Redux,作为大型React应用状态管理最常用的工具,其概念理论和实践都是很值得我们学习,分析然后在实践中深入了解的,对前端开发者能力成长很有帮助。本篇计划结合Redux容器组件和展示型组件的区别对比以及Redux与React应用最常见的连接库,react-redux源码分析,以期达到对Redux和React应用的更深层次理解。
前言
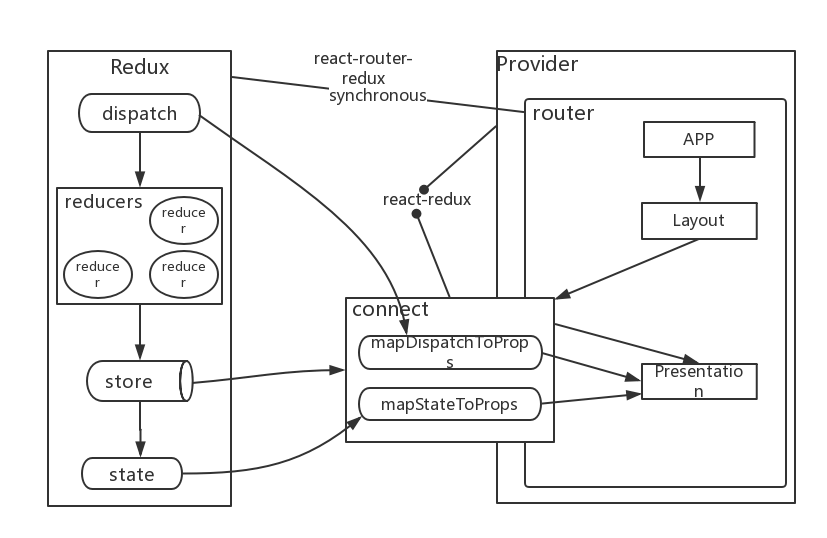
react-redux库提供Provider组件通过context方式向应用注入store,然后可以使用connect高阶方法,获取并监听store,然后根据store state和组件自身props计算得到新props,注入该组件,并且可以通过监听store,比较计算出的新props判断是否需要更新组件。
Provider
首先,react-redux库提供Provider组件将store注入整个React应用的某个入口组件,通常是应用的顶层组件。Provider组件使用context向下传递store:
// 内部组件获取redux store的键
const storeKey = 'store'
// 内部组件
const subscriptionKey = subKey || `${storeKey}Subscription`
class Provider extends Component {
// 声明context,注入store和可选的发布订阅对象
getChildContext() {
return { [storeKey]: this[storeKey], [subscriptionKey]: null }
}
constructor(props, context) {
super(props, context)
// 缓存store
this[storeKey] = props.store;
}
render() {
// 渲染输出内容
return Children.only(this.props.children)
}
}Example
import { Provider } from 'react-redux'
import { createStore } from 'redux'
import App from './components/App'
import reducers from './reducers'
// 创建store
const store = createStore(todoApp, reducers)
// 传递store作为props给Provider组件;
// Provider将使用context方式向下传递store
// App组件是我们的应用顶层组件
render(
<Provider store={store}>
<App/>
</Provider>, document.getElementById('app-node')
)connect方法
在前面我们使用Provider组件将redux store注入应用,接下来需要做的是连接组件和store。而且我们知道Redux不提供直接操作store state的方式,我们只能通过其getState访问数据,或通过dispatch一个action来改变store state。
这也正是react-redux提供的connect高阶方法所提供的能力。
Example
container/TodoList.js
首先我们创建一个列表容器组件,在组件内负责获取todo列表,然后将todos传递给TodoList展示型组件,同时传递事件回调函数,展示型组件触发诸如点击等事件时,调用对应回调,这些回调函数内通过dispatch actions来更新redux store state,而最终将store和展示型组件连接起来使用的是react-redux的connect方法,该方法接收
import {connect} from 'react-redux'
import TodoList from 'components/TodoList.jsx'
class TodoListContainer extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
this.state = {todos: null, filter: null}
}
handleUpdateClick (todo) {
this.props.update(todo);
}
componentDidMount() {
const { todos, filter, actions } = this.props
if (todos.length === 0) {
this.props.fetchTodoList(filter);
}
render () {
const { todos, filter } = this.props
return (
<TodoList
todos={todos}
filter={filter}
handleUpdateClick={this.handleUpdateClick}
/* others */
/>
)
}
}
const mapStateToProps = state => {
return {
todos : state.todos,
filter: state.filter
}
}
const mapDispatchToProps = dispatch => {
return {
update : (todo) => dispatch({
type : 'UPDATE_TODO',
payload: todo
}),
fetchTodoList: (filters) => dispatch({
type : 'FETCH_TODOS',
payload: filters
})
}
}
export default connect(
mapStateToProps,
mapDispatchToProps
)(TodoListContainer)components/TodoList.js
import React from 'react'
