if (lastProp) {
...
更新。a)将所有不存在于 nextProp 的既存style条目标记为“删除”,b)将所有nextProp 中区别于既存条目的标记为“添加”;
4)如果没有既存style,则将所有nextProp的条目标记为“添加”;
5)进行实际的DOM操作。注意 getNode() 是 ReactDOMComponentTree.getNodeFromInstance() 的一个别名,这个方法用来从ReactDOMComponent._hostNode 获取对应的DOM元素 {FIgure-III}{第三篇}。
ctl-f “ReactDOMComponent[ins]._hostNode”
CSSPropertyOperations.setValueForStyles() —更新 props
setValueForStyles: function(node, styles, component) {
var style = node.style;
for (var styleName in styles) {
if (!styles.hasOwnProperty(styleName)) {
continue;
}
// scr: DEV code or code that is not applicable
...
if (isCustomProperty) {
...
} else if (styleValue) {
style[styleName] = styleValue;
} else {
code that is not applicable this time
...
}
}
},
CSSPropertyOperations@renderers/dom/shared/CSSPropertyOperations.js
这里唯一一行有效代码是 style[styleName] = styleValue;。
所以,这里条调用栈的底牌是,Node.style[‘color’] = ‘red’。
_updateDOMChildren —检查内容有没有变(并且遍历子节点)
这里我们忽略 dangerouslySetInnerHTML 相关代码,主要看关键路径
_updateDOMChildren: function(
lastProps,
nextProps,
transaction,
context
) {
var lastContent = CONTENT_TYPES[typeof lastProps.children]
? lastProps.children
: null;
var nextContent = CONTENT_TYPES[typeof nextProps.children]
? nextProps.children
: null;
// scr: code that is not applicable
...
// Note the use of `!=` which checks for null or undefined.
// scr: used by recursing children, to be continued...
var lastChildren = lastContent != null ? null : lastProps.children;
var nextChildren = nextContent != null ? null : nextProps.children;
// scr: code that is not applicable
...
if (lastChildren != null && nextChildren == null) {
// scr: recursing children, to be continued...
this.updateChildren(null, transaction, context);
} else if (lastHasContentOrHtml && !nextHasContentOrHtml) {
// scr: DEV code and code that is not applicable
...
}
if (nextContent != null) {
if (lastContent !== nextContent) {
this.updateTextContent('' + nextContent);
// scr: DEV code
...
}
} else if (nextHtml != null) {
// scr: code that is not applicable
...
} else if (nextChildren != null) {
// scr: DEV code
...
// scr: recursing children, to be continued...
this.updateChildren(nextChildren, transaction, context);
}
},
ReactDOMComponent@renderers/dom/shared/ReactDOMComponent.js
这里唯一一行有效代码是
this.updateTextContent(‘’ + nextContent);
ReactDOMComponent.updateTextContent() —更新内容
这个函数的预期功能是将字符串从'start'更新成'end'。对于这个简单操作来说,调用栈有点深了。。。我们继续看。
updateTextContent: function(nextContent) {
var prevChildren = this._renderedChildren;
// Remove any rendered children. scr: -------> the comment applies
ReactChildReconciler.unmountChildren(prevChildren, false);
for (var name in prevChildren) {
// scr: sanity check
...
}
// Set new text content. scr: ---------------> the comment applies
var updates = [makeTextContent(nextContent)];
processQueue(this, updates);
},
function processQueue(inst, updateQueue) {
ReactComponentEnvironment.processChildrenUpdates(inst, updateQueue);
}
ReactMultiChild@renderers/shared/stack/reconciler/ReactMultiChild.js
这里的 ReactComponentEnvironment 实际是 ReactComponentBrowserEnvironment (通过注入赋值)。
...
processChildrenUpdates:
ReactDOMIDOperations.dangerouslyProcessChildrenUpdates,
...
ReactComponentBrowserEnvironment@renderers/dom/shared/ReactComponentBrowserEnvironment.js
然后.processChildrenUpdates则是 ReactDOMIDOperations.dangerouslyProcessChildrenUpdates 的一个别名
dangerouslyProcessChildrenUpdates: function(parentInst, updates) {
var node = ReactDOMComponentTree.getNodeFromInstance(parentInst);
DOMChildrenOperations.processUpdates(node, updates);
},
ReactDOMIDOperations@renderers/dom/client/ReactDOMIDOperations.js
ReactDOMComponentTree.getNodeFromInstance() 这个函数上一节刚讨论过 processUpdates: function(parentNode, updates) {
// scr: DEV code
...
for (var k = 0; k < updates.length; k++) {
var update = updates[k];
switch (update.type) {
// scr: code that is not applicable
...
case 'TEXT_CONTENT':
setTextContent(parentNode, update.content);
// scr: DEV code
...
break;
...
DOMChildrenOperations@renderers/dom/client/utils/DOMChildrenOperations.js
这个调用栈的底牌是setTextContent() {第五篇},用于直接操作 Node.textContent,符合预期。
ReactDOMComponent.updateTextContent() 的子调用栈:
|-ReactDOMComponent.updateTextContent()
|-processQueue()
|-ReactComponentEnvironment.processChildrenUpdates()
|=ReactDOMIDOperations.dangerouslyProcessChildrenUpdates()
|-ReactDOMComponentTree.getNodeFromInstance()
|-DOMChildrenOperations.processUpdates()
|-setTextContent()
|-Node.textContent = 'end'
下一篇我们会通过观察virtual DOM树变形来进一步解析Diffing算法,并完结本连载。希望您下次使用setState() 时能够更加得❤️应
感谢阅读!🐶年快乐
Originally published at holmeshe.me.