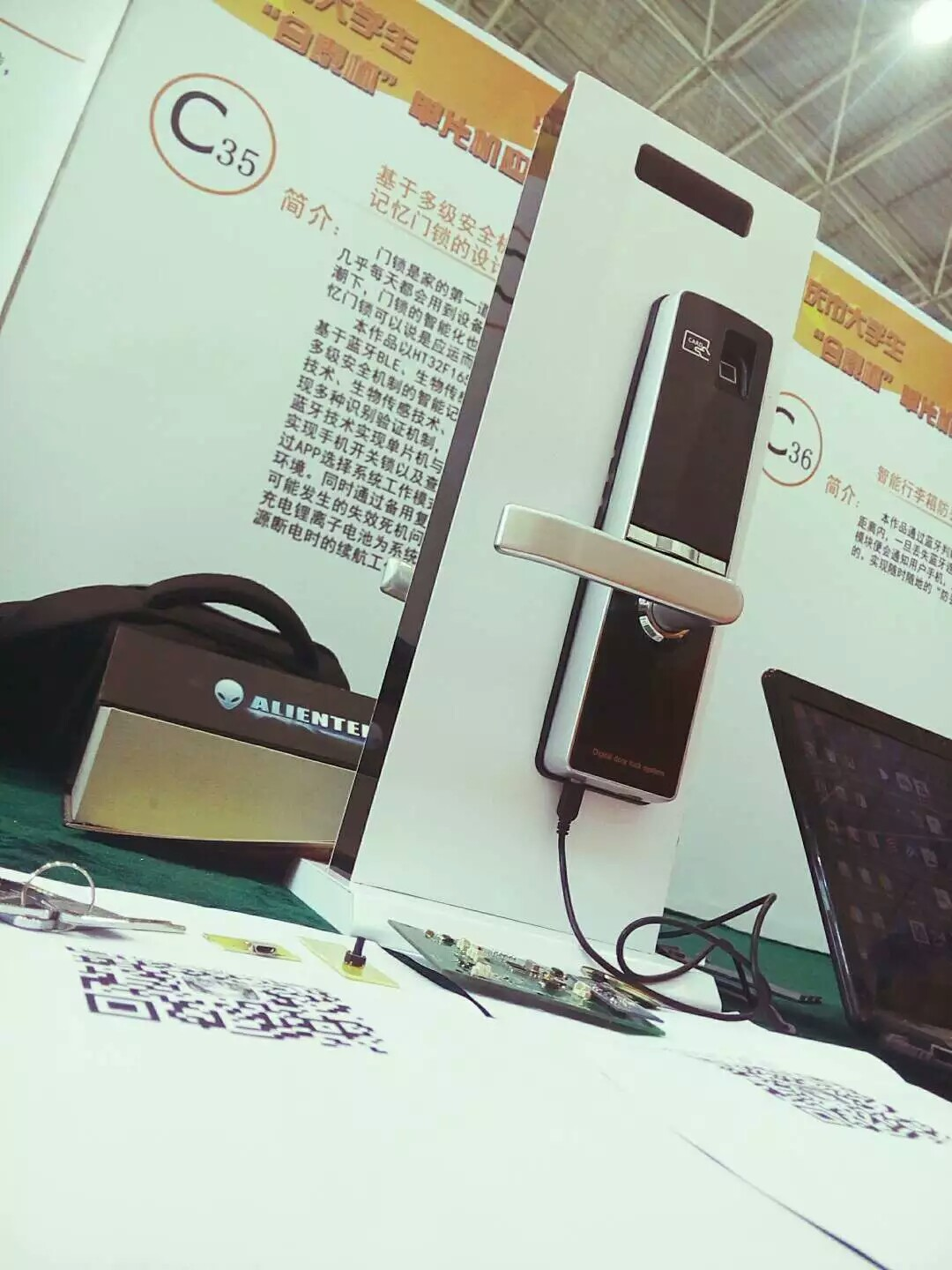
项目介绍
基于多级安全机制的蓝牙智能门锁Android客户端实现。
项目客户端基于 Android 平台,通过 CC2541 蓝牙芯片和底层进行通信,门锁部分以 HT32F1656 单片机为控制核心,基于蓝牙技术、生物传感技术,RFID 技术等,实现智能记忆门锁功能。 利用生物传感技术、RFID技术实现多种识别验证机制。通过 APP 选择系统工作模式,以适应不同的工作环境。同时通过备用复位系统,解决失效死机问题,通过备用电池电源供电系统,防止主电源断电的续航工作。
Android客户端开源地址:github.com/rockzhai/BL…
欢迎提问~ 如果喜欢,期待您的star
关于 Android-BLE
BLE:全称 Bluetooth Low Energy ,又叫做蓝牙4.0,主推就是低功耗,所以BLE技术更多的存在于只能穿戴设备和智能家居上,也正因如此,我们小组成员才会选择BLE的芯片和技术来进行开发。
关键概念
- Generic Attribute Profile(GATT) –GATT 配置文件是一个通用的规范,用于在 BLE 链路上收发数据块。BLE应用开发也是基于 GATT。
- Attribute Protocol(ATT)—GATT 在ATT协议基础上建立,也被称为GATT/ATT。ATT 对在 BLE 设备上运行进行了优化,为此,它使用了尽可能少的字节。每个属性通过一个唯一的的统一标识符(UUID)来标识,每个 String 类型UUID使用128 bit标准格式。属性通过ATT被格式化为 characteristics和services。
- Characteristic 一个 characteristic 包括一个单一变量和0-n个用来描述 characteristic 变量的 descriptor,characteristic 可以被认为是一个类型,类似于类。
- Service service 是 characteristic 的集合。
Service、Characteristic、Descriptor,这三部分都由UUID作为唯一标示符。一个蓝牙4.0的终端可以包含多个 Service,一个 Service 可以包含多个 Characteristic,一个 Characteristic 包含一个 Value 和多个 Descriptor,一个 Descriptor 包含一个 Value。一般来说,Characteristic 是手机与 BLE 终端交换数据的关键,Characteristic有较多的跟权限相关的字段,例如 PERMISSION 和 PROPERTY。Characteristic 的 PROPERTY 可以通过位运算符组合来设置读写属性,例如 READ|WRITE、READ|WRITE_NO_RESPONSE|NOTIFY,因此读取 PROPERTY 后要分解成所用的组合)。
权限
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.BLUETOOTH"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.BLUETOOTH_ADMIN"/>声明APP只为具有BLE的设备提供
<uses-feature android:name="android.hardware.bluetooth_le" android:required="true"/>可以根据需要设置 required 的值为 false。
BLE 具体设置
