作者: 一字马胡
转载标志 【2017-11-03】
更新日志
| 日期 | 更新内容 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| 2017-11-03 | 新建文章 | 初版 |
初识GraphQL
GraphQL是一种强大的DSQL,是由Facebook开源的一种用于提供数据查询服务的抽象框架,在服务端API开发中,很多时候定义一个接口返回的数据相对固定的,如果想要获取更多的信息,或者仅需要某个接口的某个信息的时候,基于restful API的接口就显得不那么灵活了,对于这些需求,服务端要么再定义一个新的接口,返回合适的数据,要么客户端就得通过一个庞大的接口来获取一小部分信息,GraphQL的出现就是为了解决这些问题的,GraphQL并不是一门具体的语言实现的某种框架,它是一系列协议文档组成的项目,GraphQL是和语言无关的,而且到现在为止已经有很多语言的实现版本,可以在 awesome-graphql看到哪些语言实现了GraphQL,如果想要了解具体的GraphQL定义,可以参考graphql。本文以及本GraphQL系列将只关心Java版本的GraphQL实现,具体的Java版本的GraphQL可以参考graphql-java。下面是官方对GraphQL的描述,很简洁,但是很直观:
GraphQL is a query language for APIs and a runtime for fulfilling those queries with your existing data.
下面的图片展示了GraphQL的工作模型:
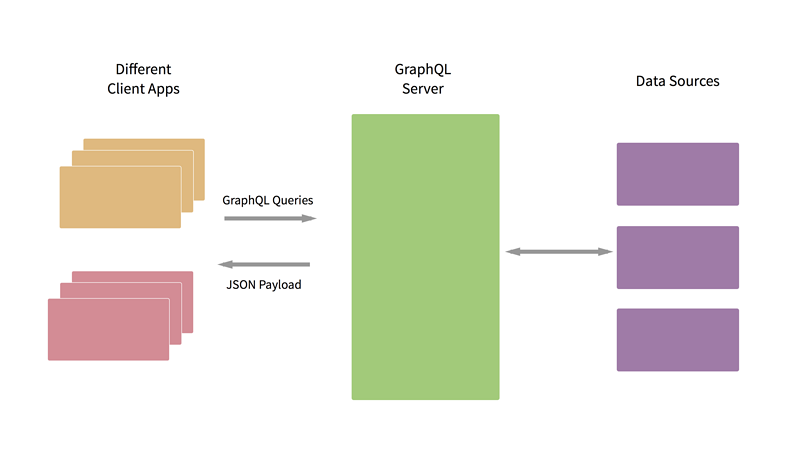
从这张图片可以看出,GraphQL的位置处于Client和DataSource之间,可以把这一层理解为服务端的API层,所谓API层,就是聚合多个数据源,进行一些业务逻辑的处理,然后提供一些接口给Client调用。而GraphQL就工作在这一层,它相当于是对DataSource的一层抽象,它可以承接Client的请求,然后根据GraphQL的执行引擎来从DataSource获取数据,然后进行处理之后返回json结果给Client,这和Restful的模式没有什么差别,但是GraphQL的强大之处在于GraphQL类似于MySql,Client发送的请求类似于Sql语句,这些Sql语句经过GraphQL解析执行之后返回具体的数据,所以GraphQL具有很好的动态性,Client可以根据不同的需求来使用不同的Sql语句来请求服务端,而GraphQL会解析这些Sql,并且精准的返回结果。这就完美的解决了文章开头提到的难题。使用GraphQL来做服务端API层的开发无疑会减轻服务端开发工程师的很多压力,而且对于Client来说也是很友好的,因为Client不需要想请求Restful接口一样只能获取相对固定的数据,Client可以根据自己的需求使用不同的查询语句来请求GraphQL,使用GraphQL会减少很多冗余的数据传输,并且可以减少很多服务端API层的接口开发工作,API层只需要开发GraphQL服务端,然后告诉Client这些数据的组织结构,然后Client就可以组装出合适的查询语句来请求数据。使用GraphQL进一步将前后端分离(Restful使得前后端分离),后端开发和前端开发可以各自进行,使用GraphQL很多时候服务端是在丰富可以提供的数据,或者优化聚合DataSource来提高响应速度。使用GraphQL还有很多优点,可以研究GraphQL并且使用GraphQL来开发服务端API来体验。本文剩下的内容将基于GraphQL-Java和Spring-boot来实现一个简单的应用,以此来说明使用GraphQL的方法以及使用GraphQL的优势。
需要补充的一点是,上面提到了GraphQL查询语句(上文使用了Sql代替,但不是Sql),这是一种类似于json的结构化数据,可以很轻易的理解它的本意,这也是GraphQL的一个优点,它的查询语句对工程师是很友好的。下文会分析到。
GraphQL 实战
本GraphQL系列的文章基于Java语言以及GraphQL-Java来分析,这一点注意一下。本文的GraphQL示例使用Spring-boot来开发,使用的IDE为idea 17,强烈建议Javaer使用IDEA来开发,可以明显提高开发效率。
为了可以快速上手,下面展示了本文使用的示例的代码结构:
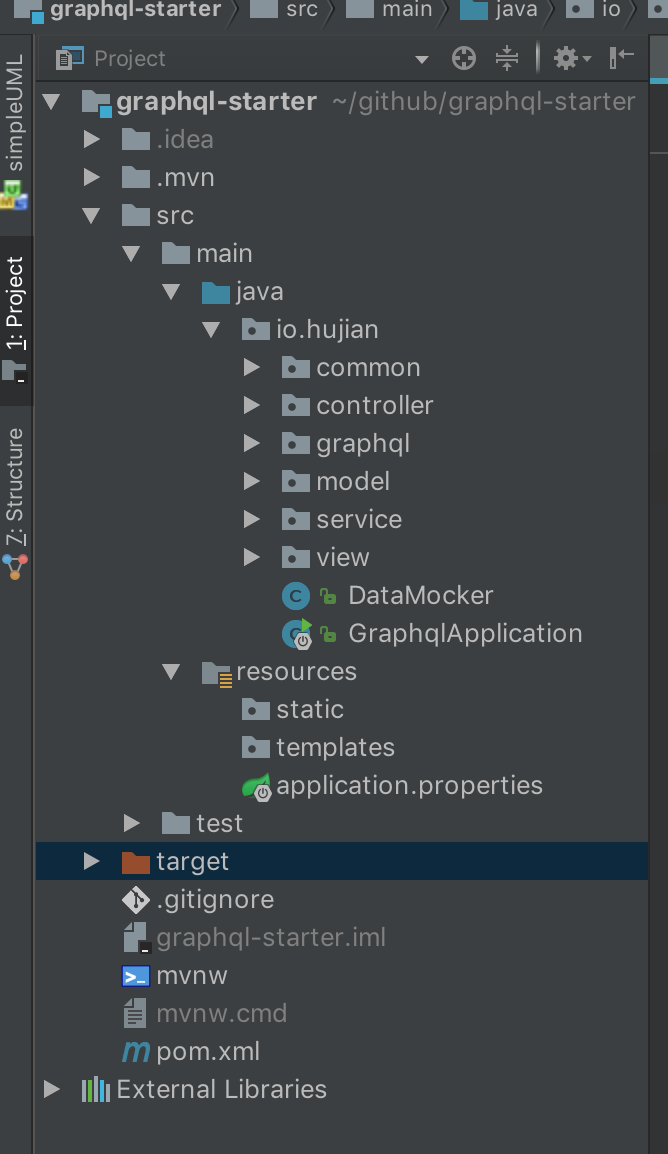
可以根据各个包名来理解这个包管理的类,比如service管理的是一系列service,而view包下是一些需要返回给Client的渲染View。关于如何新建一个Spring-boot项目的过程不再本文的叙述范围之内(唯一说明的一点是,需要Web模块支持),下面根据一些关键步骤来引导如何实现一个GraphQL demo。
