卡尔曼滤波器基于五个方程
Two prediction equations:
State Extrapolation Equation - prediction or estimation of the future state, based on the known present estimation.
Covariance Extrapolation Equation - the measure of uncertainty in our prediction.
Two update equations:
State Update Equation - estimation of the current state, based on the known past estimation and present measurement.
Covariance Update Equation - the measure of uncertainty in our estimation.
Kalman Gain Equation – required for computation of the update equations. The Kalman Gain is actually a "weighting" parameter for the measurement and the past estimations. It defines the weight of the past estimation and the weight of the measurement in estimating the current state.
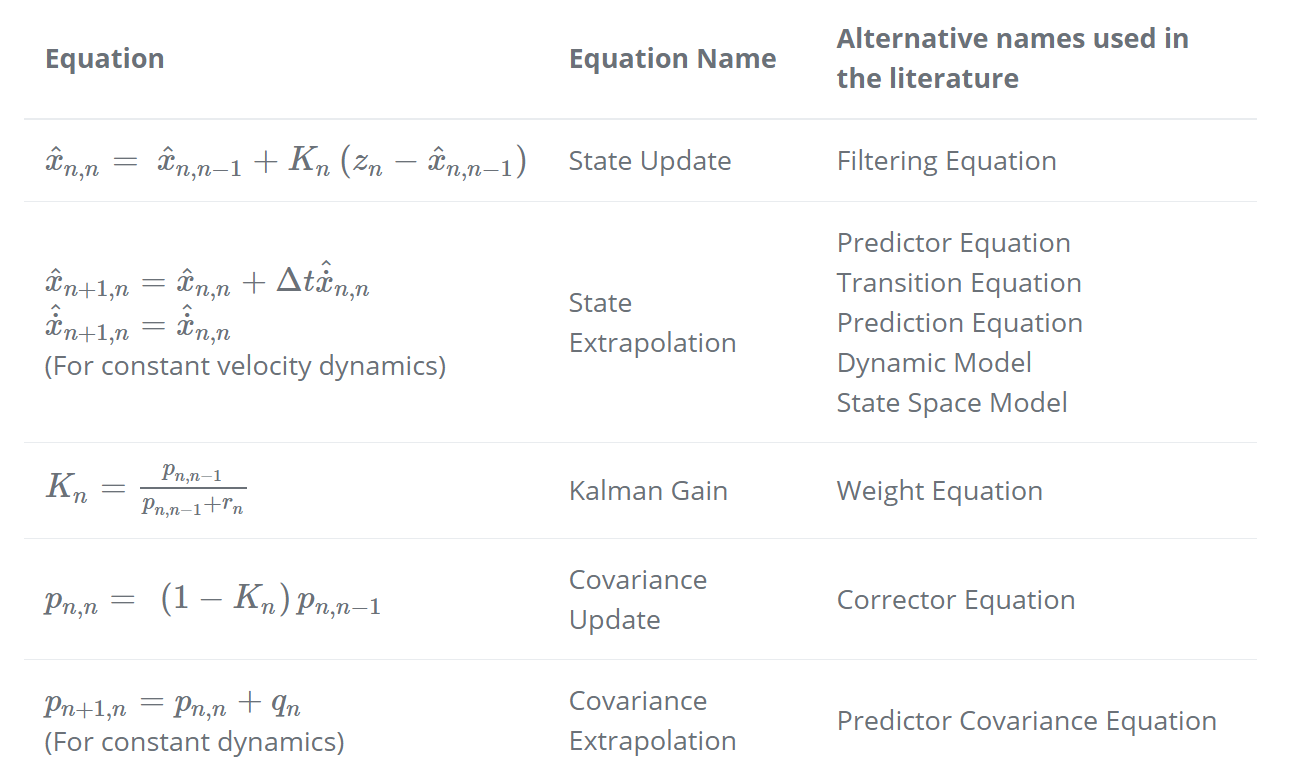
注1:状态外推方程取决于系统动力学(物理模型)。
注2:上表显示了针对特定情况定制的卡尔曼滤波方程的特殊形式。方程的一般形式将在后面的矩阵表示法中给出。现在,我们的目标是理解卡尔曼滤波器的概念
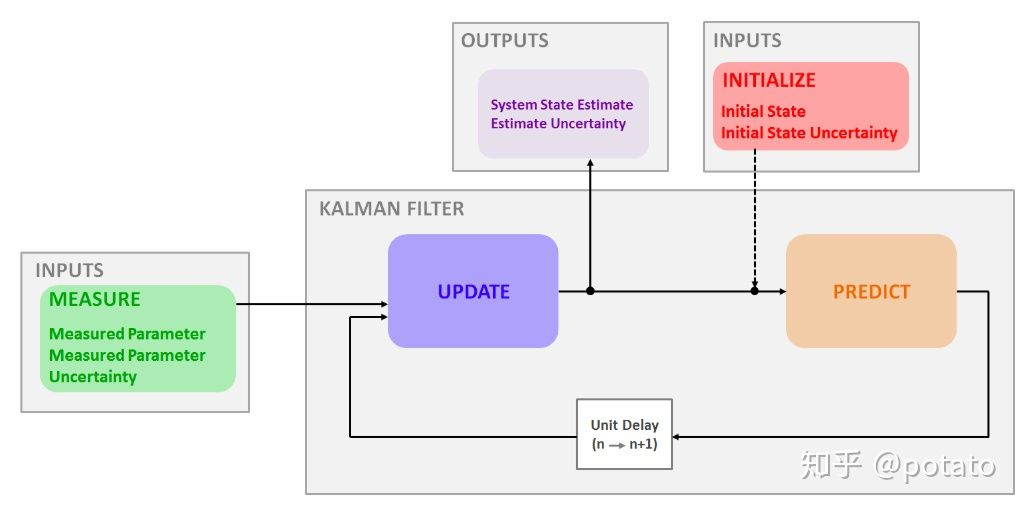
“测量,更新,预测”算法
α β γ滤波器:
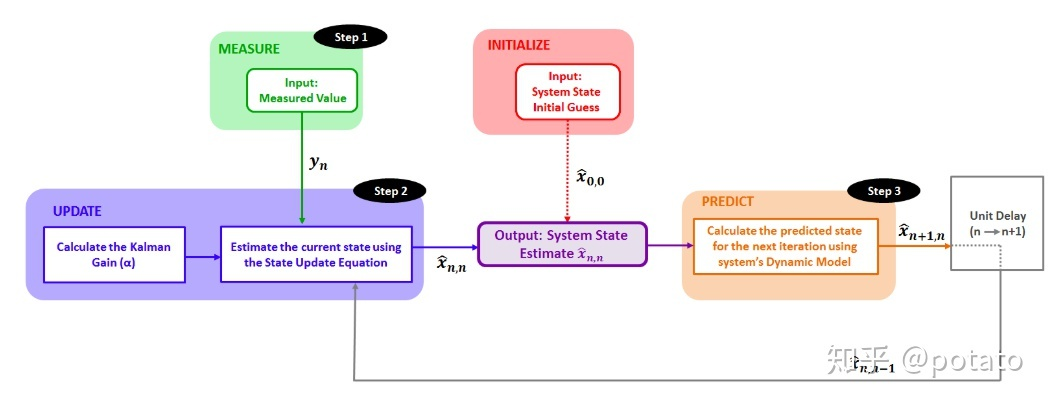
kalman filter:
卡尔曼增益直觉性思考
高卡尔曼增益:
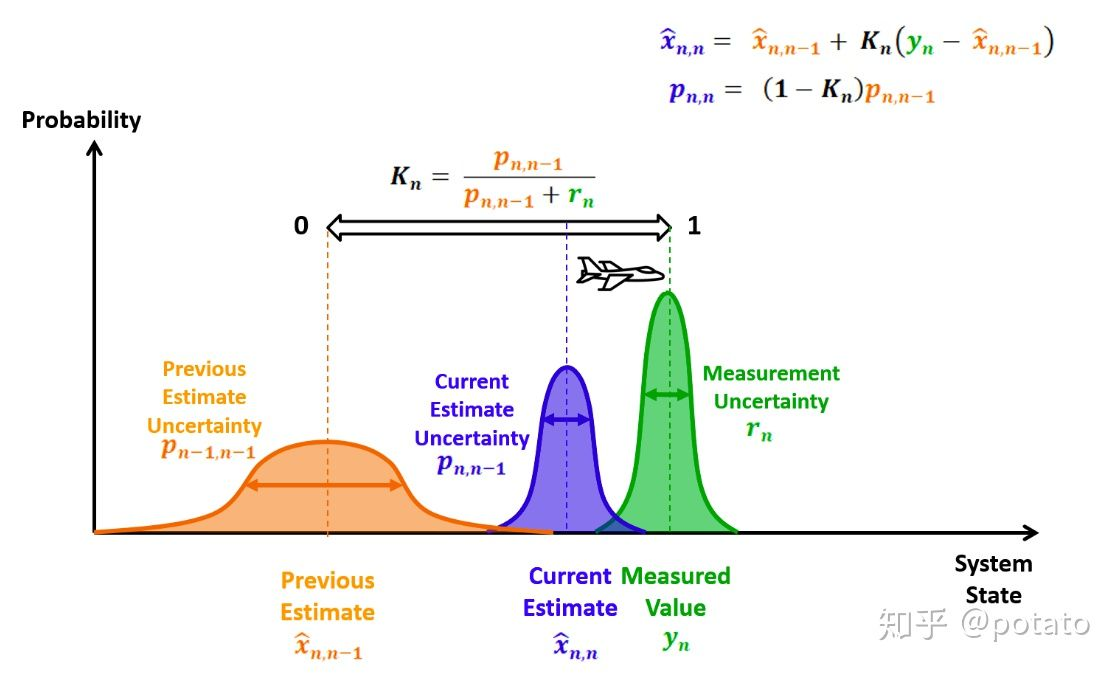
低卡尔曼增益
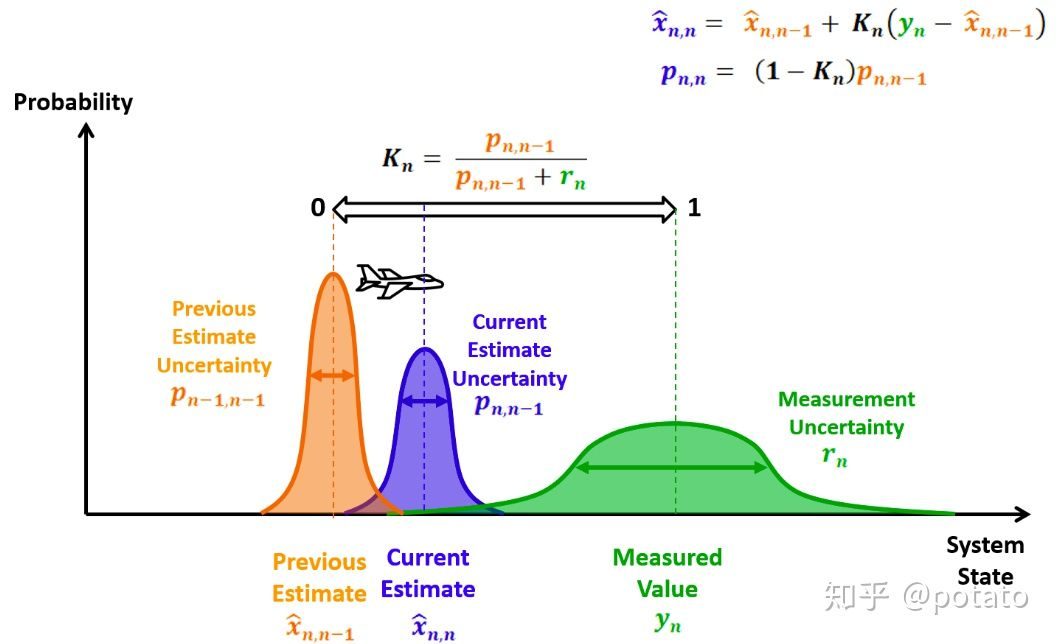