当然,在进行设置之前要先检查设备是否支持 BLE,现在主流机型都是完美支持 BLE 的,在检查过后,可以直接启动蓝牙:
-
获取 BluetoothAdapter
需要注意的是,在 Android 中,只有一个蓝牙适配器,APP要使用它和系统进行交互。在这里我们使用 getSystemSrvice() 返回 BluetoothManager。//蓝牙相关 final BluetoothManager bluetoothManager = (BluetoothManager) getSystemService(Context.BLUETOOTH_SERVICE); mBluetoothAdapter = bluetoothManager.getAdapter(); Log.i(TAG, "mBluetoothAdapter = " + mBluetoothAdapter); -
开启蓝牙
//打开蓝牙并获取蓝牙地址 mBluetoothAdapter.enable(); mActionbar.setSubtitle("蓝牙已打开"); myBleAddress = mBluetoothAdapter.getAddress(); -
搜索设备
mBluetoothAdapter.startLeScan(mLeScanCallback); -
处理搜索结果
// 设备搜索结果 private BluetoothAdapter.LeScanCallback mLeScanCallback = new BluetoothAdapter.LeScanCallback() { @Override public void onLeScan(final BluetoothDevice device, int rssi, byte[] scanRecord) { runOnUiThread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { //5F:52:CC:7F:86:55 //20:91:48:50:5C:8E //D4:F5:13:78:E9:63 //20:91:48:50:58:DE 这里的为测试CC2541蓝牙mac地址 if (device.getAddress().equals("20:91:48:50:58:DE")) { scanLeDevice(false); Log.e(TAG, device.getAddress()); Log.e(TAG, device.getName()); boolean bRet = mBLE.connect(device.getAddress()); try { //这里与硬件交互的时候,有时候不稳定,故2s等待,保证链接稳定 Thread.sleep(2000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } if (bRet) { mActionbar.setSubtitle("已连接,请登录"); Log.e(TAG, "connect+++++success"); Log.e(TAG, Constant.HEAD_CHAR + "0B" + Constant.SEND_ADDRESS + Constant.SEVER_BLUETOOTH + myBleAddress + Constant.END_CHAR); } } } }); // rssi Log.i(TAG, "rssi = " + rssi); Log.i(TAG, "mac = " + device.getAddress()); Log.i(TAG, "scanRecord.length = " + scanRecord.length); } }; -