import PropTypes from 'prop-types'
import Todo from './Todo'
const TodoList = ({ todos, handleUpdateClick }) => (
<ul>
{todos.map(todo => (
<Todo key={todo.id} {...todo} handleUpdateClick={handleUpdateClick} />
))}
</ul>
)
TodoList.propTypes = {
todos: PropTypes.array.isRequired
).isRequired,
handleUpdateClick: PropTypes.func.isRequired
}
export default TodoListcomponents/Todo.js
import React from 'react'
import PropTypes from 'prop-types'
class Todo extends React.Component {
constructor(...args) {
super(..args);
this.state = {
editable: false,
todo: this.props.todo
}
}
handleClick (e) {
this.setState({
editable: !this.state.editable
})
}
update () {
this.props.handleUpdateClick({
...this.state.todo
text: this.refs.content.innerText
})
}
render () {
return (
<li
onClick={this.handleClick}
style={{
contentEditable: editable ? 'true' : 'false'
}}
>
<p ref="content">{text}</p>
<button onClick={this.update}>Save</button>
</li>
)
}
Todo.propTypes = {
handleUpdateClick: PropTypes.func.isRequired,
text: PropTypes.string.isRequired
}
export default Todo容器组件与展示型组件
在使用Redux作为React应用的状态管理容器时,通常贯彻将组件划分为容器组件(Container Components)和展示型组件(Presentational Components)的做法,
| Presentational Components | Container Components | |
|---|---|---|
| 目标 | UI展示 (HTML结构和样式) | 业务逻辑(获取数据,更新状态) |
| 感知Redux | 无 | 有 |
| 数据来源 | props | 订阅Redux store |
| 变更数据 | 调用props传递的回调函数 | Dispatch Redux actions |
| 可重用 | 独立性强 | 业务耦合度高 |
应用中大部分代码是在编写展示型组件,然后使用一些容器组件将这些展示型组件和Redux store连接起来。
connect()源码分析
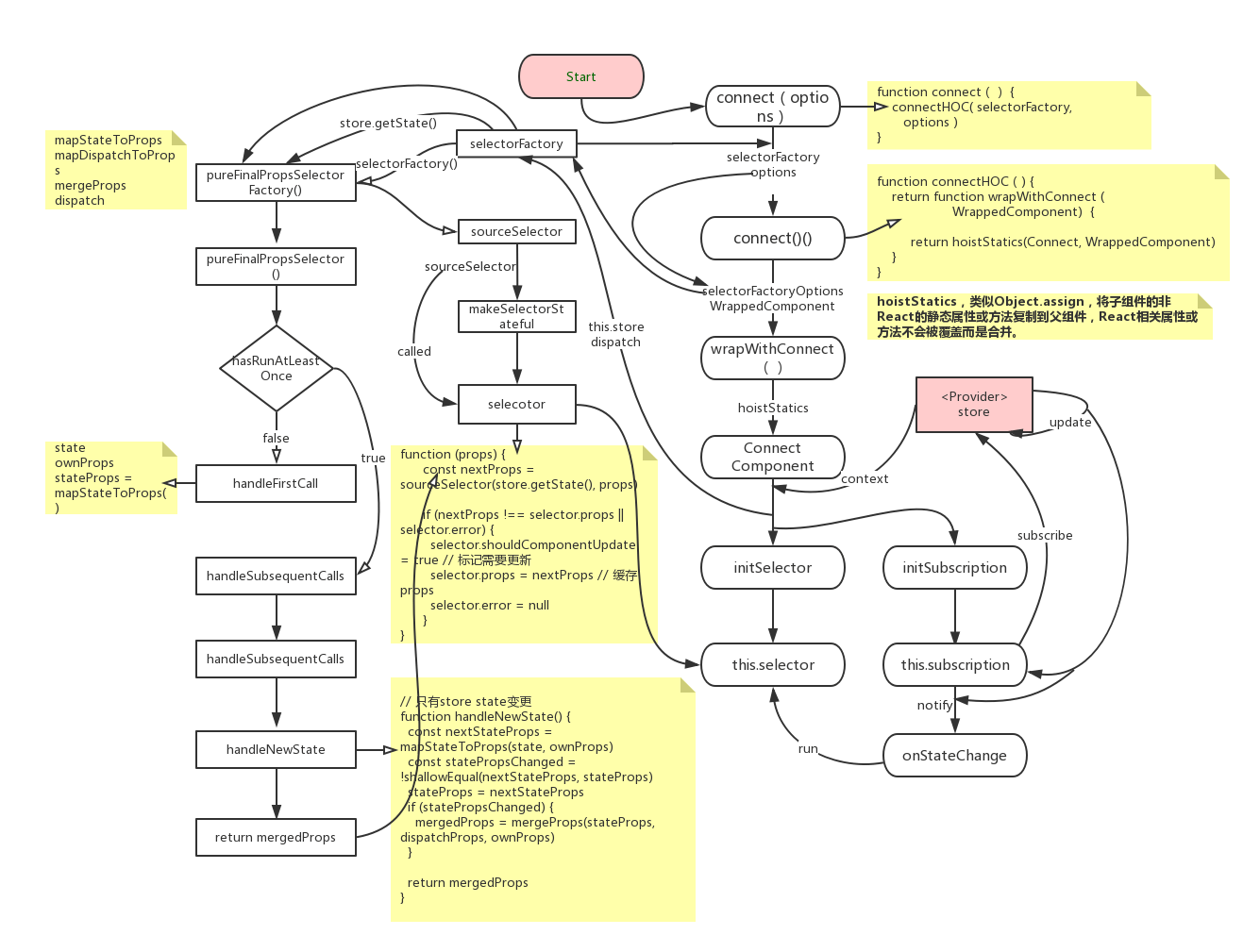
connectHOC = connectAdvanced;
mergePropsFactories = defaultMergePropsFactories;
selectorFactory = defaultSelectorFactory;
function connect (
mapStateToProps,
mapDispatchToProps,
mergeProps,
{
pure = true,
areStatesEqual = strictEqual, // 严格比较是否相等
areOwnPropsEqual = shallowEqual, // 浅比较
areStatePropsEqual = shallowEqual,
areMergedPropsEqual = shallowEqual,
renderCountProp, // 传递给内部组件的props键,表示render方法调用次数
// props/context 获取store的键
storeKey = 'store',
...extraOptions
} = {}
) {
const initMapStateToProps = match(mapStateToProps, mapStateToPropsFactories, 'mapStateToProps')
const initMapDispatchToProps = match(mapDispatchToProps, mapDispatchToPropsFactories, 'mapDispatchToProps')
const initMergeProps = match(mergeProps, mergePropsFactories, 'mergeProps')
// 调用connectHOC方法
connectHOC(selectorFactory, {
// 如果mapStateToProps为false,则不监听store state
shouldHandleStateChanges: Boolean(mapStateToProps),
// 传递给selectorFactory
initMapStateToProps,
initMapDispatchToProps,
initMergeProps,
pure,
areStatesEqual,
areOwnPropsEqual,
areStatePropsEqual,
areMergedPropsEqual,
renderCountProp, // 传递给内部组件的props键,表示render方法调用次数
// props/context 获取store的键