创建Model类
这一步很简单,将你需要创建的Model类放到model包下,比如本文的示例想要实现的一个场景是,有一些作者,每个作者可能写了多篇文章,每篇文章都只有一个作者,而每篇文章下面可能没有评论,或者有评论,评论的数量不限,下面是几个关键的类信息:
public class AuthorModel {
private int authorId; // the author id
private int authorAge; // the age
private int authorLevel; // the level
private String authorAddr; // the address
private List<Integer> friends; // the friends of the author
}
public class ContentModel {
private int contentId; // the content id
private int authorId; // the author id
private int commentSize; // the comment size of this content
private String text; // the text
private List<Integer> commentIds; // the Comment id list
}
public class CommentModel {
private int commentId; // the comment id
private int authorId; // the author of this comment
private int ofContentId; // the content id
private String content; // the content of this comment
}
为了实验GraphQL的复杂查询,下面是两个增强类,分别是对AuthorModel类和ContentModel类的增强,可以看到增强之后的类更符合我们的想法:
public class CompletableAuthorModel extends AuthorModel{
private List<AuthorModel> friendsCompletableInfo;
private List<CompletableContentModel> contentModelList;
}
public class CompletableContentModel extends ContentModel{
private List<CommentModel> commentModelList; // the comment info list of this content
}
本文展示的所有代码都可以在github上找到源码,所以本文就不完整的展示所有代码了。
Mock数据
为了测试GraphQL,你需要有一些数据,本文为了快速测试GraphQL,所以Mock的数据比较简单,没有和数据库交互,其实在真实的服务端API层开发中,很多时候是不需要和数据库交互的,更多的是使用RPC来从一些微服务中获取我们需要的数据,一个RPC服务其实就是一个数据源,API层的工作就是在聚合这些数据源,然后进行一些业务逻辑的处理,来提供接口供Client访问。具体的Mock代码可以在DataMock这个类中找到。
当然,有了数据源之后还需要进行一些业务逻辑的处理,本文使用一些Service来模拟这种处理,主要做的其实是将Author、Content以及Comment这三个Model联系起来,很好理解。
定义GraphQLOutputType
现在,你以及定义好了Model类了,并且已经有数据和业务逻辑处理程序了,下面就来定义一些GraphQLOutputType,这些GraphQLOutputType就是服务端可以提供的输出,你可以提供什么样的输出就怎么定义,下面首先展示的是AuthorModel这个GraphQLOutputType,然后展示了它的增强输出CompletableAuthor,可以作为参考:
/* basic outPutType */
private GraphQLOutputType author;
/* richness & completable outPutType */
private GraphQLOutputType completableAuthor;
/* The Author */
author = newObject().name("AuthorModel")
.field(GraphQLFieldDefinition.newFieldDefinition().name("authorId").type(Scalars.GraphQLInt))