进行实时通信
通过 writeCharacteristic 方法进行数据的写入操作:
public static void writeChar(byte[] bytes) { Log.i(TAG, "Message = " + bytes); if (gattCharacteristic_char != null) { gattCharacteristic_char.setValue(bytes); mBLE.writeCharacteristic(gattCharacteristic_char); } }通过 onCharacteristicWrite 方法来读取蓝牙方法所过来的数据:
private BluetoothLeClass.OnDataAvailableListener mOnDataAvailable = new BluetoothLeClass.OnDataAvailableListener() { /** * BLE终端数据被读的事件 */ @Override public void onCharacteristicRead(BluetoothGatt gatt, BluetoothGattCharacteristic characteristic, int status) { Log.e(TAG, "onCharRead " + gatt.getDevice().getName() + " read " + characteristic.getUuid().toString() + " -> " + Utils.bytesToHexString(characteristic.getValue())); } /** * 收到BLE终端写入数据回调 */ @Override public void onCharacteristicWrite(BluetoothGatt gatt, BluetoothGattCharacteristic characteristic) { // Log.e(TAG, "onCharWrite " + gatt.getDevice().getName() + " write " // + characteristic.getUuid().toString() + " -> " // + new String(characteristic.getValue())); String str = Utils.bytesToHexString(characteristic.getValue()); Log.e(TAG, "+++++++++++++++++++++" + str); //这里处理蓝牙方发送过来的数据。。。。 } };
问题总结
连接调试
首先在客户端开发中,并不需要在程序中设置波特率,因为这并不是串口开发,而 BLE 在 Android 中高度集成,只需要满足上述的条件即可进行通信,而 BLE 设备开发是需要设置的,这个可以根据自己的需要进行设计,同时在客户端进行自己开发调试的时候,串口助手中一定要设置波特兰,当然,这个数值来自我们硬件开发的同学。
数据传输
开发中发现硬件对数据的解析是处于对 byte 流的解析,而最初客户端发送的数据位 String 类型的,这时候在串口调试中串口助手是可以显示客户端发送的数据,而 BLE 芯片却无法收到,解决方法是将 String 转化成 byte 流进行传输。
//字符串转byte
public static byte[] hexStringToBytes(String hexString) {