storeKey = 'store',
...extraOptions // 其他配置项
});
}strictEquall
function strictEqual(a, b) { return a === b }shallowEquall
const hasOwn = Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty
function is(x, y) {
if (x === y) {
return x !== 0 || y !== 0 || 1 / x === 1 / y
} else {
return x !== x && y !== y
}
}
export default function shallowEqual(objA, objB) {
if (is(objA, objB)) return true
if (typeof objA !== 'object' || objA === null ||
typeof objB !== 'object' || objB === null) {
return false
}
const keysA = Object.keys(objA)
const keysB = Object.keys(objB)
if (keysA.length !== keysB.length) return false
for (let i = 0; i < keysA.length; i++) {
if (!hasOwn.call(objB, keysA[i]) ||
!is(objA[keysA[i]], objB[keysA[i]])) {
return false
}
}
return true
}shallowEqual({x:{}},{x:{}}) // false
shallowEqual({x:1},{x:1}) // trueconnectAdvanced高阶函数
function connectAdvanced (
selectorFactory,
{
renderCountProp = undefined, // 传递给内部组件的props键,表示render方法调用次数
// props/context 获取store的键
storeKey = 'store',
...connectOptions
} = {}
) {
// 获取发布订阅器的键
const subscriptionKey = storeKey + 'Subscription';
const contextTypes = {
[storeKey]: storeShape,
[subscriptionKey]: subscriptionShape,
};
const childContextTypes = {
[subscriptionKey]: subscriptionShape,
};
return function wrapWithConnect (WrappedComponent) {
const selectorFactoryOptions = {
// 如果mapStateToProps为false,则不监听store state
shouldHandleStateChanges: Boolean(mapStateToProps),
// 传递给selectorFactory
initMapStateToProps,
initMapDispatchToProps,
initMergeProps,
...connectOptions,
...others
renderCountProp, // render调用次数
shouldHandleStateChanges, // 是否监听store state变更
storeKey,
WrappedComponent
}
// 返回拓展过props属性的Connect组件
return hoistStatics(Connect, WrappedComponent)
}
}selectorFactory
selectorFactory函数返回一个selector函数,根据store state, 展示型组件props,和dispatch计算得到新props,最后注入容器组件,selectorFactory函数结构形如:
(dispatch, options) => (state, props) => ({
thing: state.things[props.thingId],
saveThing: fields => dispatch(actionCreators.saveThing(props.thingId, fields)),
})注:redux中的state通常指redux store的state而不是组件的state,另此处的props为传入组件wrapperComponent的props。
function defaultSelectorFactory (dispatch, {
initMapStateToProps,
initMapDispatchToProps,
initMergeProps,
...options
}) {
const mapStateToProps = initMapStateToProps(dispatch, options)
const mapDispatchToProps = initMapDispatchToProps(dispatch, options)
const mergeProps = initMergeProps(dispatch, options)
// pure为true表示selectorFactory返回的selector将缓存结果;
// 否则其总是返回一个新对象
const selectorFactory = options.pure
? pureFinalPropsSelectorFactory
: impureFinalPropsSelectorFactory
// 最终执行selector工厂函数返回一个selector
return selectorFactory(
mapStateToProps,
mapDispatchToProps,
