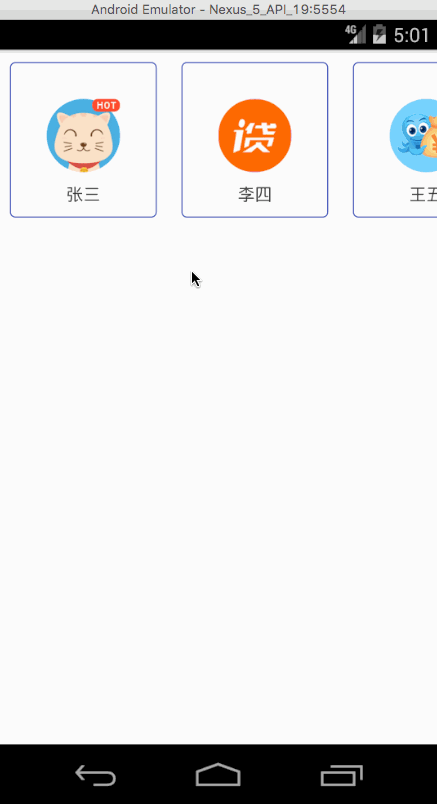
序言:最近接到一个任务,做一个类似上面自动翻页的功能。可以看到,这一屏中有三张图片显示出来了,有两张没有显示完全,看到设计图的时候第一反应是可以用viewpager来实现,但是任务却跟你开了一个天大的玩笑,要求是以最左边的图片为基准,也就是说,左边的图片也得显示完全,就像下图所示,后来仔细想想viewpager好像没有这样的功能,也有可能是我不知道,我也没有找到这样的文章或者信息,希望知道的简友私戳交流一下,感激不尽,好了,言归正传
在开始之前呢,首先介绍一个Google最新(其实在24.2.0版本的时候就已经发布了)发布的一个东西SnapHelper,这玩意儿是对RecyclerView功能的一个拓展,有兴趣的同学可以去看看它的源码,SnapHelper的实现原理是监听RecyclerView.OnFlingListener中的onFling接口,可以使RecyclerView实现类似ViewPager的功能,无论怎么滑动最终停留在某页正中间,那它和ViewPager的区别是什么呢?就是ViewPager不能一次连续滑动多张图片,而且不能定制(停在左边,还是停在右边)。下面我们一起来看看吧!
首先导入所需要的包,最低版本是v7-24.2.0,低了就没有这个类了:
compile 'com.android.support:appcompat-v7:24.2.0'
compile 'com.android.support:recyclerview-v7:24.2.0'这里系统自带有一个类LinearSnapHelper,LinearSnapHelper继承自SnapHelper,这个默认是让视图停在中间的,你只需要将RecyclerView和LinearSnapHelper绑定在一起就行了:
LinearSnapHelper mLinearSnapHelper = new LinearSnapHelper();
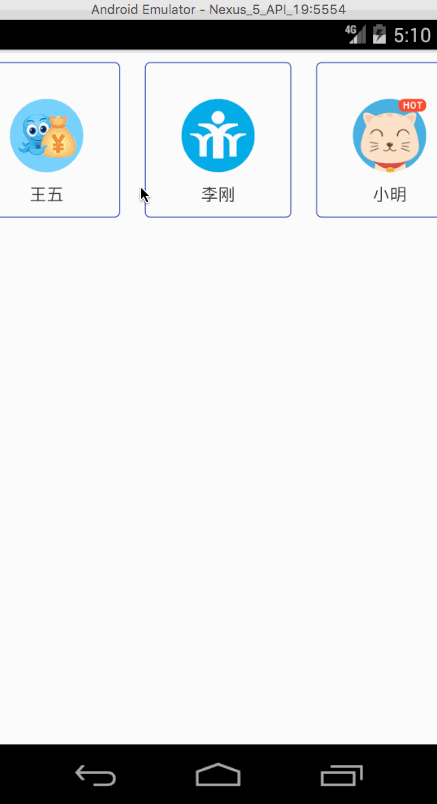
mLinearSnapHelper.attachToRecyclerView(mRecyclerview);效果如下:
当然了,SnapHelper的功能绝不仅仅在此,你还可以定制化,让他停在左边,或者右边,而你不需要重新继承SnapHelper,直接继承LinearSnapHelper就可以了,这里面有很多写好的方法,然后你再重写里面的两个方法:
(1)、calculateDistanceToFinalSnap:当拖拽或滑动结束时会回调该方法,返回一个out = int[2],out[0]x轴,out[1] y轴 ,这个值就是需要修正的你需要的位置的偏移量。
(2)、findSnapView:这个方法用来获取特定的视图,当返回null时,表示没有获取到任何视图 。
完整的代码:
public class LeftSnapHelper extends LinearSnapHelper {
private OrientationHelper mHorizontalHelper;
/**
* 当拖拽或滑动结束时会回调该方法,该方法返回的是一个长度为2的数组,out[0]表示横轴,x[1]表示纵轴,这两个值就是你需要修正的位置的偏移量
*
* @param layoutManager
* @param targetView
* @return
*/
@Override
public int[] calculateDistanceToFinalSnap(RecyclerView.LayoutManager layoutManager, View targetView) {
//注:由于是横向滚动,在这里我们只考虑横轴的值
int[] out = new int[2];
if (layoutManager.canScrollHorizontally()) {
out[0] = distanceToStart(targetView, getHorizontalHelper(layoutManager));
} else {
out[0] = 0;
}
return out;
}
/**
* 这个方法是计算偏移量
*
* @param targetView
* @param helper
* @return
*/
private int distanceToStart(View targetView, OrientationHelper helper) {
return helper.getDecoratedStart(targetView) - helper.getStartAfterPadding();
}
@Override
public View findSnapView(RecyclerView.LayoutManager layoutManager) {
return findStartView(layoutManager, getHorizontalHelper(layoutManager));
}
/**
* 找到第一个显示的view
* @param layoutManager
* @param helper
* @return
*/
private View findStartView(RecyclerView.LayoutManager layoutManager,
OrientationHelper helper) {
if (layoutManager instanceof LinearLayoutManager) {
int firstChild = ((LinearLayoutManager) layoutManager).findFirstVisibleItemPosition();
int lastChild = ((LinearLayoutManager) layoutManager).findLastVisibleItemPosition();
if (firstChild == RecyclerView.NO_POSITION) {
return null;
}
//这是为了解决当翻到最后一页的时候,最后一个Item不能完整显示的问题