.field(GraphQLFieldDefinition.newFieldDefinition().name("authorAge").type(Scalars.GraphQLInt))
.field(GraphQLFieldDefinition.newFieldDefinition().name("authorLevel").type(Scalars.GraphQLInt))
.field(GraphQLFieldDefinition.newFieldDefinition().name("authorAddr").type(Scalars.GraphQLString))
.field(GraphQLFieldDefinition.newFieldDefinition().name("friends").type(GraphQLList.list(Scalars.GraphQLInt)))
.build();
/* the completable author information */
completableAuthor = newObject().name("CompletableAuthor")
.field(GraphQLFieldDefinition.newFieldDefinition().name("authorId").type(Scalars.GraphQLInt))
.field(GraphQLFieldDefinition.newFieldDefinition().name("authorAge").type(Scalars.GraphQLInt))
.field(GraphQLFieldDefinition.newFieldDefinition().name("authorLevel").type(Scalars.GraphQLInt))
.field(GraphQLFieldDefinition.newFieldDefinition().name("authorAddr").type(Scalars.GraphQLString))
.field(GraphQLFieldDefinition.newFieldDefinition().name("friends").type(GraphQLList.list(Scalars.GraphQLInt)))
.field(GraphQLFieldDefinition.newFieldDefinition().name("friendsCompletableInfo").type(GraphQLList.list(author)))
.field(GraphQLFieldDefinition.newFieldDefinition().name("contentModelList").type(GraphQLList.list(completableContent)))
.build();
完整的GraphQLOutputType定义可以参考项目(文章结尾)。上面有很多类似于“. type”的操作,GraphQL提供了很多类型,可以与各种语言中的类型系统进行对接,比如Scalars.GraphQLInt可以和Java中的Integer对接,而Scalars.GraphQLString和Java中的String对接,GraphQL除了支持这种Scalars类型外,还支持GraphList、Objects、以及Interfaces、Unions、Enums等,完整的类型系统可以参考文章 GraphQL Type System,本文仅使用到了Scalars和GraphList。
定义Schema
定义好了一些GraphQLOutputType之后,就可以来定义GraphQL的Schema了,下面是本文使用的示例的Schema定义:
/* set up the schema */
schema = GraphQLSchema.newSchema()
.query(newObject()
.name("graphqlQuery")
.field(createAuthorField())
.field(createContentField())
.field(createCommentField())
.field(createCompletableContentField())
.field(createCompletableAuthorField()))
.build();
/**
* query single author
* @return the single author's information
*/
private GraphQLFieldDefinition createAuthorField() {
return GraphQLFieldDefinition.newFieldDefinition()
.name("author")