mergeProps,
dispatch,
options
);
}pureFinalPropsSelectorFactory
function pureFinalPropsSelectorFactory (
mapStateToProps,
mapDispatchToProps,
mergeProps,
dispatch,
{ areStatesEqual, areOwnPropsEqual, areStatePropsEqual }
) {
let hasRunAtLeastOnce = false
let state
let ownProps
let stateProps
let dispatchProps
let mergedProps
// 返回合并后的props或state
// handleSubsequentCalls变更后合并;handleFirstCall初次调用
return function pureFinalPropsSelector(nextState, nextOwnProps) {
return hasRunAtLeastOnce
? handleSubsequentCalls(nextState, nextOwnProps)
: handleFirstCall(nextState, nextOwnProps)
}
}handleFirstCall
function handleFirstCall(firstState, firstOwnProps) {
state = firstState
ownProps = firstOwnProps
stateProps = mapStateToProps(state, ownProps) // store state映射到组件的props
dispatchProps = mapDispatchToProps(dispatch, ownProps)
mergedProps = mergeProps(stateProps, dispatchProps, ownProps) // 合并后的props
hasRunAtLeastOnce = true
return mergedProps
}defaultMergeProps
export function defaultMergeProps(stateProps, dispatchProps, ownProps) {
// 默认合并props函数
return { ...ownProps, ...stateProps, ...dispatchProps }
}handleSubsequentCalls
function handleSubsequentCalls(nextState, nextOwnProps) {
// shallowEqual浅比较
const propsChanged = !areOwnPropsEqual(nextOwnProps, ownProps)
// 深比较
const stateChanged = !areStatesEqual(nextState, state)
state = nextState
ownProps = nextOwnProps
// 处理props或state变更后的合并
// store state及组件props变更
if (propsChanged && stateChanged) return handleNewPropsAndNewState()
if (propsChanged) return handleNewProps()
if (stateChanged) return handleNewState()
return mergedProps
}计算返回新props
只要展示型组件自身props发生变更,则需要重新返回新合并props,然后更新容器组件,无论store state是否变更:
// 只有展示型组件props变更
function handleNewProps() {
// mapStateToProps计算是否依赖于展示型组件props
if (mapStateToProps.dependsOnOwnProps)
stateProps = mapStateToProps(state, ownProps)
// mapDispatchToProps计算是否依赖于展示型组件props
if (mapDispatchToProps.dependsOnOwnProps)
dispatchProps = mapDispatchToProps(dispatch, ownProps)
mergedProps = mergeProps(stateProps, dispatchProps, ownProps)
return mergedProps
}
// 展示型组件props和store state均变更
function handleNewPropsAndNewState() {
stateProps = mapStateToProps(state, ownProps)
// mapDispatchToProps计算是否依赖于展示型组件props
if (mapDispatchToProps.dependsOnOwnProps)
dispatchProps = mapDispatchToProps(dispatch, ownProps)
mergedProps = mergeProps(stateProps, dispatchProps, ownProps)
return mergedProps
}计算返回stateProps
通常容器组件props变更由store state变更推动,所以只有store state变更的情况较多,而且此处也正是使用Immutable时需要注意的地方:不要在mapStateToProps方法内使用toJS()方法。
当mapStateToProps两次返回的props对象未有变更时,不需要重新计算,直接返回之前合并得到的props对象即可,之后在selector追踪对象中比较两次selector函数返回值是否有变更时,将返回false,容器组件不会触发变更。