【结论】:
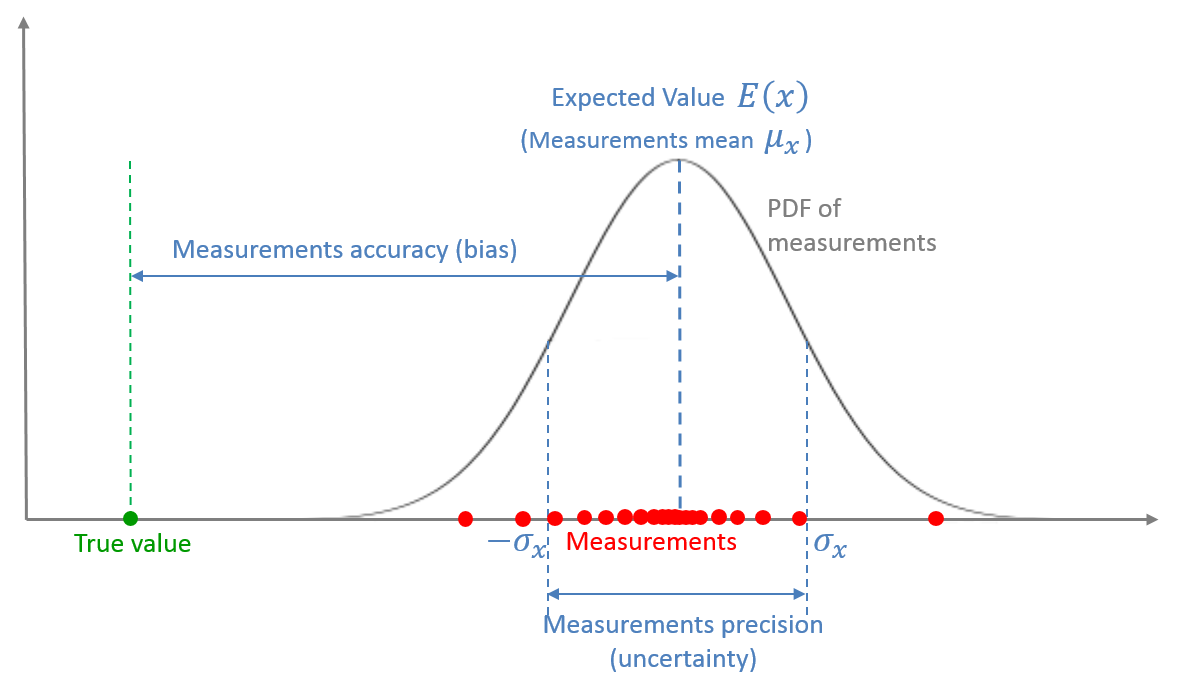
①previous estimation和measurement谁的【不确定度】小(概率分布的宽度小),current estimate就会偏向谁的方向进行更新
②kalman gain就是迭代更新式中的【加权系数】
滞后误差lag error
-
系统动力模型与实际不符。
-
过程模型的可靠性。我们选择了非常低的过程噪声(q=0.0001),而实际温度波动要大得多。 有两种可能的方法解决滞后误差问题:
-
如果我们知道液体温度是线性变化的,我们可以定义一个将温度可能的线性变化考虑进去的新模型。在案例4中我们就是这么做的。这个一个好方法。然而,如果温度改变不能被建模,这个方法也不足以提升卡尔曼增益的性能。
-