.argument(newArgument().name("authorId").type(Scalars.GraphQLInt).build())
.type(author)
.dataFetcher((DataFetchingEnvironment environment) -> {
//get the author id here
int authorId = environment.getArgument("authorId");
return this.authorService.getAuthorByAuthorId(authorId);
}).build();
}
/**
* completable author information
* @return the author
*/
private GraphQLFieldDefinition createCompletableAuthorField() {
return GraphQLFieldDefinition.newFieldDefinition()
.name("completableAuthor")
.argument(newArgument().name("authorId").type(Scalars.GraphQLInt).build())
.type(completableAuthor)
.dataFetcher((DataFetchingEnvironment environment) -> {
int authorId = environment.getArgument("authorId");
//get the completable info of author by authorId
//System.out.println("request for createCompletableAuthorField:" + authorId);
return authorService.getCompletableAuthorByAuthorId(authorId);
}).build();
}
上面只展示了author和completableAuthor两个GraphQLFieldDefinition的定义,服务端实际的聚合数据源的操作就需要写在这些GraphQLFieldDefinition里面,每个GraphQLFieldDefinition类似于一个服务端的API集合,并且它可以有一些入参,相当于restful的参数,你需要根据这些参数聚合DataSource来返回合适的数据。
提供查询接口
下面的代码展示了使用GraphQl来承接Client的查询请求的方法:
package io.hujian.graphql;
import graphql.GraphQL;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* Created by hujian06 on 2017/11/2.
*
* the facade of the graphQl
*/
public class GraphqlFacade {
private static final GraphqlProvider PROVIDER = new GraphqlProvider();
private static final GraphQL GRAPH_QL = GraphQL.newGraphQL(PROVIDER.getSchema()).build();
/**
* query by the Graphql
* @param ghql the query
* @return the result
*/
public static Map<String, Object> query(String ghql) {
if (ghql == null || ghql.isEmpty()) {
return Collections.emptyMap();
}
return GRAPH_QL.execute(ghql).getData();
}
}
提供接口
为了测试GraphQL,需要提供一个查询接口,下面的代码展示了如何使用Spring-boot来提供接口的方法:
package io.hujian.controller;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import io.hujian.graphql.GraphqlFacade;
import io.hujian.view.CheckView;
import io.hujian.view.MockerDataView;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* Created by hujian06 on 2017/11/2.