因为对比多次mapStateToProps返回的结果时是使用浅比较,所以不推荐使用Immutable.toJS()方法,其每次均返回一个新对象,对比将返回false,而如果使用Immutable且其内容未变更,则会返回true,可以减少不必要的重新渲染。
// 只有store state变更
function handleNewState() {
const nextStateProps = mapStateToProps(state, ownProps)
// 浅比较
const statePropsChanged = !areStatePropsEqual(nextStateProps, stateProps)
stateProps = nextStateProps
// 计算得到的新props变更了,才需要重新计算返回新的合并props
if (statePropsChanged) {
mergedProps = mergeProps(stateProps, dispatchProps, ownProps)
}
// 若新stateProps未发生变更,则直接返回上一次计算得出的合并props;
// 之后selector追踪对象比较两次返回值是否有变更时将返回false;
// 否则返回使用mergeProps()方法新合并得到的props对象,变更比较将返回true
return mergedProps
}hoist-non-react-statics
类似Object.assign,将子组件的非React的静态属性或方法复制到父组件,React相关属性或方法不会被覆盖而是合并。
hoistStatics(Connect, WrappedComponent)Connect Component
真正的Connect高阶组件,连接redux store state和传入组件,即将store state映射到组件props,react-redux使用Provider组件通过context方式注入store,然后Connect组件通过context接收store,并添加对store的订阅:
class Connect extends Component {
constructor(props, context) {
super(props, context)
this.state = {}
this.renderCount = 0 // render调用次数初始为0
// 获取store,props或context方式
this.store = props[storeKey] || context[storeKey]
// 是否使用props方式传递store
this.propsMode = Boolean(props[storeKey])
// 初始化selector
this.initSelector()
// 初始化store订阅
this.initSubscription()
}
componentDidMount() {
// 不需要监听state变更
if (!shouldHandleStateChanges) return
// 发布订阅器执行订阅
this.subscription.trySubscribe()
// 执行selector
this.selector.run(this.props)
// 若还需要更新,则强制更新
if (this.selector.shouldComponentUpdate) this.forceUpdate()
}
// 渲染组件元素
render() {
const selector = this.selector
selector.shouldComponentUpdate = false; // 重置是否需要更新为默认的false
// 将redux store state转化映射得到的props合并入传入的组件
return createElement(WrappedComponent, this.addExtraProps(selector.props))
}
}addExtraProps()
给props添加额外的props属性:
// 添加额外的props
addExtraProps(props) {
const withExtras = { ...props }
if (renderCountProp) withExtras[renderCountProp] = this.renderCount++;// render 调用次数
if (this.propsMode && this.subscription) withExtras[subscriptionKey] = this.subscription
return withExtras
}初始化selector追踪对象initSelector
Selector,选择器,根据redux store state和组件的自身props,计算出将注入该组件的新props,并缓存新props,之后再次执行选择器时通过对比得出的props,决定是否需要更新组件,若props变更则更新组件,否则不更新。
使用initSelector方法初始化selector追踪对象及相关状态和数据:
// 初始化selector
initSelector() {
// 使用selector工厂函数创建一个selector
const sourceSelector = selectorFactory(this.store.dispatch, selectorFactoryOptions)
// 连接组件的selector和redux store state
this.selector = makeSelectorStateful(sourceSelector, this.store)
// 执行组件的selector函数
this.selector.run(this.props)
}makeSelectorStateful()
创建selector追踪对象以追踪(tracking)selector函数返回结果:
function makeSelectorStateful(sourceSelector, store) {
// 返回selector追踪对象,追踪传入的selector(sourceSelector)返回的结果