if (hexString == null || hexString.equals("")) {
return null;
}
hexString = hexString.toUpperCase();
int length = hexString.length() / 2;
char[] hexChars = hexString.toCharArray();
byte[] d = new byte[length];
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
int pos = i * 2;
d[i] = (byte) (charToByte(hexChars[pos]) << 4 | charToByte(hexChars[pos + 1]));
}
return d;
}协议商定
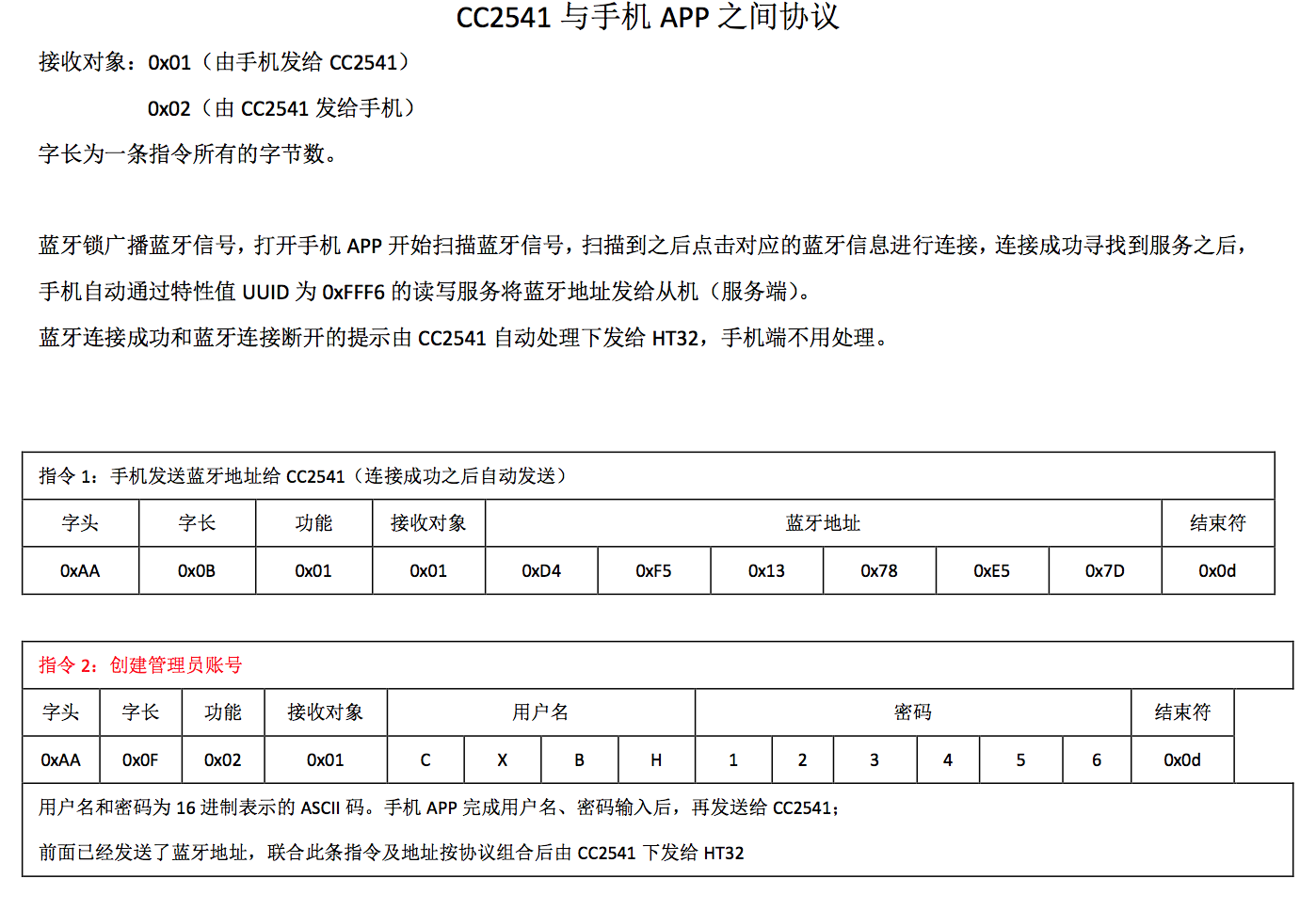
在与硬件交互的开发中,我们不能像开发应用一样通过 JOSN 或者 XML 等类似的数据进行数据通信,要采用基于十六进制硬件底层的通信协议,协议截图(图片无法加载可以移步 这里 ):
因此我们要对所传和所解析的数据进行十六进制的相互转换:
// 转化字符串为十六进制编码
public static String toHexString(String s) {
String str = "";
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
int ch = (int) s.charAt(i);
String s4 = Integer.toHexString(ch);
str = str + s4;
}
return str;
}
// 转化十六进制编码为字符串
public static String hexToString(String s) {
byte[] baKeyword = new byte[s.length() / 2];
for (int i = 0; i < baKeyword.length; i++) {
try {
baKeyword[i] = (byte) (0xff & Integer.parseInt(s.substring(
i * 2, i * 2 + 2), 16));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
try {
s = new String(baKeyword, "utf-8");// UTF-16le:Not
} catch (Exception e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
return s;
}题外话
该智能锁除了外壳之外,均是几个小伙伴一同安装和调试出来的,从机械结构到程序开发,一起熬了一周,直到参加比赛答辩的前一个多小时,我们遇到了一个致命的 BUG 不知如何是好,紧急调程序、拆卸、重新安装,似乎完全忘了我们是连续熬了四五个晚上的通宵,庆幸的是现场演示的一整天和答辩的过程中设备和程序未出现任何问题,也拿下了该比赛重庆市一等奖和最佳 MCU 程序设计奖,比赛前那几个小时,说真的都想过直接放弃,但是最后还是坚持下来了,感谢锲而不舍的小伙伴,现在虽然接近毕业,这个作品也是一年前的作品,但是我还是想写出来,最主要的不是为了分享技术,而是想说对技术的坚持。
希望能在技术这条路上继续前进,只要一直坚持,不到最后一秒,谁也不知道结果,或许接下来就是柳暗花明,或许接下来就是另一个世外桃源。
附上实拍效果图一张给大家(图片无法加载可以移步这里 ) :