if (lastChild == layoutManager.getItemCount() - 1) {
return layoutManager.findViewByPosition(lastChild);
}
View child = layoutManager.findViewByPosition(firstChild);
//得到此时需要左对齐显示的条目
if (helper.getDecoratedEnd(child) >= helper.getDecoratedMeasurement(child) / 2
&& helper.getDecoratedEnd(child) > 0) {
return child;
} else {
return layoutManager.findViewByPosition(firstChild + 1);
}
}
return super.findSnapView(layoutManager);
}
/**
* 获取视图的方向
*
* @param layoutManager
* @return
*/
private OrientationHelper getHorizontalHelper(@NonNull RecyclerView.LayoutManager layoutManager) {
if (mHorizontalHelper == null) {
mHorizontalHelper = OrientationHelper.createHorizontalHelper(layoutManager);
}
return mHorizontalHelper;
}
}当然了,你也可以让它停在右边:只需要在上面的基础上修改findSnapView方法即可:
public class RightSnapHelper extends LinearSnapHelper {
private OrientationHelper mHorizontalHelper;
/**
* 当拖拽或滑动结束时会回调该方法,该方法返回的是一个长度为2的数组,out[0]表示横轴,x[1]表示纵轴,这两个值就是你需要修正的位置的偏移量
*
* @param layoutManager
* @param targetView
* @return
*/
@Override
public int[] calculateDistanceToFinalSnap(RecyclerView.LayoutManager layoutManager, View targetView) {
//注:由于是横向滚动,在这里我们只考虑横轴的值
int[] out = new int[2];
if (layoutManager.canScrollHorizontally()) {
out[0] = distanceToEnd(targetView, getHorizontalHelper(layoutManager));
} else {
out[0] = 0;
}
return out;
}
/**
* 这个方法是计算偏移量
*
* @param targetView
* @param helper
* @return
*/
private int distanceToEnd(View targetView, OrientationHelper helper) {
return helper.getDecoratedEnd(targetView) - helper.getEndAfterPadding();
}
@Override
public View findSnapView(RecyclerView.LayoutManager layoutManager) {
return findEndView(layoutManager, getHorizontalHelper(layoutManager));
}
/**
* 找到第一个显示的view
*
* @param layoutManager
* @param helper
* @return
*/
private View findEndView(RecyclerView.LayoutManager layoutManager, OrientationHelper helper) {
if (layoutManager instanceof LinearLayoutManager) {
int lastChild = ((LinearLayoutManager) layoutManager).findLastVisibleItemPosition();
if (lastChild == RecyclerView.NO_POSITION) {
return null;
}
View child = layoutManager.findViewByPosition(lastChild);
//得到此时需要右对齐显示的条目
if (helper.getDecoratedStart(child) >= helper.getDecoratedMeasurement(child) / 2
&& helper.getDecoratedStart(child) > 0) {
return child;
} else {
return layoutManager.findViewByPosition(lastChild - 1);
}
}
return super.findSnapView(layoutManager);
}
/**
* 获取视图的方向
*
* @param layoutManager
* @return
*/
private OrientationHelper getHorizontalHelper(@NonNull RecyclerView.LayoutManager layoutManager) {
if (mHorizontalHelper == null) {
mHorizontalHelper = OrientationHelper.createHorizontalHelper(layoutManager);
}
return mHorizontalHelper;
}
}效果:

那如何让它能无限的滑动呢?