另一方面,由于我们的模型并没有被很好的定义,因此我们可以同感增加过程噪声(q)来提高模型可靠度。细节见下一个案例。
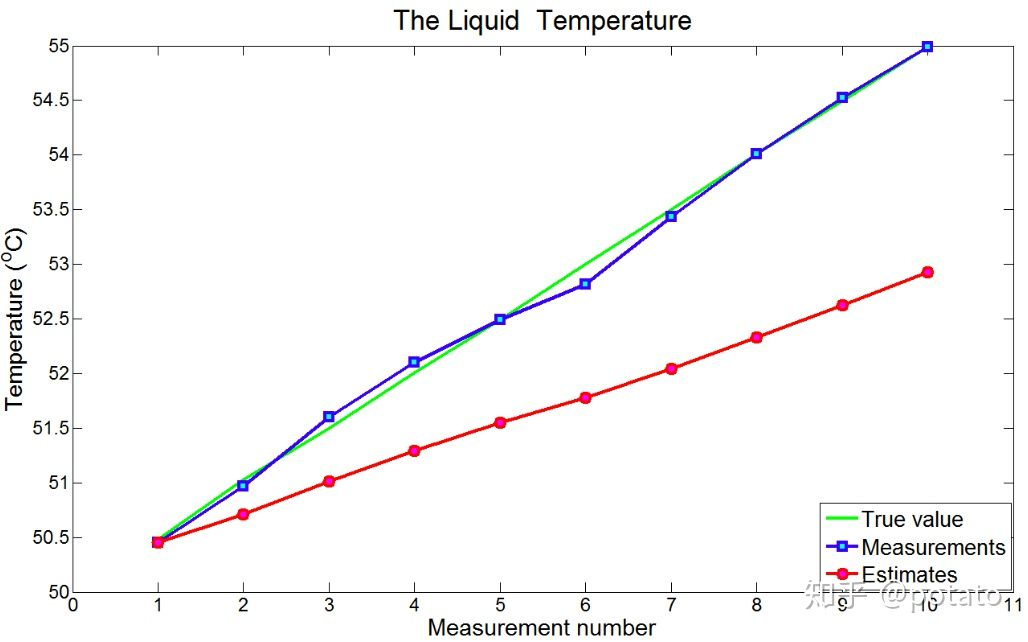
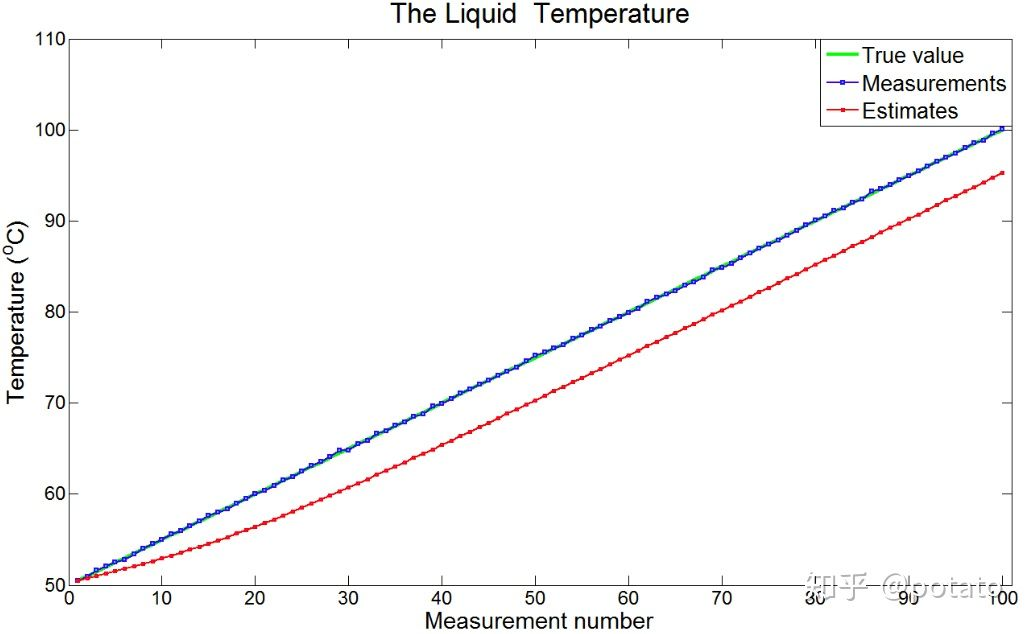
注意:滞后误差应为常数,因此估计曲线应与真值曲线具有相同的斜率。上面的图只显示了前10个测量值,不足以收敛。下图显示了前100个具有恒定滞后误差的测量。
迭代过程
过程噪声方差Process Noise Variance的字母表示:q
协方差外推方程Covariance Extrapolation Equation将会包含过程噪声方差Process Noise Variance。
测量误差的方差用r表示
详细迭代过程见案例6: 估计罐中液体的温度