*
* the graphql controller
*/
@Controller
@RequestMapping(value = "dsql/api/")
public class GraphqlController {
/**
* query the hsql by the graphql
* @param ghql the query string like:->
* "{
* author(authorId:2)
* {
* authorId,
* authorAge,
* authorAddr,
* friends
* }
* }"
* the response like:->
* "{
* "author": {
* "authorId": 2,
* "authorAge": 32,
* "authorAddr": "Ty-0021",
* "friends": [1]
* }
* }"
*
* @param request r
* @param response r
* @throws IOException e
*/
@RequestMapping(value = "query/{ghql}")
public void graphqlQuery(@PathVariable("ghql") String ghql, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws IOException {
String result = JSON.toJSONString(GraphqlFacade.query(ghql));
System.out.println("request query:" + ghql + " \nresult:" + result);
//query the result.
response.getOutputStream().write(result.getBytes());
}
}
现在就可以来测试GraphQL是否可以正常工作了,先来一个简单的测试,比如,我们想要查询id为1的Author的信息,但是只想要知道AuthorAge以及AuthorLevel两个信息,查询的具体语句如下:
{
author(authorId:1) {
authorAge,
authorLevel
}
}
相应的查询结果如下:
{
"author": {
"authorAge": 24,
"authorLevel": 10
}
}
现在需求变了,Client不仅想要获取作者的年龄和级别,还想要知道作者的地址,那么服务端不需要改变任何内容,Client只需要改变Query就可以,新的Query为:
{
author(authorId:1) {
authorAge,
authorLevel,
authorAddr
}
}
这次查询的返回内容如下:
{
"author": {
"authorAge": 24,
"authorLevel": 10,
"authorAddr": "Fib-301"
}
}
为了说明GraphQL的强大,下面提供一个较为丰富复杂的查询以及其输出内容,首先展示了请求的响应内容:
{
"completableAuthor": {
"authorId": 1,
"authorLevel": 10,
"authorAge": 24,
"authorAddr": "Fib-301",
"friends": [
2,
3
],
"contentModelList": [
{
"contentId": 1,
"authorId": 1,
"text": "This is a test content!",
"commentModelList": [
{
"commentId": 2,
"authorId": 1,
"content": "i thing so."
}
]
}
],
"friendsCompletableInfo": [
{
"authorId": 2,
"authorAge": 32,
"authorLevel": 4,
"friends": [
1
]
},
{
"authorId": 3,
"authorAge": 14,
"authorLevel": 2,
"friends": [
2
]
}
]
}
}
对应的请求为:
{
completableAuthor(authorId:1) {
authorId,
authorLevel,
authorAge,
authorAddr,
friends,
contentModelList {
contentId,
authorId,
text,
commentModelList {
commentId,
authorId,
content
}
},
friendsCompletableInfo {
authorId,
authorAge,
authorLevel,
friends
}
}
}
结语
GraphQL不仅支持Query,还支持写操作,但是考虑到服务端API大部分的内容时聚合数据源而不是写数据,所以本文没有涉及相应的内容,但是后续的GraphQL系列中将会涉及GraphQL的所有支持的操作,并且分析这些操作的具体实现细节,最后,分享出本文涉及的项目的工程地址,如果不出意外,可以成功执行,注意设置application.properties,比如日志输出级别,服务器启动端口等,本文的项目的启动端口为8600,所以,如果你想要进行试验的话,需要在启动了项目之后再浏览器输入下面的地址:
http://127.0.0.1:8080/dsql/api/query/{your_query}
项目地址:GraphQL-Starter