这个当然是要在Adapter里面“做手脚”了,让获取Item总数的方法返回Integer.MAX_VALUE就可以了:
@Override
public int getItemCount() {
return Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}然后在onBindViewHolder中获取list中的值时相应的取余就好了:
@Override
public void onBindViewHolder(RecyclerViewHolder holder, int position) {
Glide.with(mContext).load(mList.get(position % mList.size())
.getImageUrl()).placeholder(R.mipmap.ic_launcher)
.into(holder.ivImage);
holder.tvName.setText(mList.get(position % mList.size()).getName());
}好了,做到这里就完成了80%了,接下来我们要让它能够自动滚动,如何能自动滚动呢?这里可以参考一下ViewPager中自动滚动的效果,这里LZ使用的是Timer来实现,Timer有一个每隔多长时间执行一次的功能,在这里正好:
private int cnt = 2; //表示当前最右边显示的item的position
private boolean isSlidingByHand = false; //表示是否是手在滑动
private boolean isSlidingAuto = true; //表示是否自动滑动
timer.schedule(new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run() {
if (isSlidingAuto) {
myHandler.sendEmptyMessage(CHANGE_ITEM);
}
}
}, 1000, 3000);考虑到这里有两种滑动,一种是用户手动的滑动,另一种是我们的Timer来出发滑动,我们还得对RecyclerView设置监听,来简单判断一下是用户触发的还是Timer触发的:
alRecyclerview.addOnScrollListener(new RecyclerView.OnScrollListener() {
@Override
public void onScrollStateChanged(RecyclerView recyclerView, int newState) {
LinearLayoutManager manager = (LinearLayoutManager) recyclerView.getLayoutManager();
int firstVisibleItemPosition = manager.findFirstVisibleItemPosition();
switch (newState) {
case SCROLL_STATE_IDLE: //(静止没有滚动)
if (isSlidingByHand) {
Message msg = myHandler.obtainMessage();
msg.arg1 = firstVisibleItemPosition;
msg.what = CHANGE_ITEM;
myHandler.sendMessage(msg);
}
break;
case SCROLL_STATE_DRAGGING: //(正在被外部拖拽,一般为用户正在用手指滚动)
isSlidingByHand = true;
isSlidingAuto = false;
break;
case SCROLL_STATE_SETTLING: //(自动滚动)
if (isSlidingByHand) {
isSlidingAuto = false;
} else {
isSlidingAuto = true;
}
break;
}
}
});最后的处理结果当然是交给Handler来了:
private static class MyHandler extends Handler {
//采用弱引用的方式,防止内存泄漏
WeakReference<CenterActivity> weakReference;
public MyHandler(CenterActivity mActivity) {
this.weakReference = new WeakReference<>(mActivity);
}
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
final CenterActivity mActivity = weakReference.get();
Log.d(TAG, "handleMessage: " + "handler is running");
if (mActivity.isSlidingByHand) {
mActivity.cnt = msg.arg1;
mActivity.isSlidingByHand = false;
mActivity.isSlidingAuto = true;
mActivity.cnt+=2;
//让RecyclerView平滑的滚动
mActivity.alRecyclerview.smoothScrollToPosition(++mActivity.cnt);
} else {
mActivity.alRecyclerview.smoothScrollToPosition(++mActivity.cnt);
}
}
}这样差不多就好了,但是还有一个问题不知道各位有没有关注到,滚动的时候并没有那么平滑,找了好久不知道是什么原因,希望知道的朋友底下评论告知一声。
参考文章:
OrientationHelper API
Android24.2.0支持库中的SnapHelper学习和使用
感谢以上资料的帮助。
源码我已上传至Github,想了解的朋友可以自行下载,当然,如果有更好的想法,也可以一起交流。