const selector = {
// 执行组件的selector函数
run: function runComponentSelector(props) {
// 根据store state和组件props执行传入的selector函数,计算得到nextProps
const nextProps = sourceSelector(store.getState(), props)
// 比较nextProps和缓存的props;
// false,则更新所缓存的props并标记selector需要更新
if (nextProps !== selector.props || selector.error) {
selector.shouldComponentUpdate = true // 标记需要更新
selector.props = nextProps // 缓存props
selector.error = null
}
}
}
// 返回selector追踪对象
return selector
}初始化订阅initSubscription
初始化监听/订阅redux store state:
// 初始化订阅
initSubscription() {
if (!shouldHandleStateChanges) return; // 不需要监听store state
// 判断订阅内容传递方式:props或context,两者不能混杂
const parentSub = (this.propsMode ? this.props : this.context)[subscriptionKey]
// 订阅对象实例化,并传入事件回调函数
this.subscription = new Subscription(this.store,
parentSub,
this.onStateChange.bind(this))
// 缓存订阅器发布方法执行的作用域
this.notifyNestedSubs = this.subscription.notifyNestedSubs
.bind(this.subscription)
}订阅类实现
组件订阅store使用的订阅发布器实现:
export default class Subscription {
constructor(store, parentSub, onStateChange) {
// redux store
this.store = store
// 订阅内容
this.parentSub = parentSub
// 订阅内容变更后的回调函数
this.onStateChange = onStateChange
this.unsubscribe = null
// 订阅记录数组
this.listeners = nullListeners
}
// 订阅
trySubscribe() {
if (!this.unsubscribe) {
// 若传递了发布订阅器则使用该订阅器订阅方法进行订阅
// 否则使用store的订阅方法
this.unsubscribe = this.parentSub
? this.parentSub.addNestedSub(this.onStateChange)
: this.store.subscribe(this.onStateChange)
// 创建订阅集合对象
// { notify: function, subscribe: function }
// 内部包装了一个发布订阅器;
// 分别对应发布(执行所有回调),订阅(在订阅集合中添加回调)
this.listeners = createListenerCollection()
}
}
// 发布
notifyNestedSubs() {
this.listeners.notify()
}
}订阅回调函数
订阅后执行的回调函数:
onStateChange() {
// 选择器执行
this.selector.run(this.props)
if (!this.selector.shouldComponentUpdate) {
// 不需要更新则直接发布
this.notifyNestedSubs()
} else {
// 需要更新则设置组件componentDidUpdate生命周期方法
this.componentDidUpdate = this.notifyNestedSubsOnComponentDidUpdate
// 同时调用setState触发组件更新
this.setState(dummyState) // dummyState = {}
}
}
// 在组件componentDidUpdate生命周期方法内发布变更
notifyNestedSubsOnComponentDidUpdate() {
// 清除组件componentDidUpdate生命周期方法
this.componentDidUpdate = undefined
// 发布
this.notifyNestedSubs()
}其他生命周期方法
getChildContext () {
// 若存在props传递了store,则需要对其他从context接收store并订阅的后代组件隐藏其对于store的订阅;
// 否则将父级的订阅器映射传入,给予Connect组件控制发布变化的顺序流
const subscription = this.propsMode ? null : this.subscription
return { [subscriptionKey]: subscription || this.context[subscriptionKey] }
}
// 接收到新props
componentWillReceiveProps(nextProps) {
this.selector.run(nextProps)
}
// 是否需要更新组件
shouldComponentUpdate() {
return this.selector.shouldComponentUpdate
}
componentWillUnmount() {
// 重置selector
}